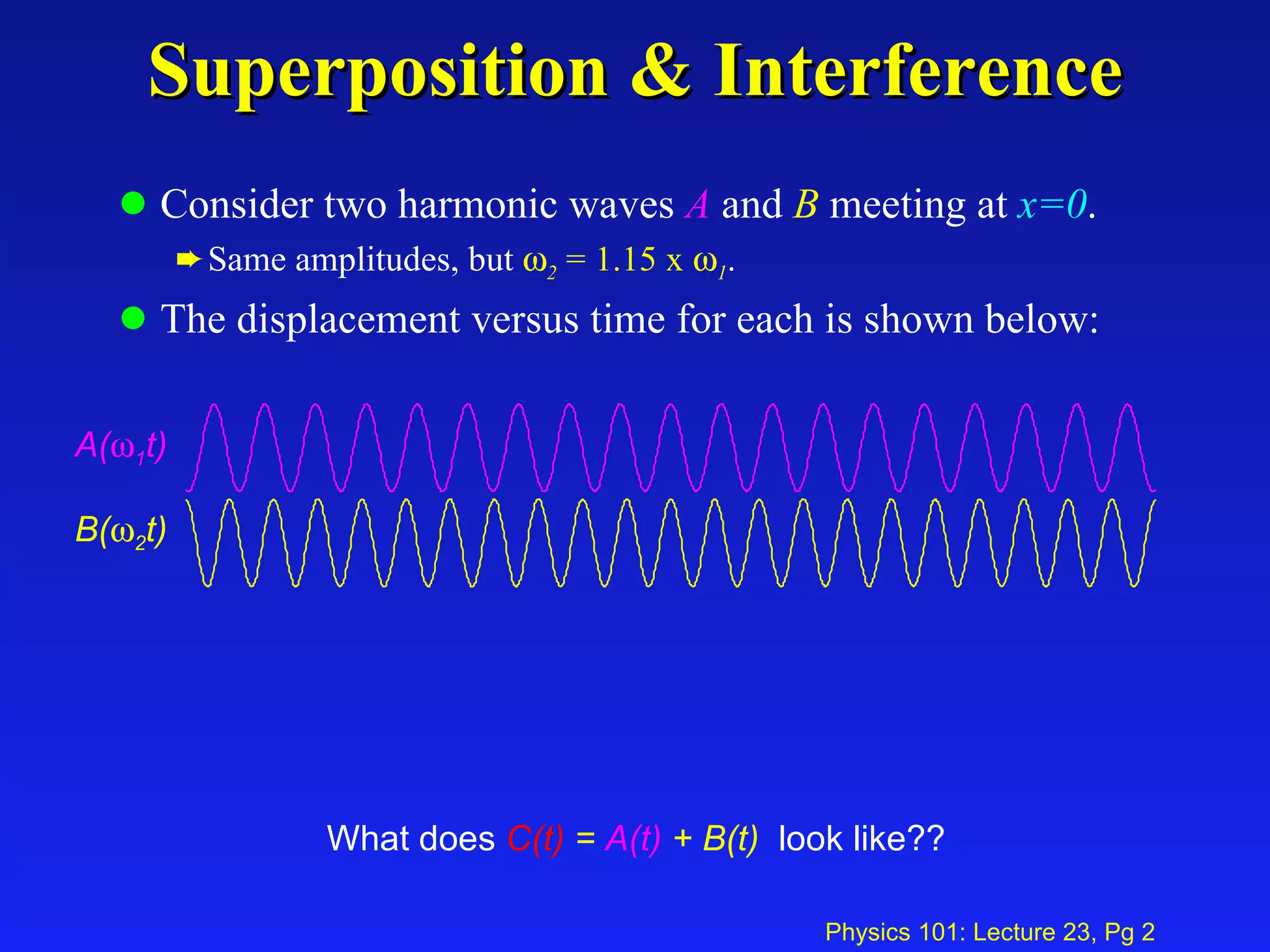
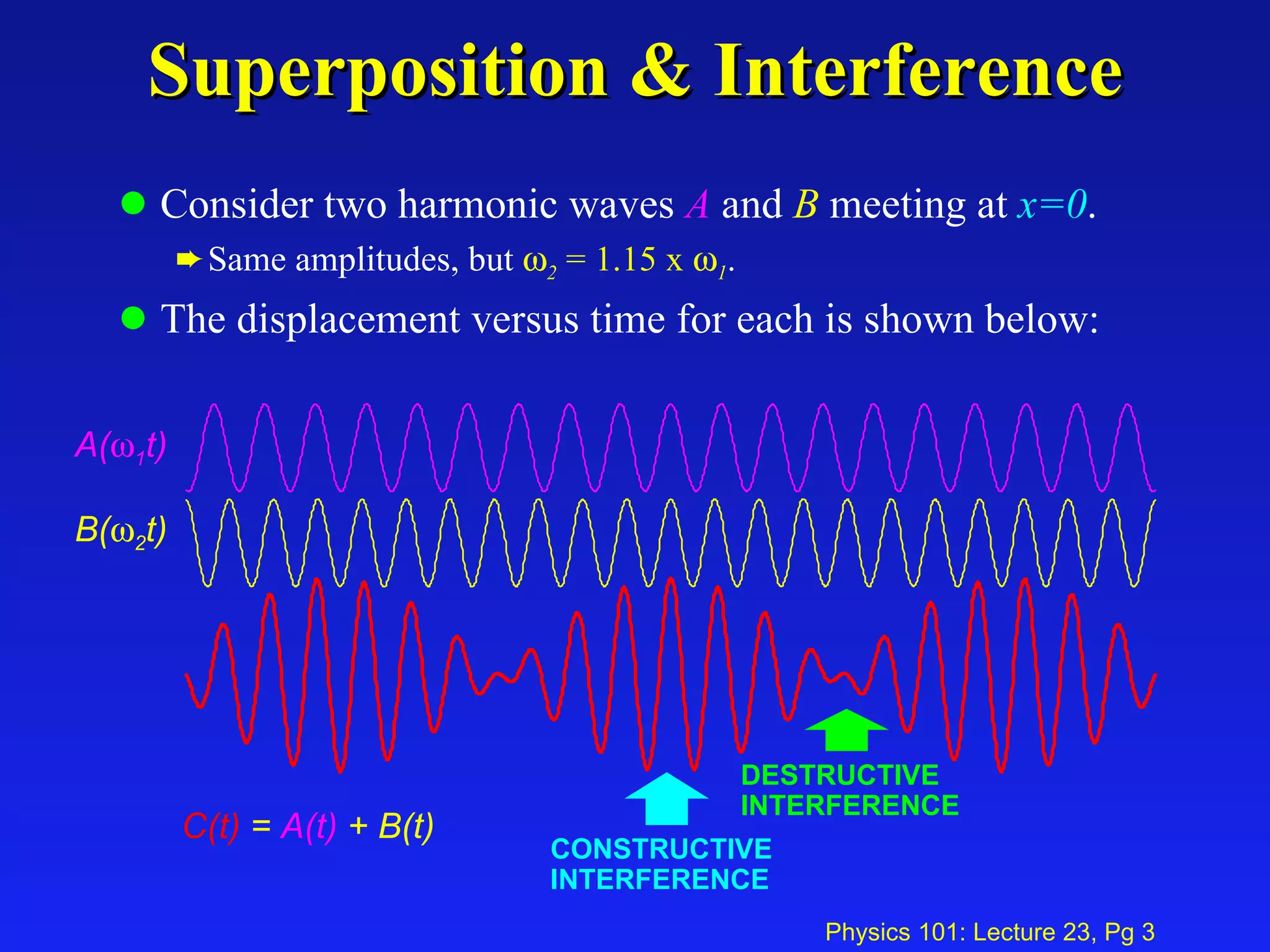
