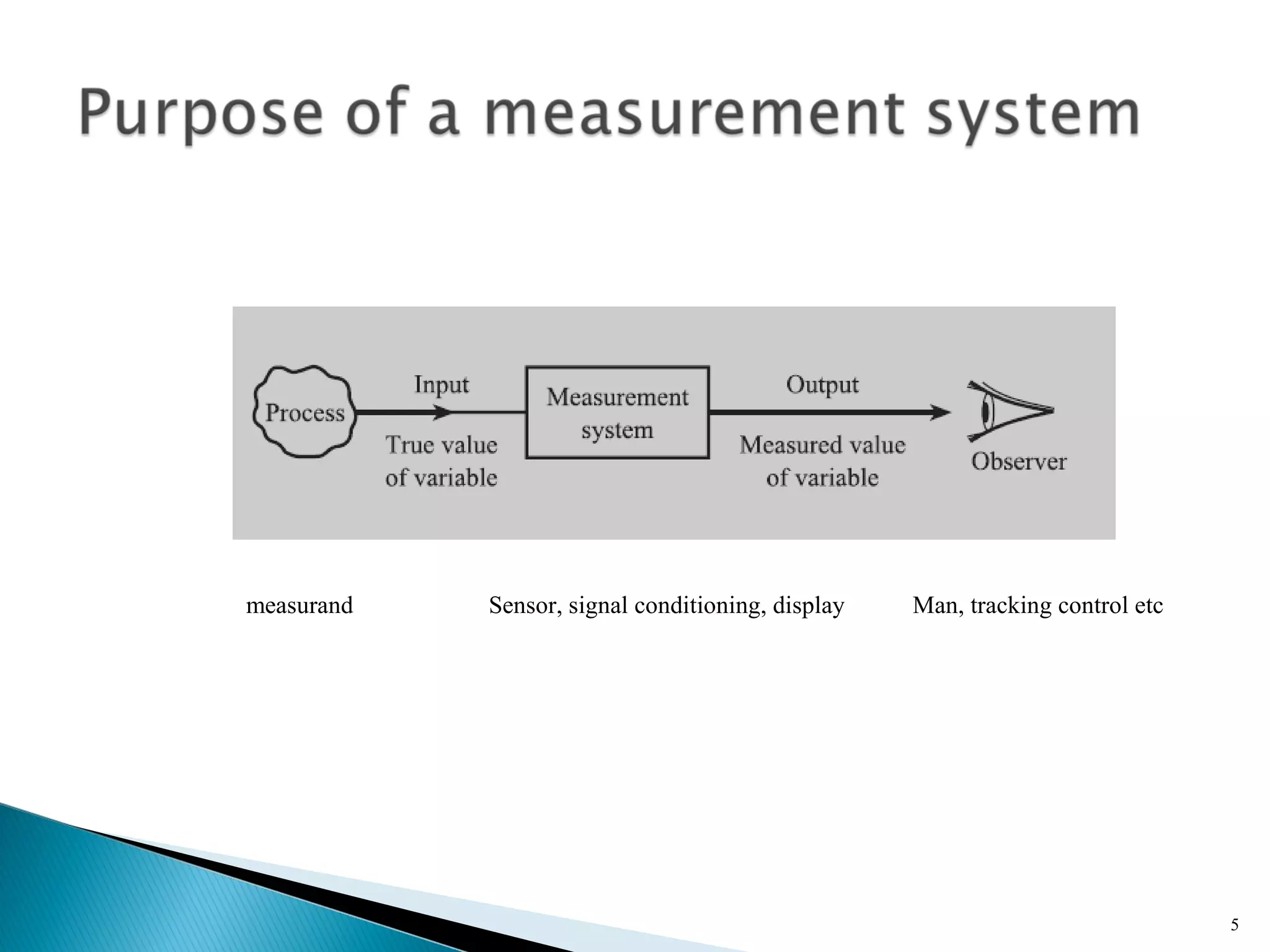
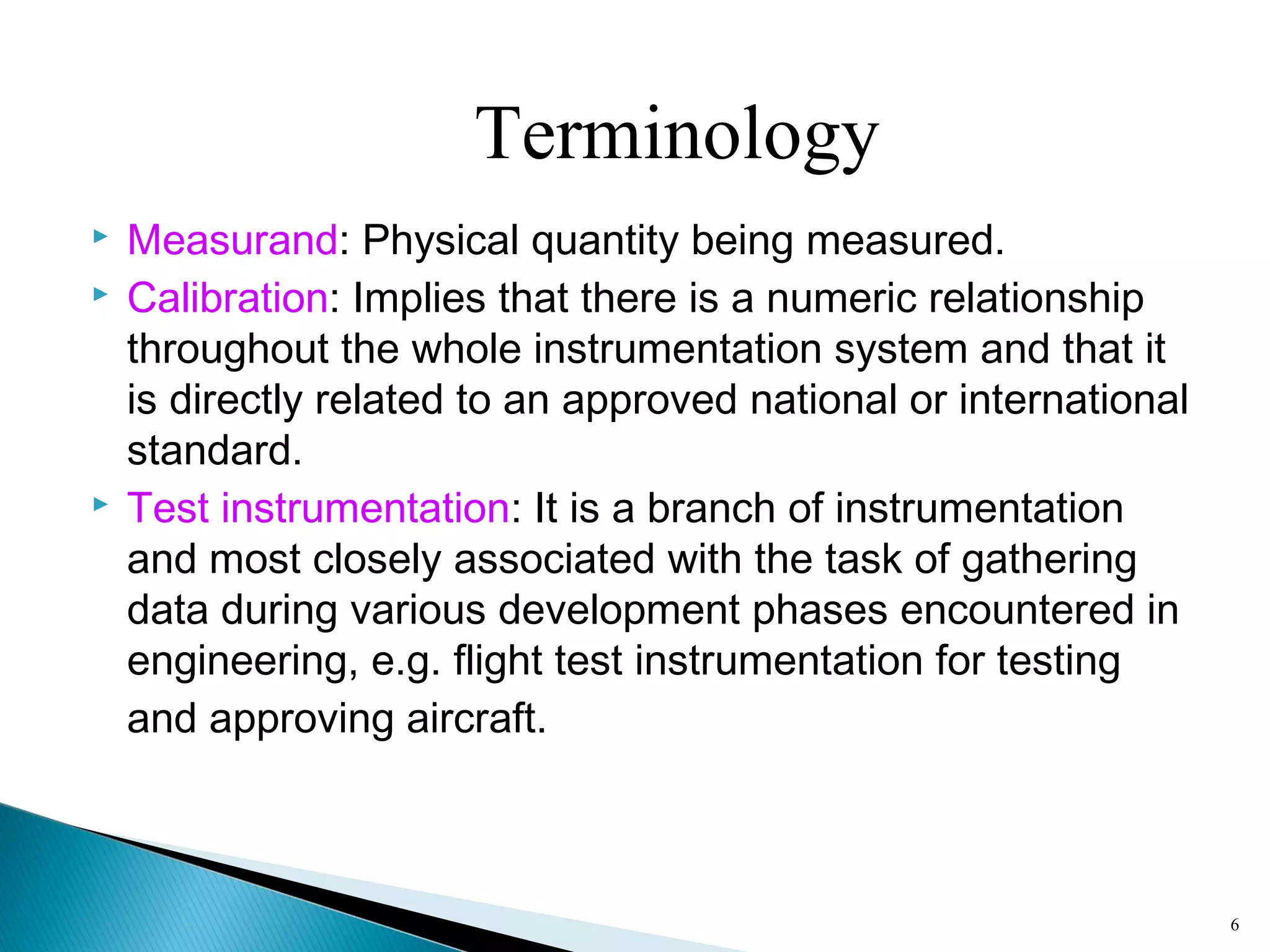
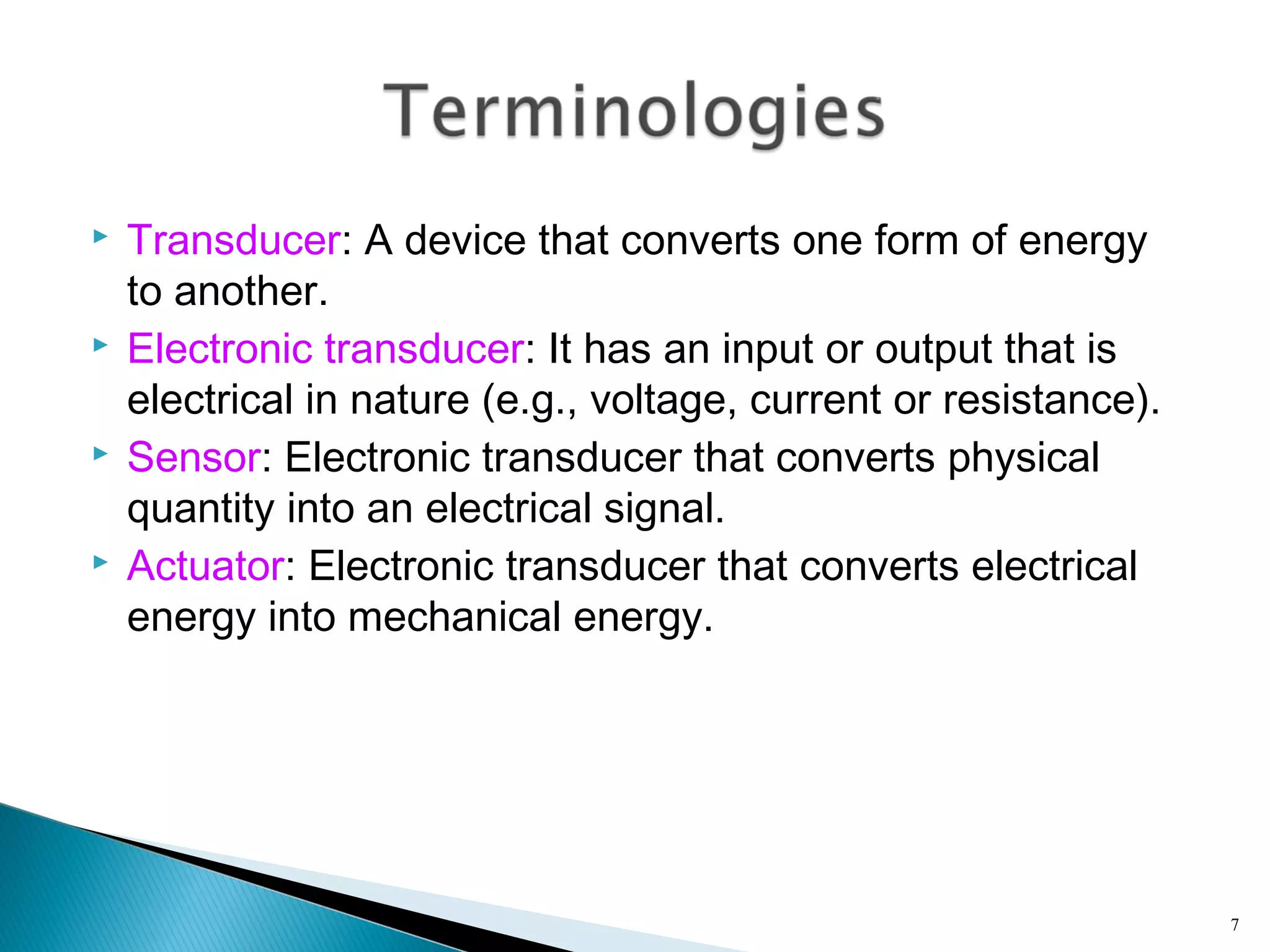
