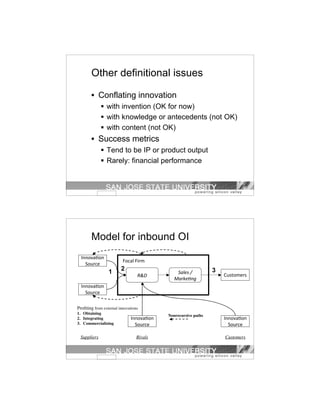
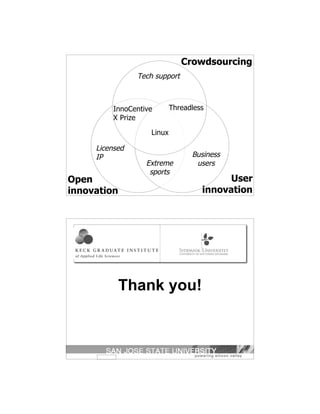
The document discusses a study on inbound open innovation, presenting a three-phase process model based on a review of 280 publications. It defines open innovation and crowdsourcing while exploring their concepts, methodologies, and potential gaps in research. Key elements include obtaining, integrating, and commercializing innovations, as well as implications for businesses and future research directions.