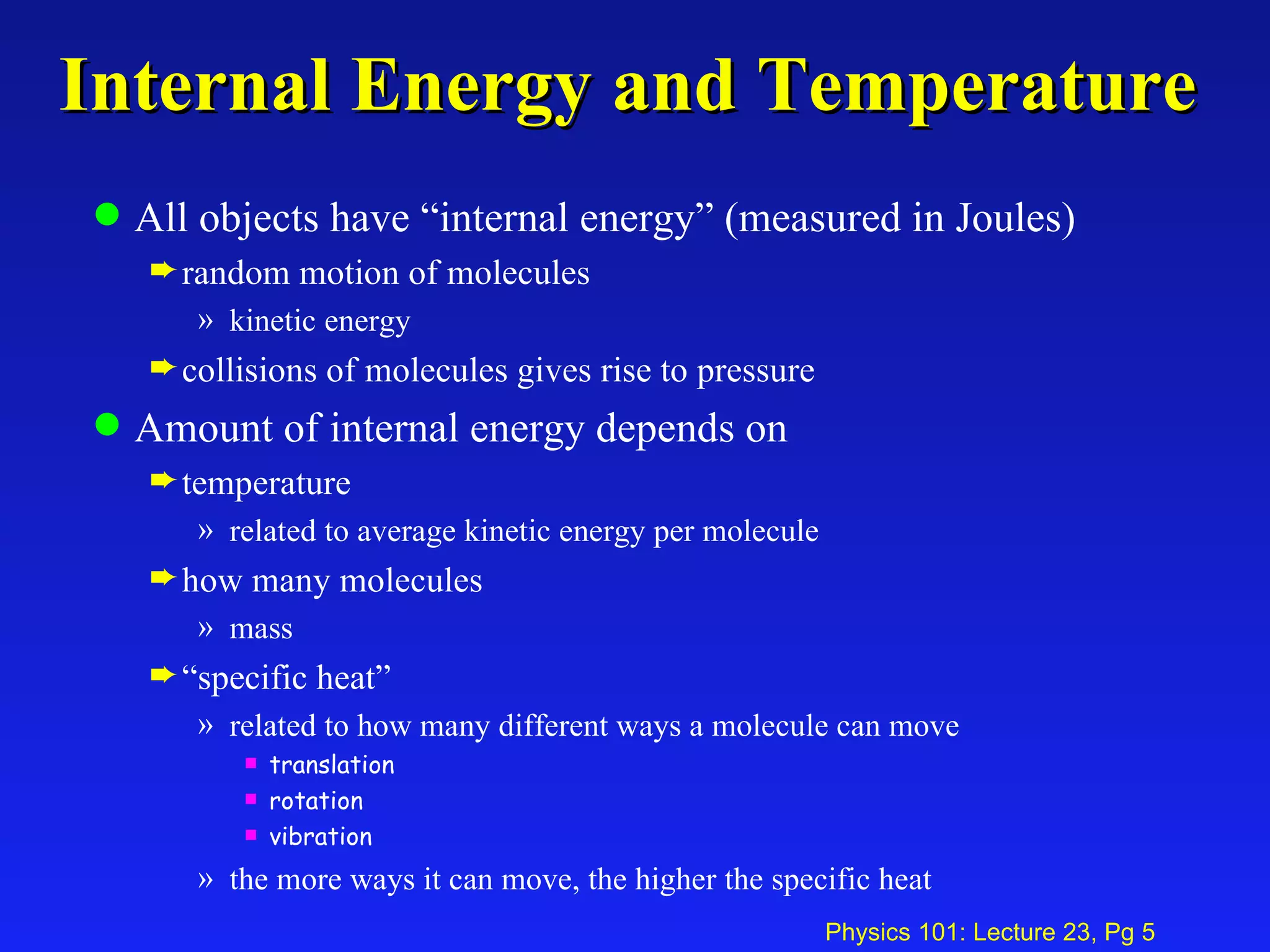
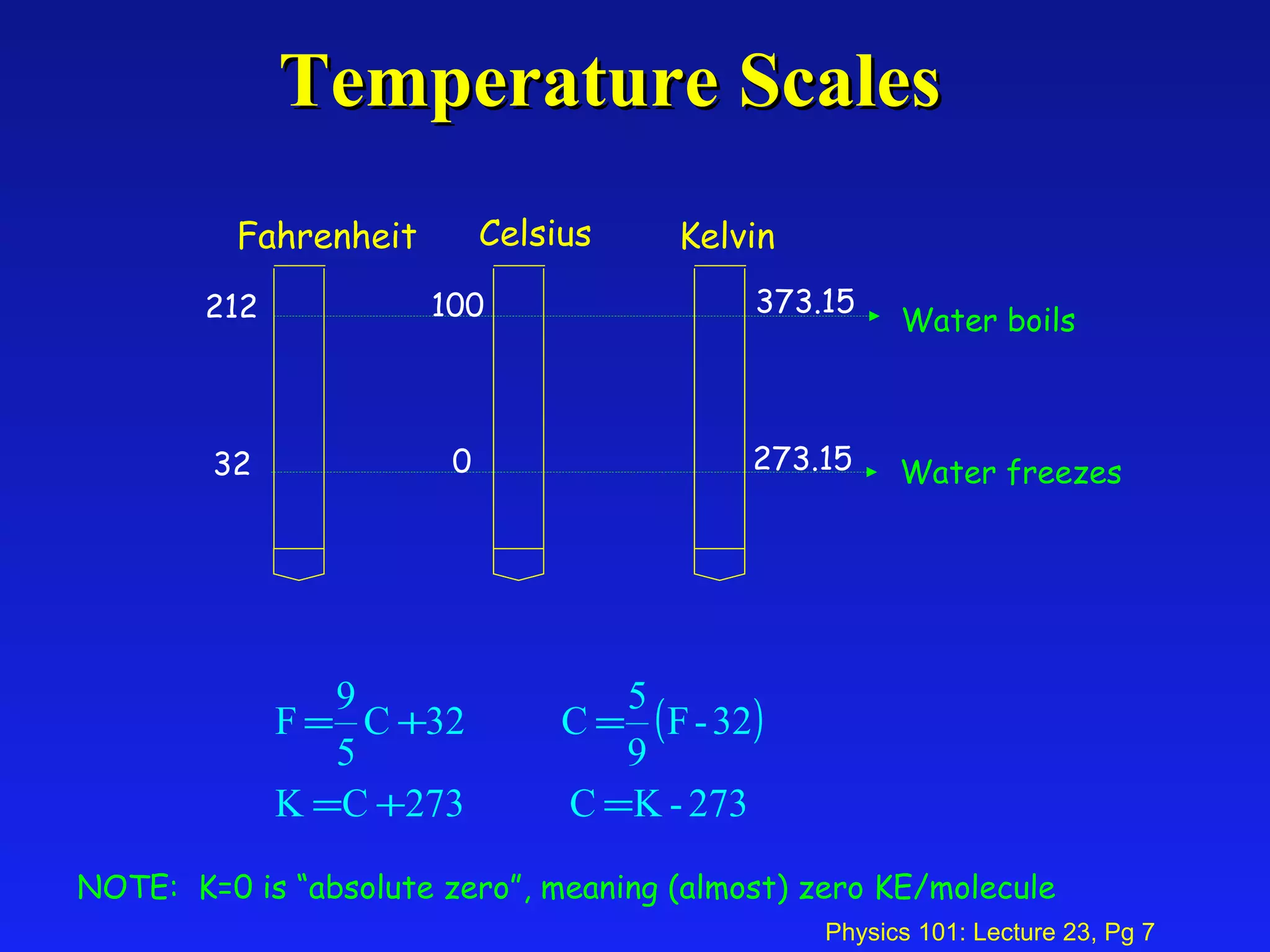
This document