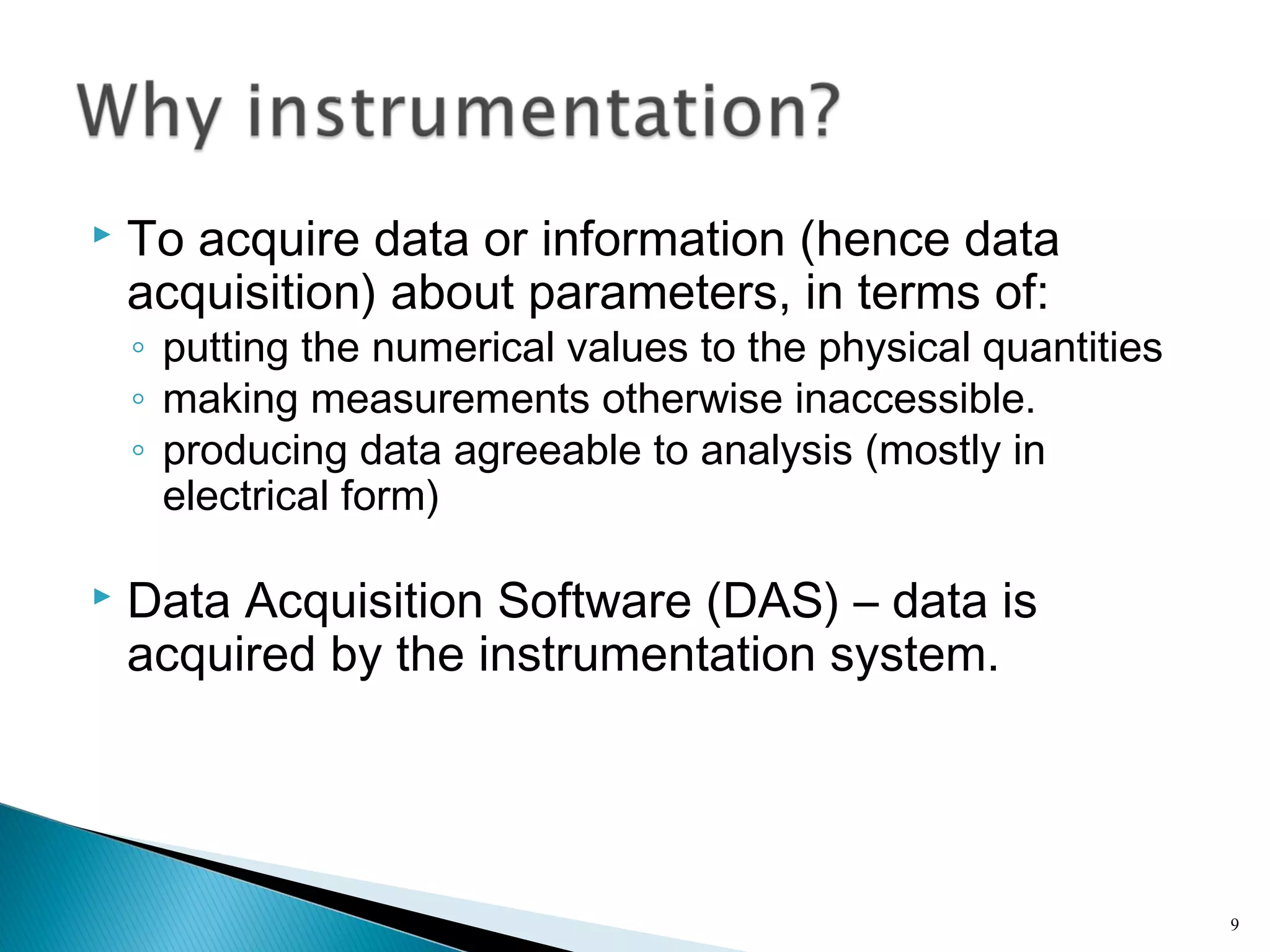
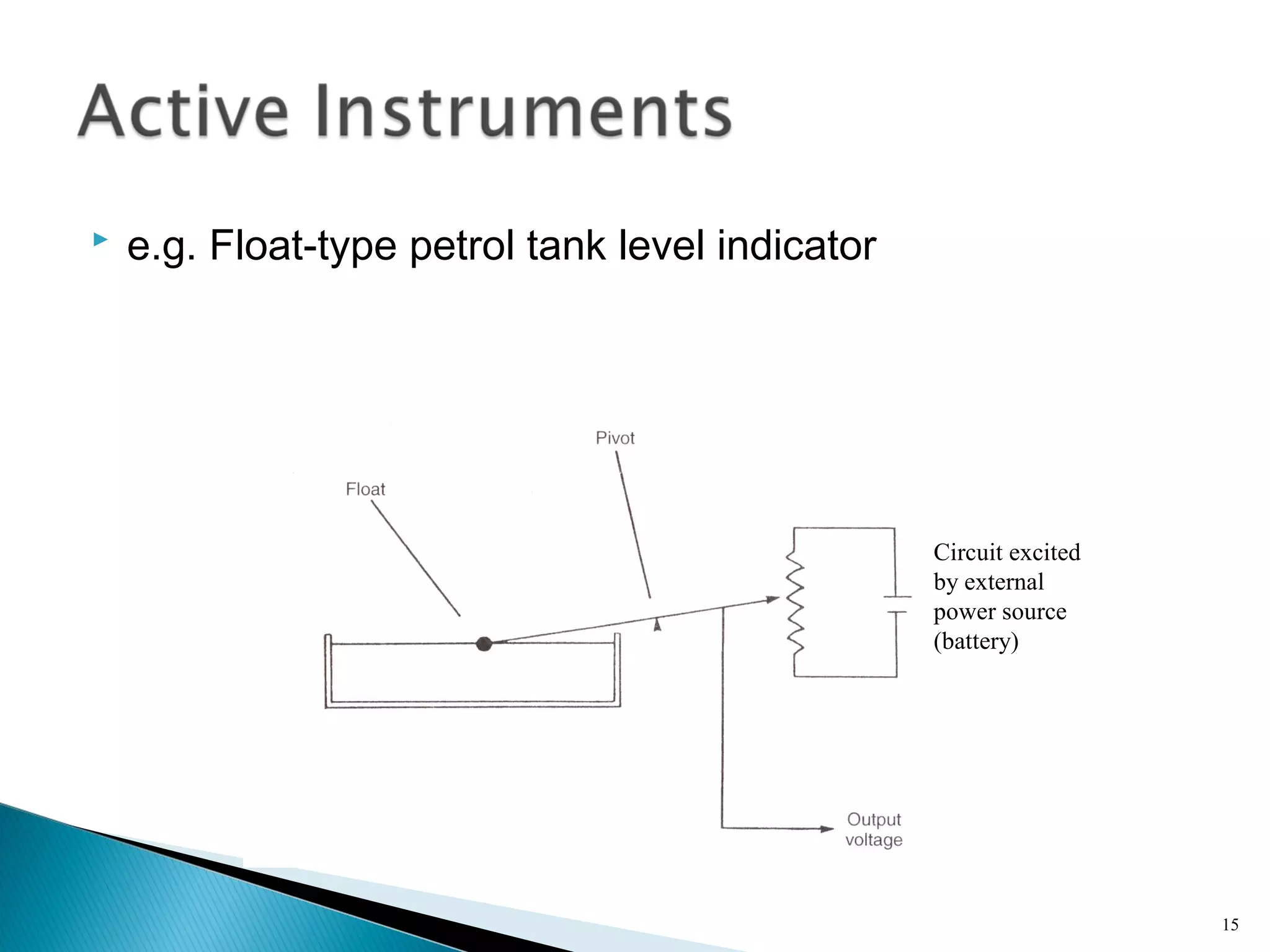
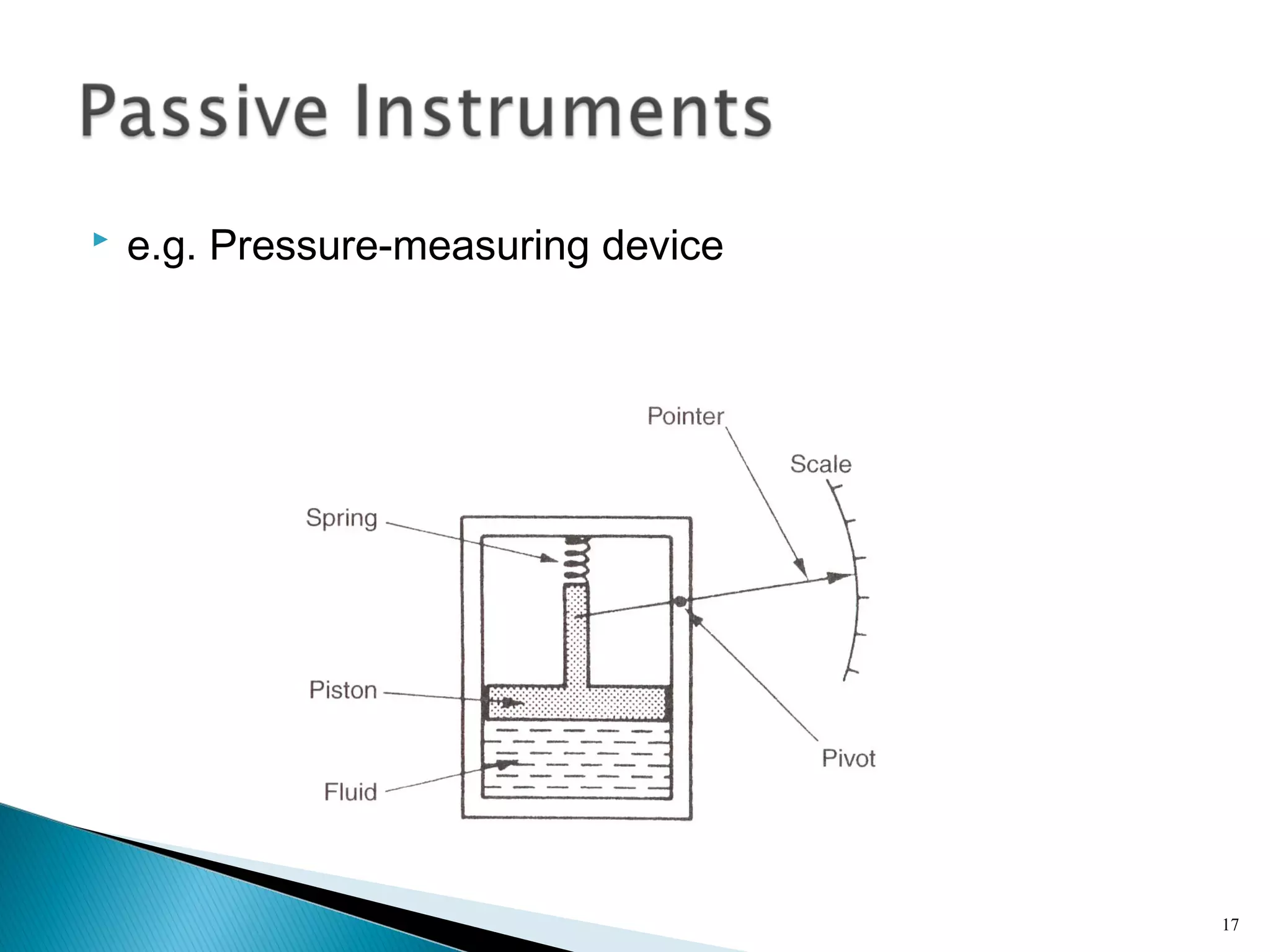
