Embed presentation
Download to read offline


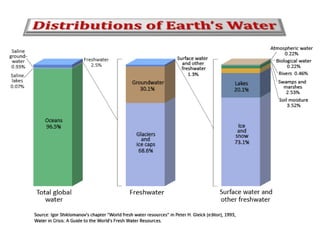


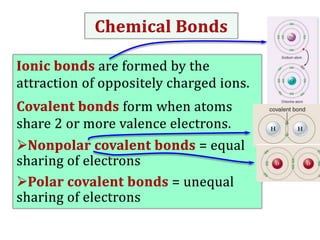
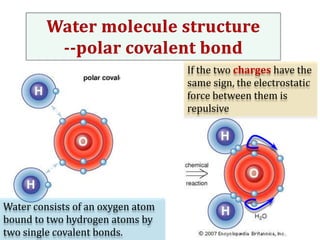
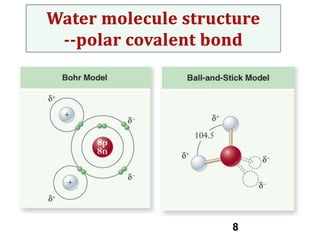
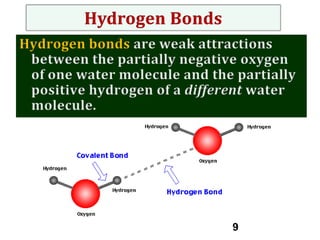
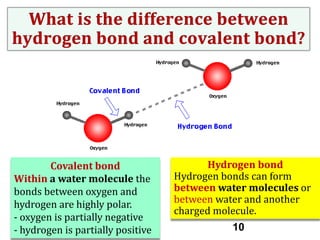
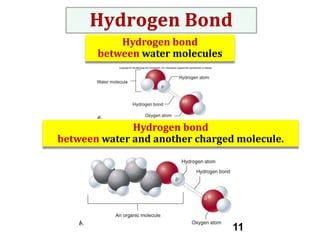


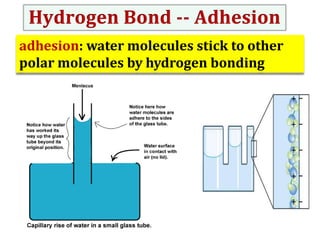
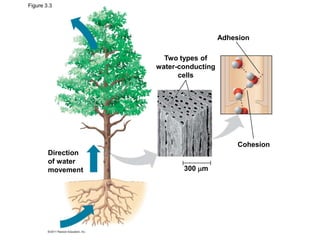


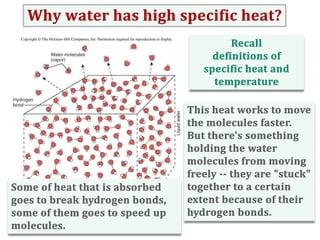
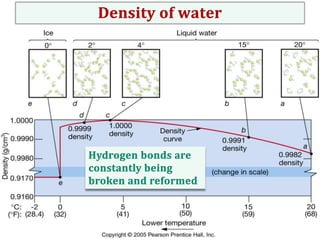


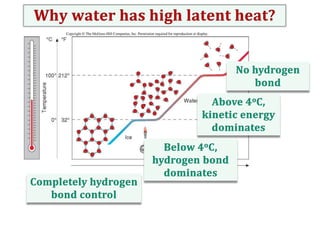

Water consists of an oxygen atom bound to two hydrogen atoms by two covalent bonds. Within a water molecule, the bonds between oxygen and hydrogen are highly polar, with oxygen being partially negative and hydrogen being partially positive. This polarity allows hydrogen bonds to form between water molecules or between water and other charged molecules, giving water its cohesive and adhesive properties.






