summarizes key points from a physics lecture on temperature and ideal gases:
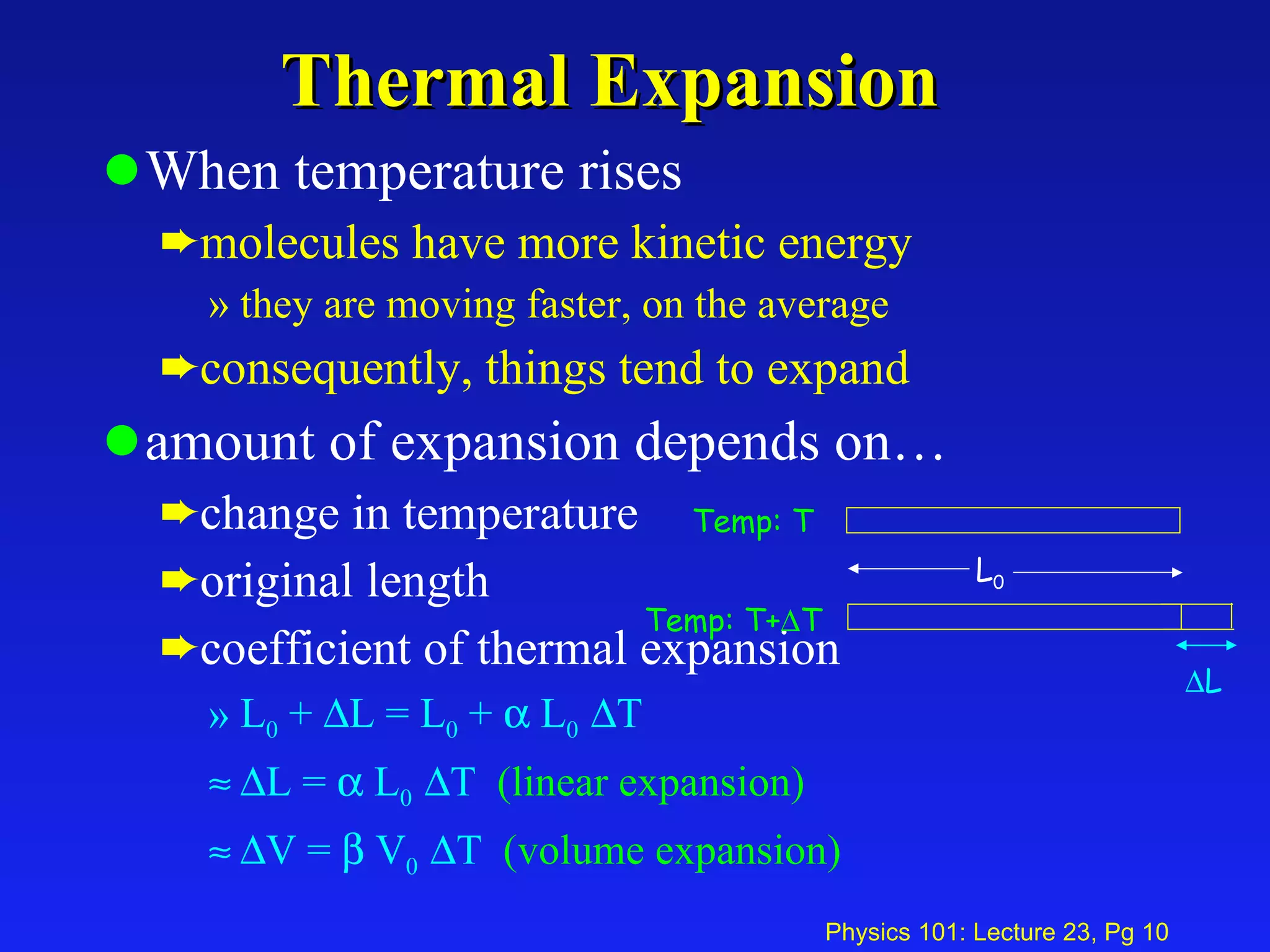
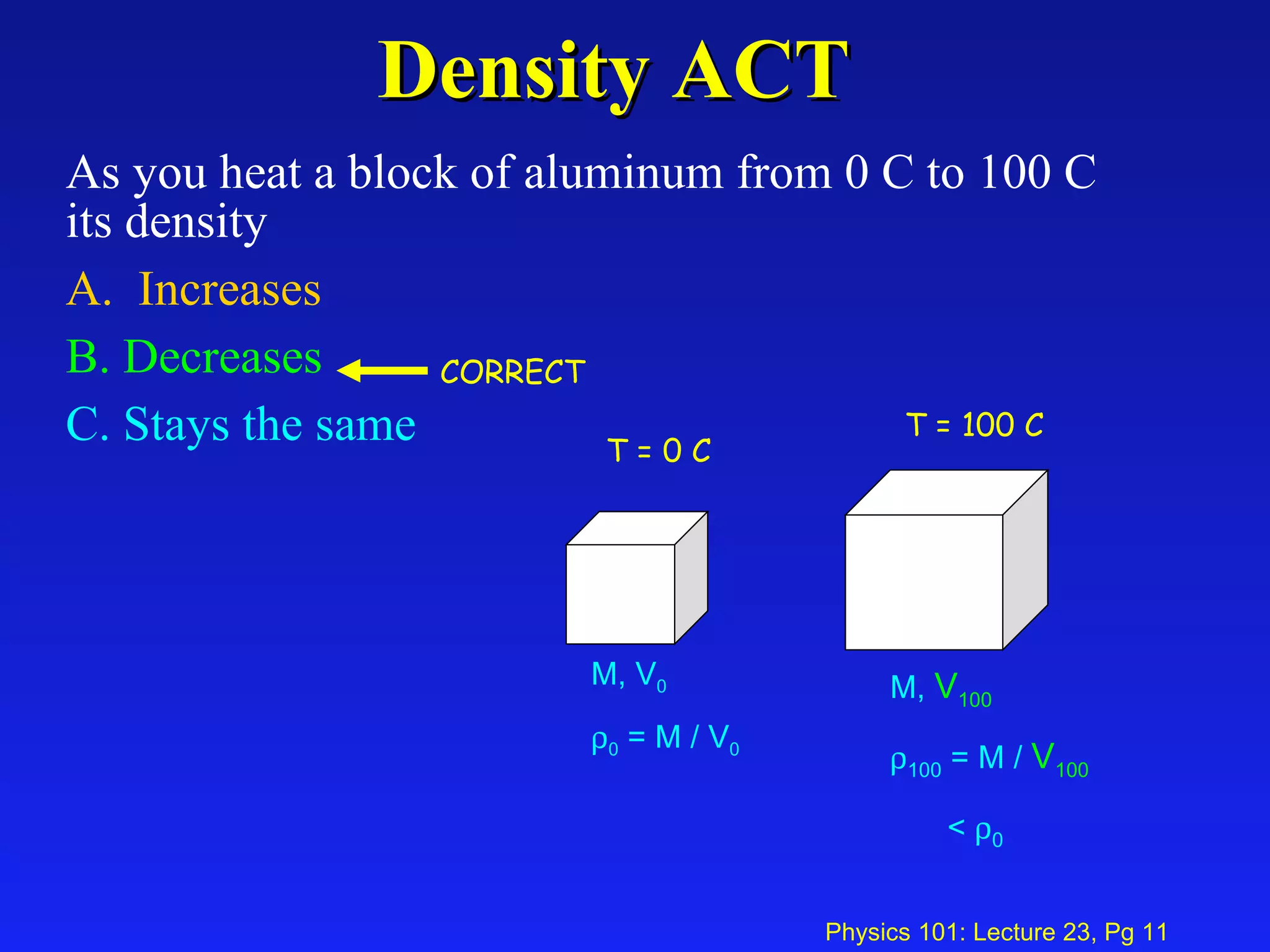
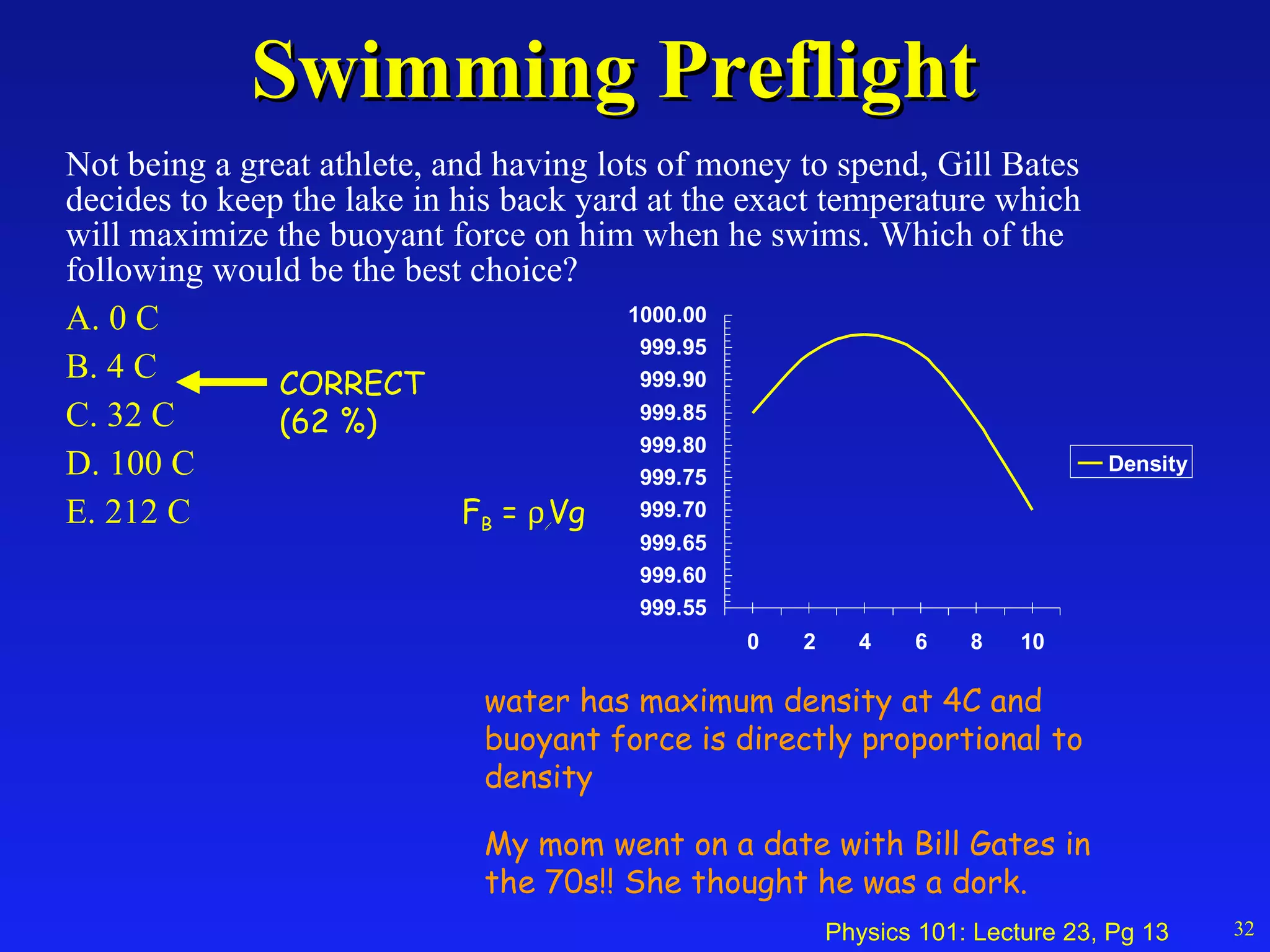