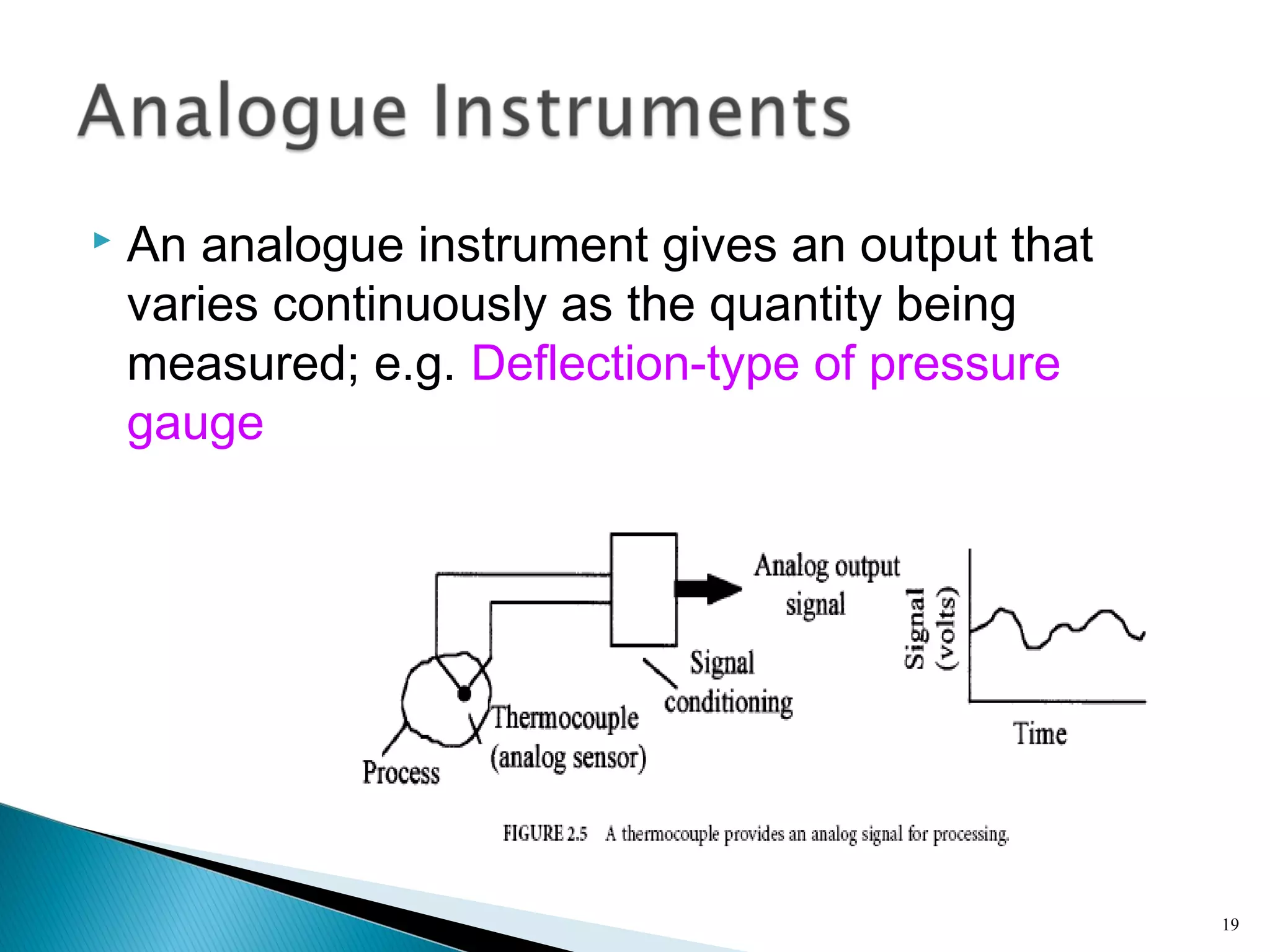
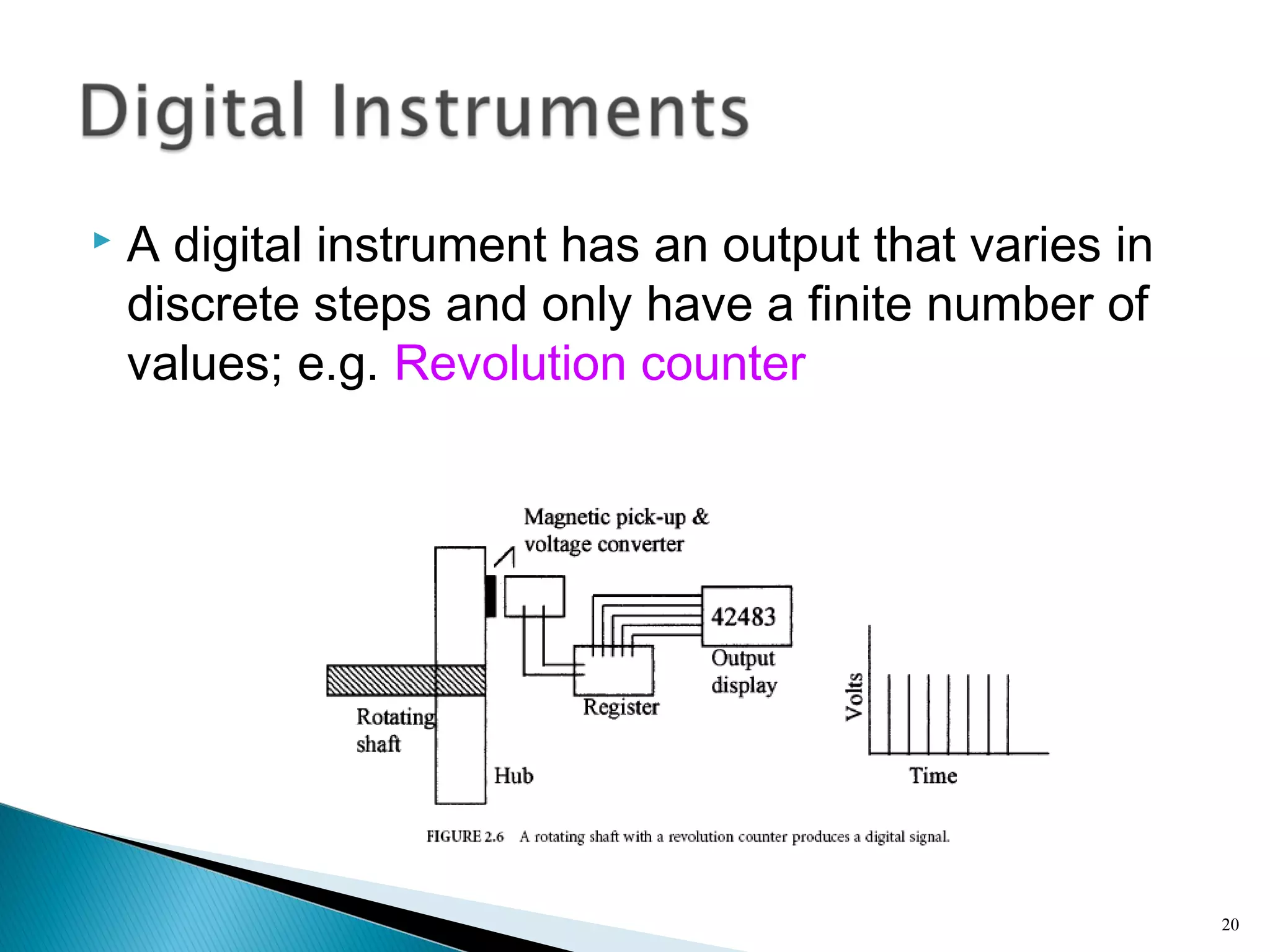
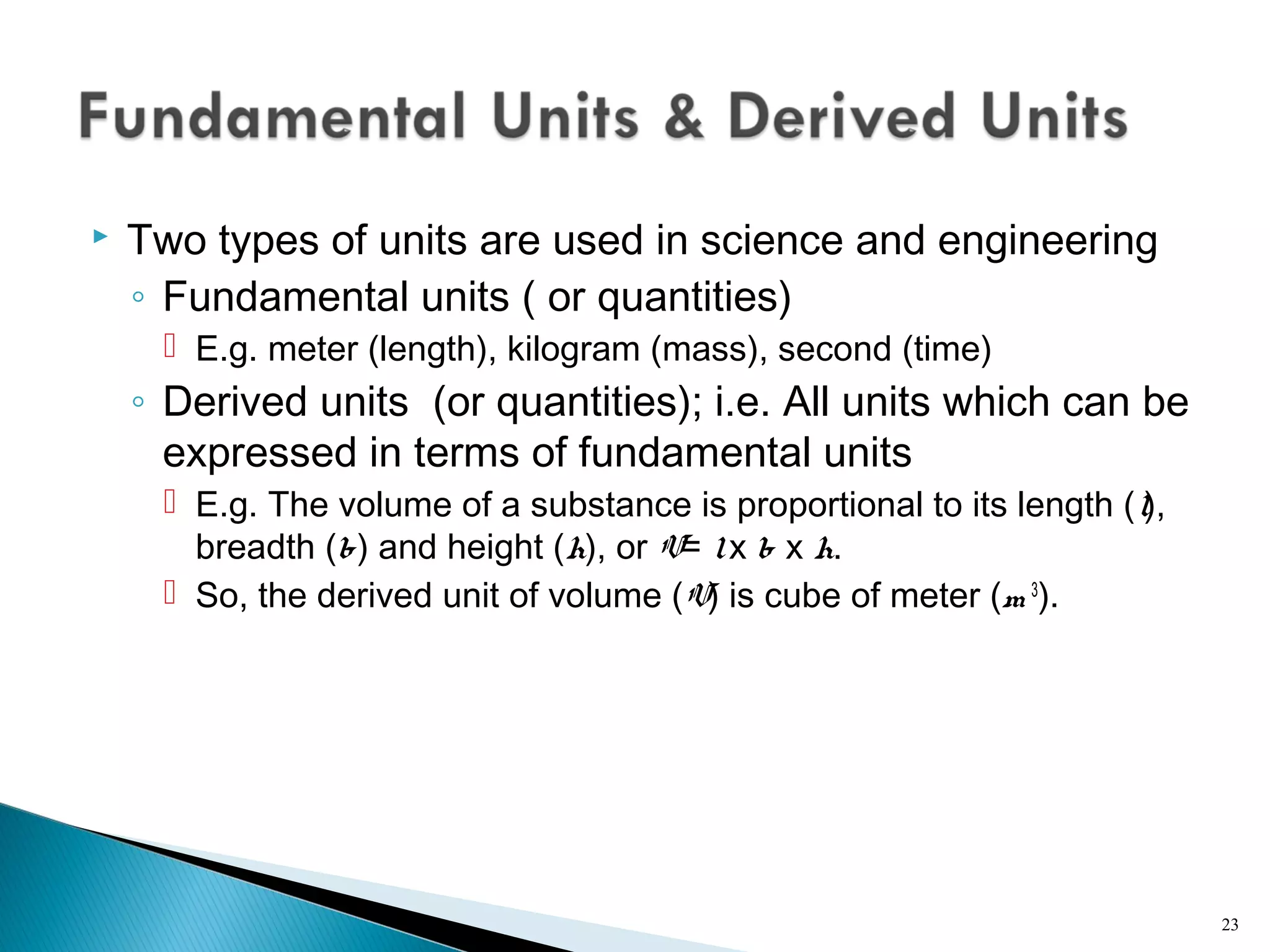