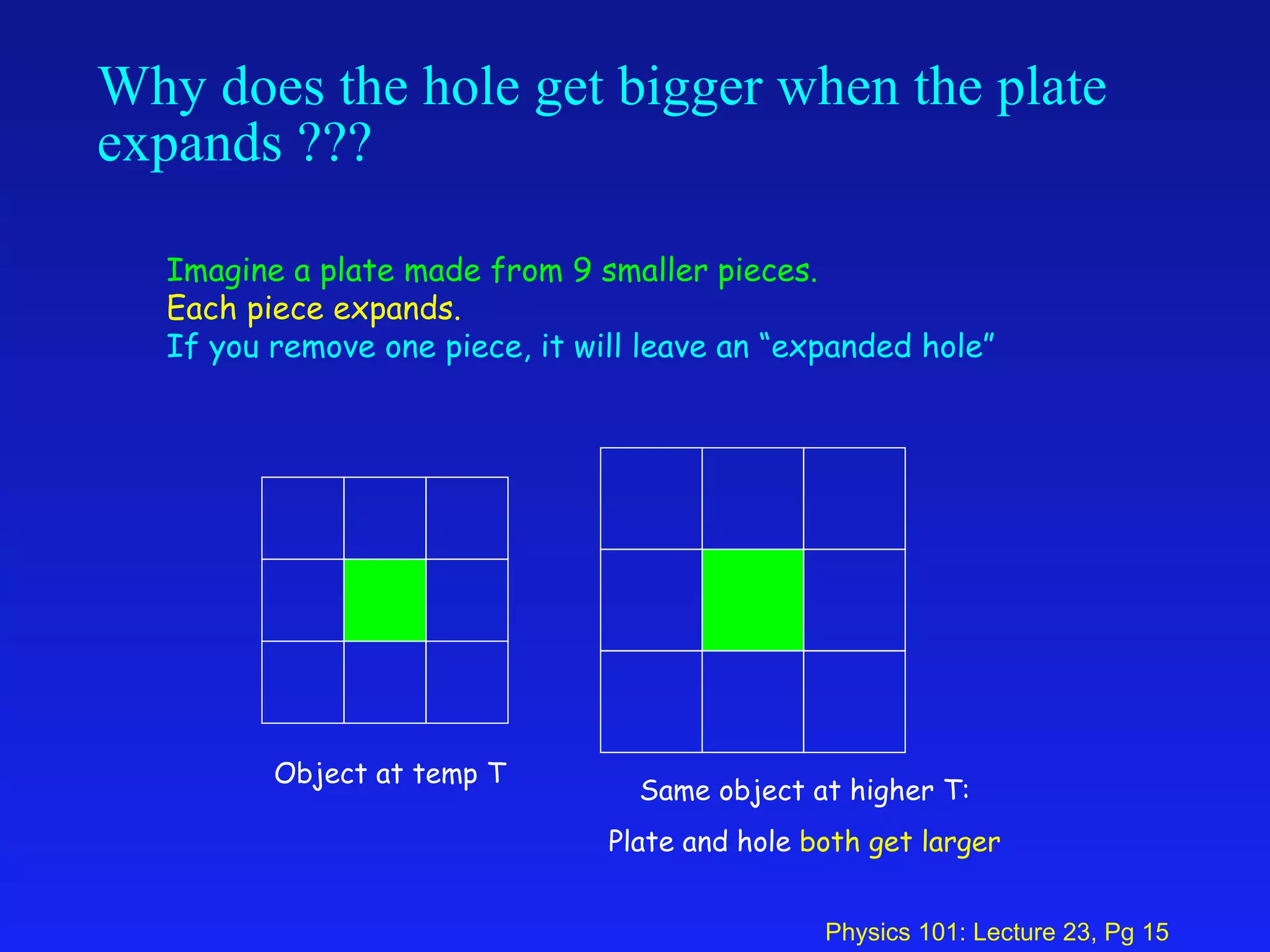
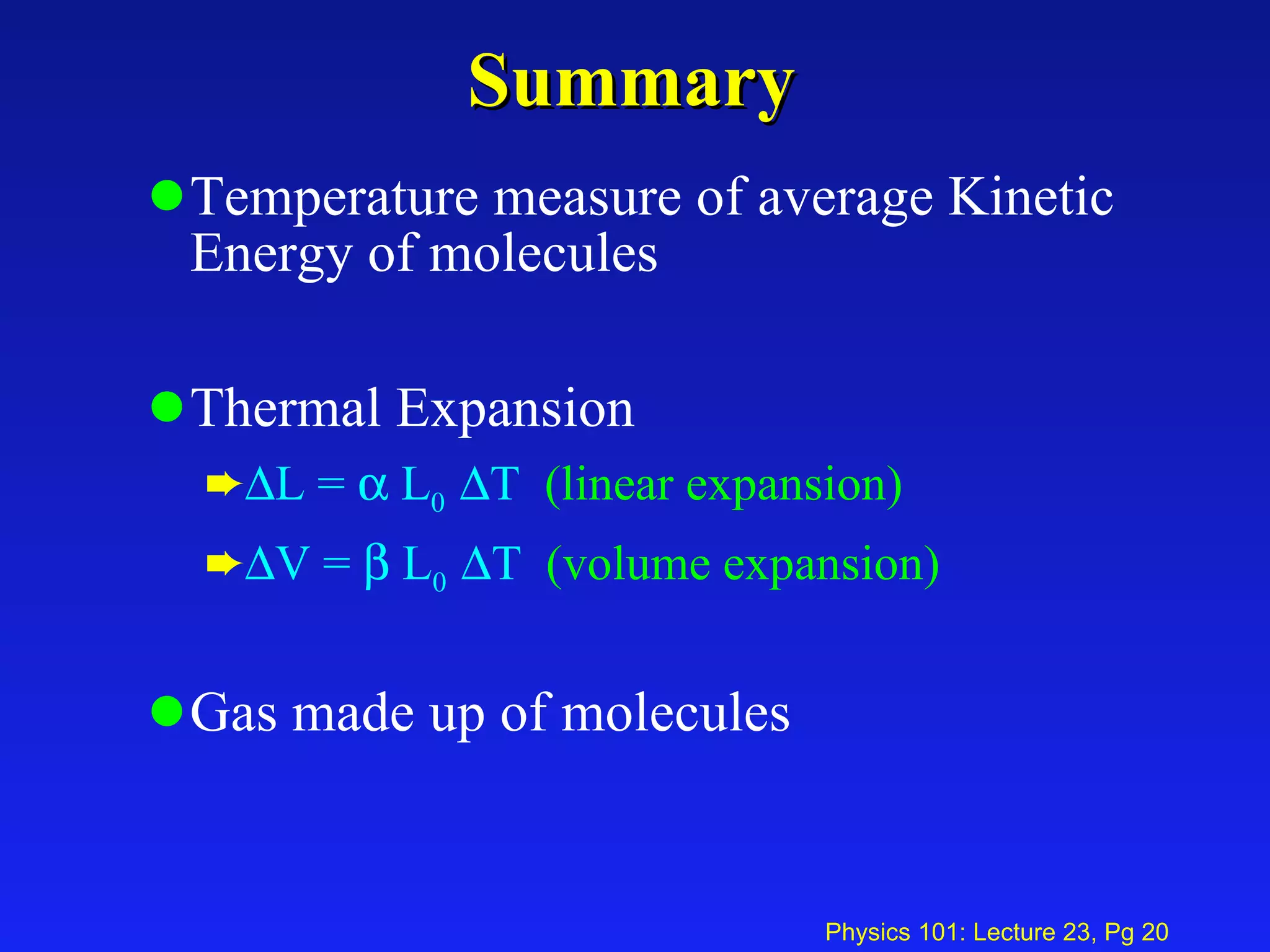
1. Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of molecules in an object. When temperature increases, molecules move faster and objects expand through thermal expansion.