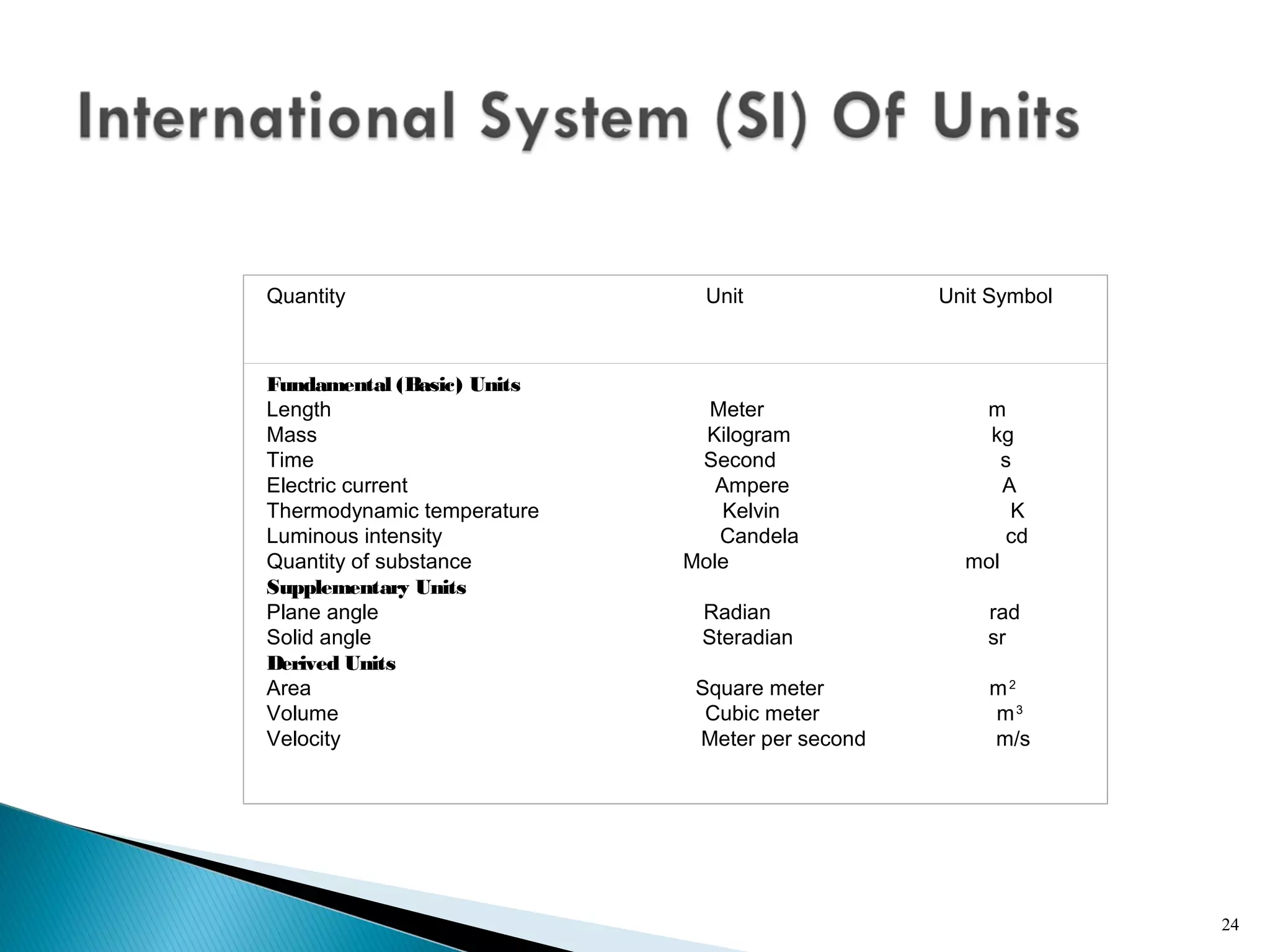
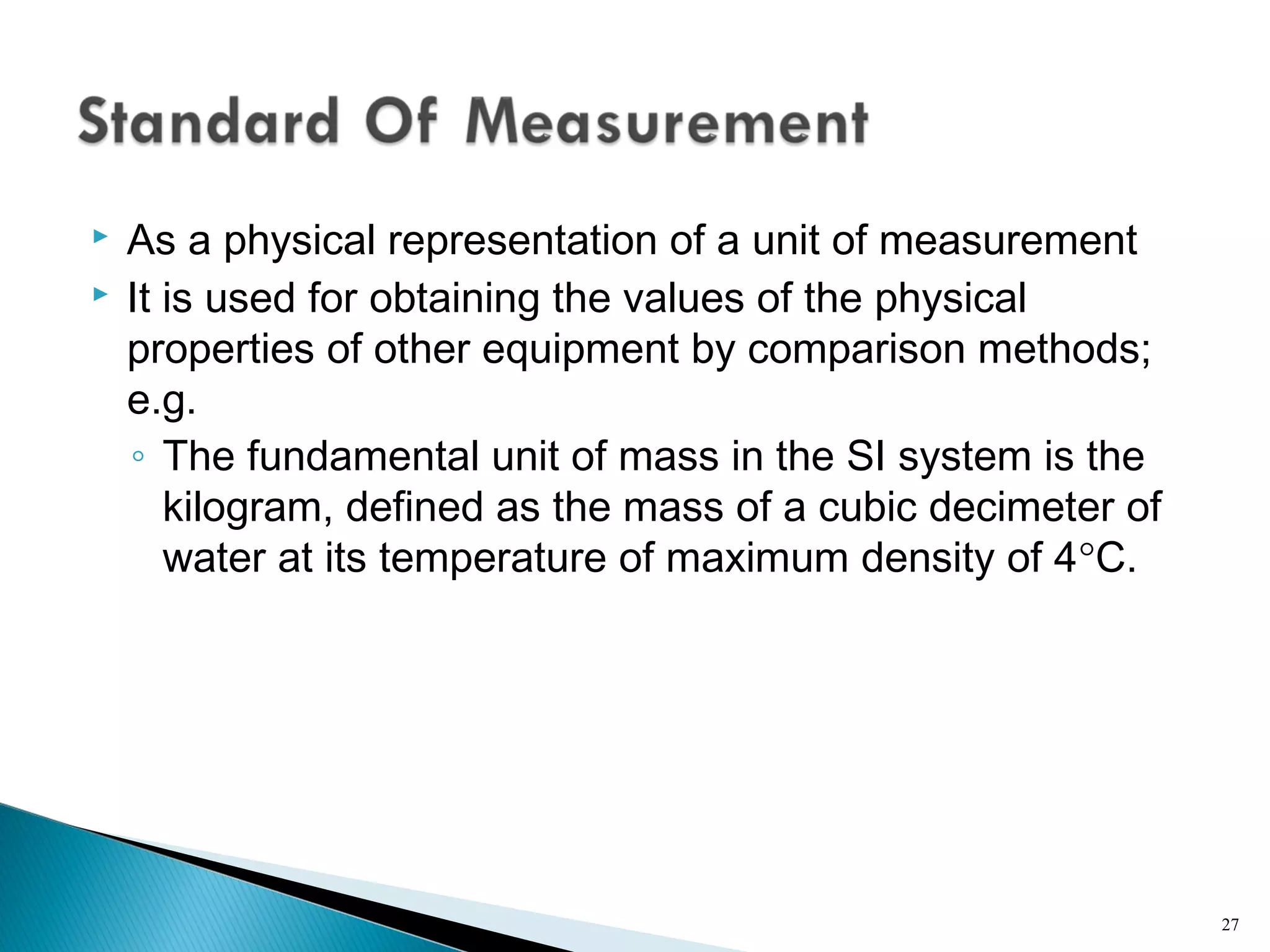
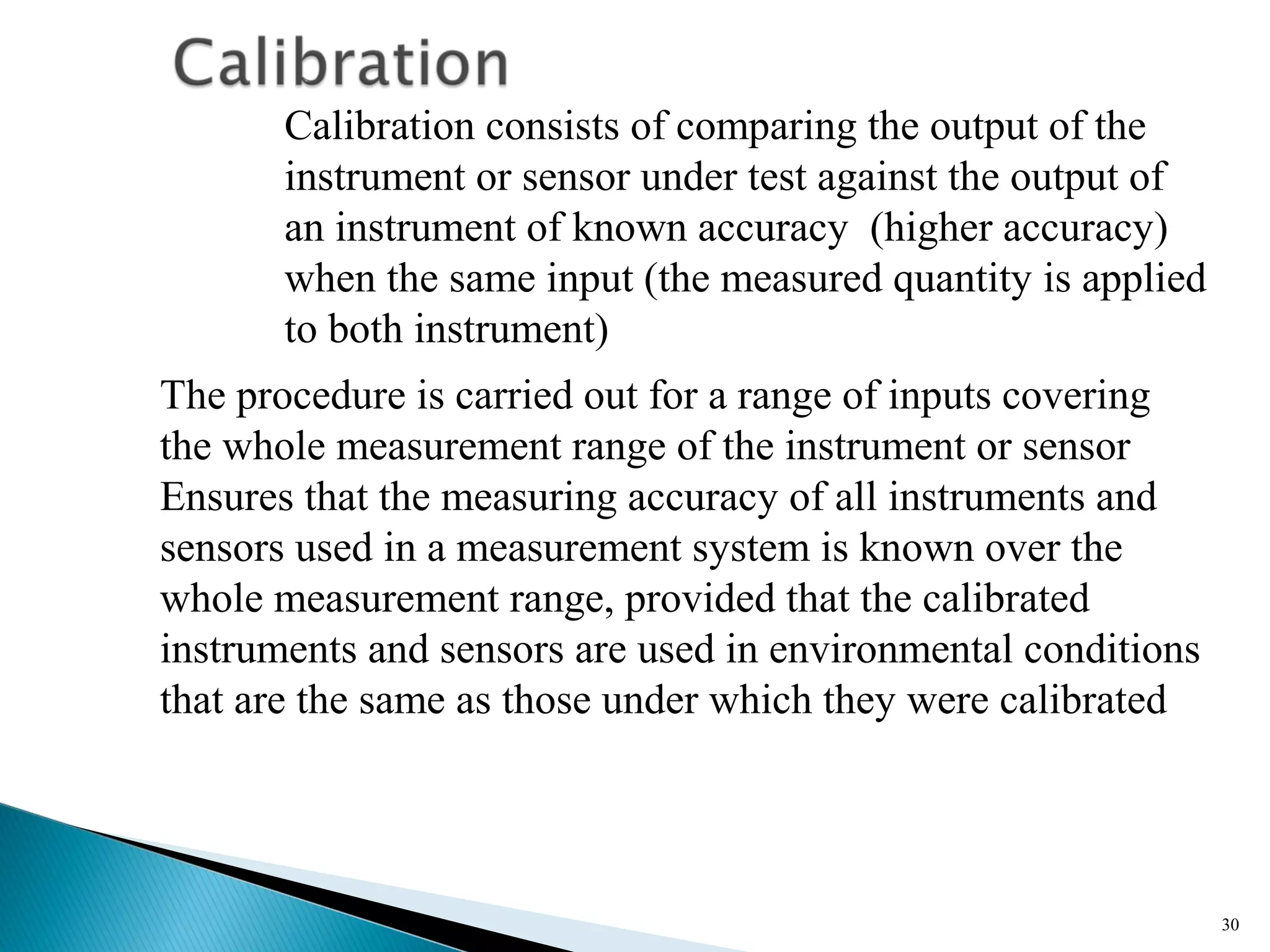
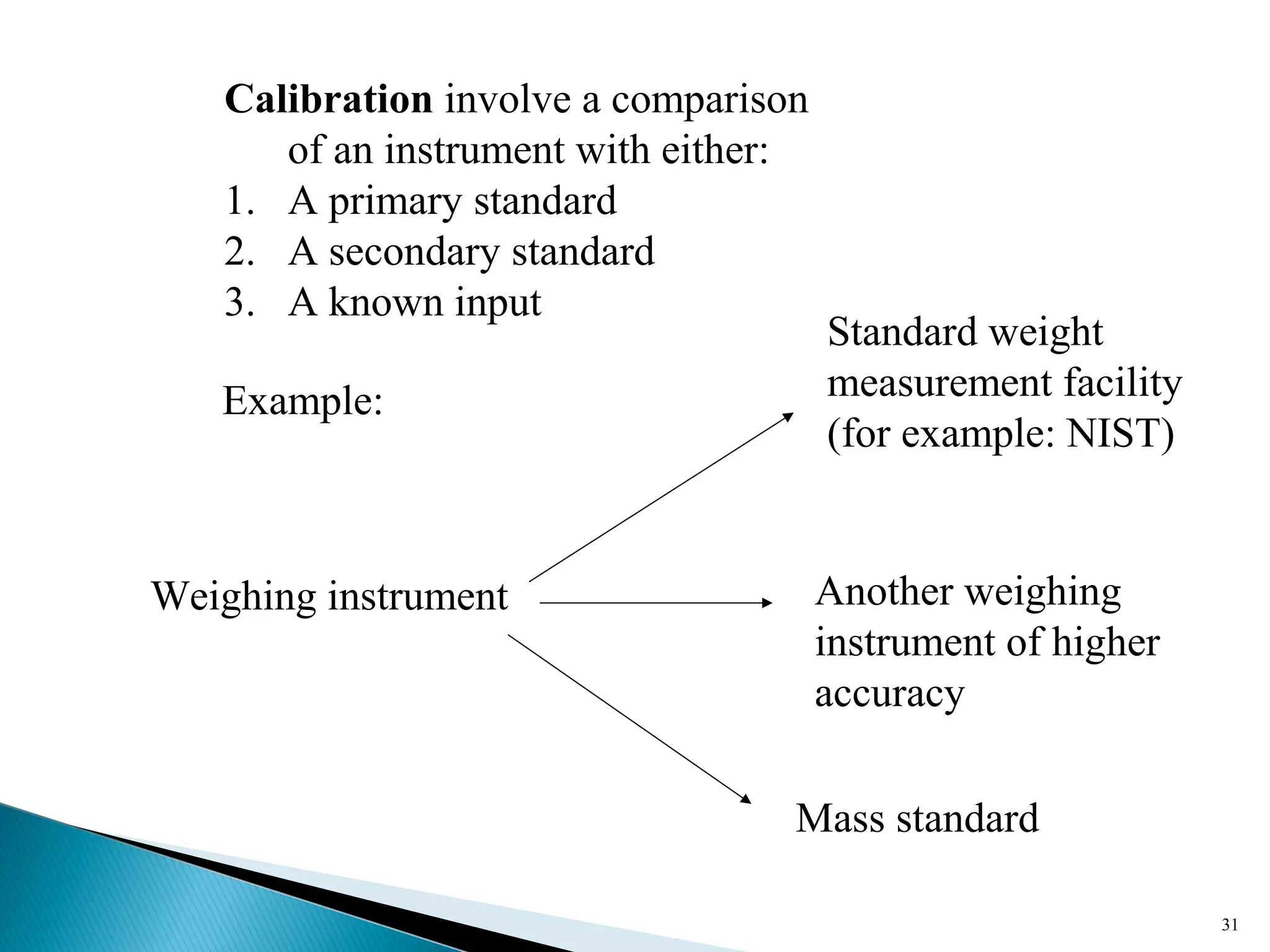
This lecture introduces measurement and instrumentation. It defines measurement and instrumentation, discusses types of measurements and instruments. It reviews units of measurement, standards of measurement, and calibration. Measurement and instrumentation are used in various applications including home appliances, vehicles, and industrial processes to monitor and control parameters and improve operations.