2. Thermal expansion is described by the equations ΔL = αL0ΔT for linear expansion and ΔV = βV0ΔT for volume expansion, where α and β are coefficients of thermal expansion.
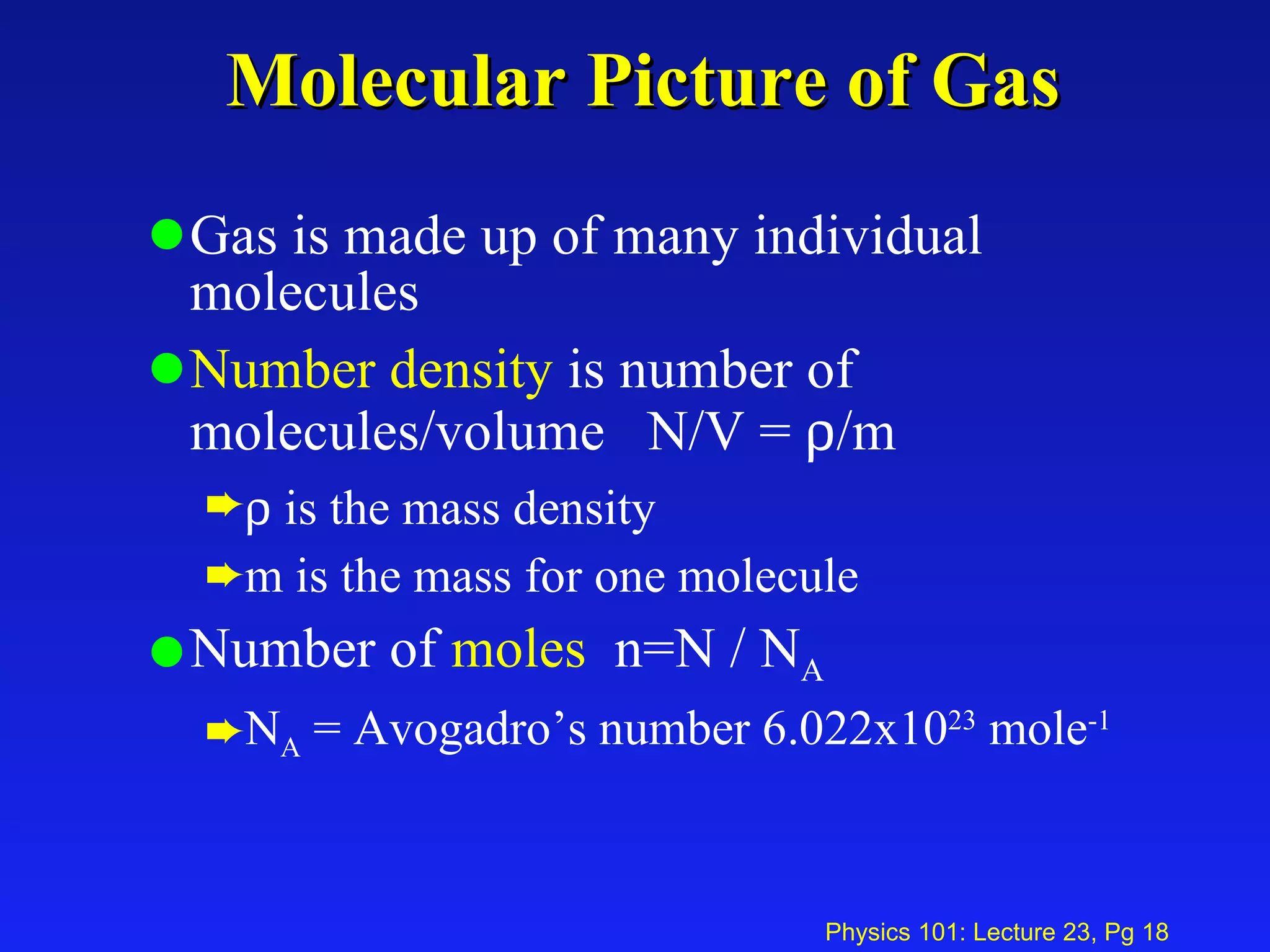
3. An ideal gas is made up of many individual molecules, with properties like number density (number of molecules per volume) described using concepts like number of moles and Avogadro's number.