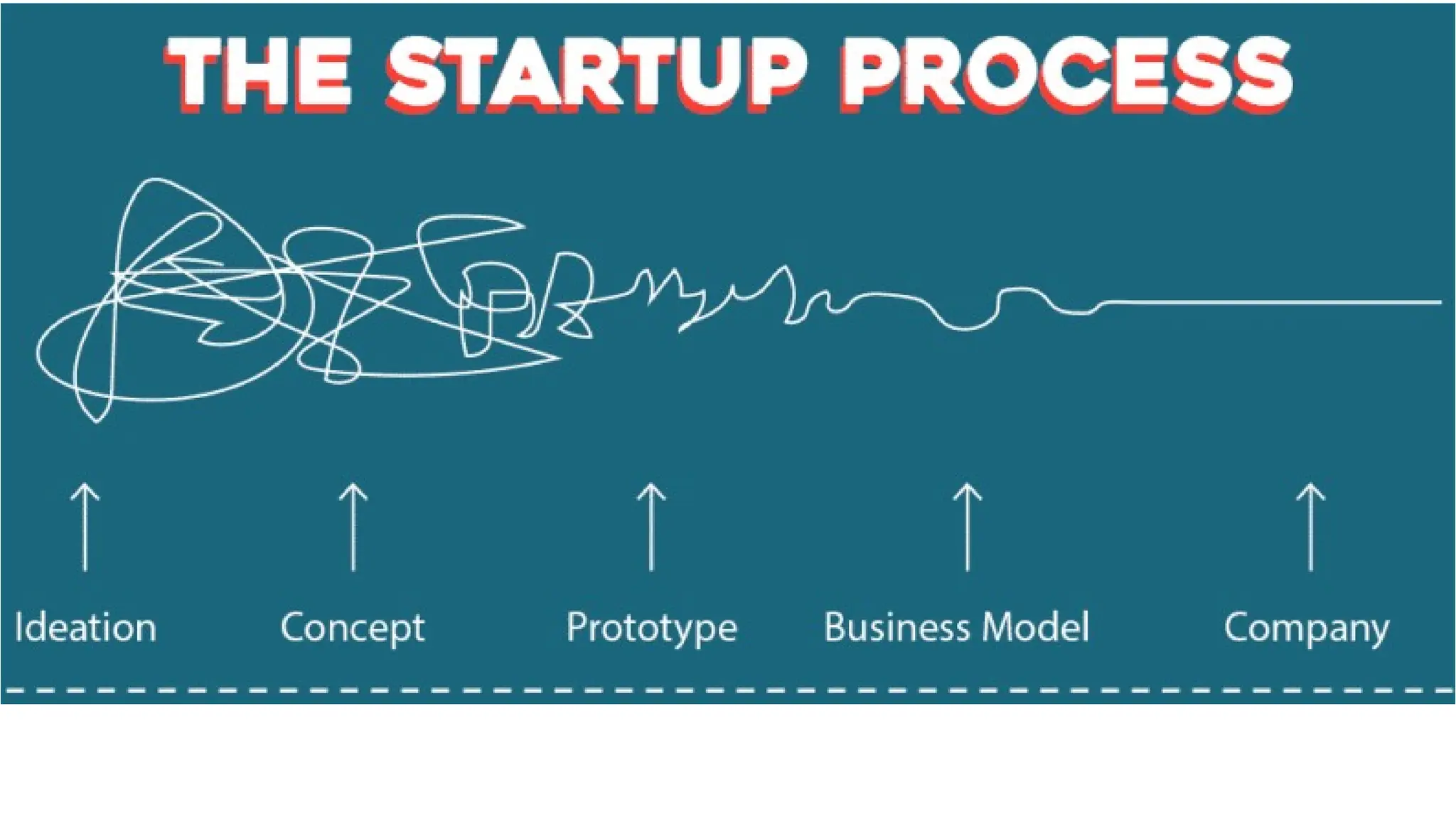
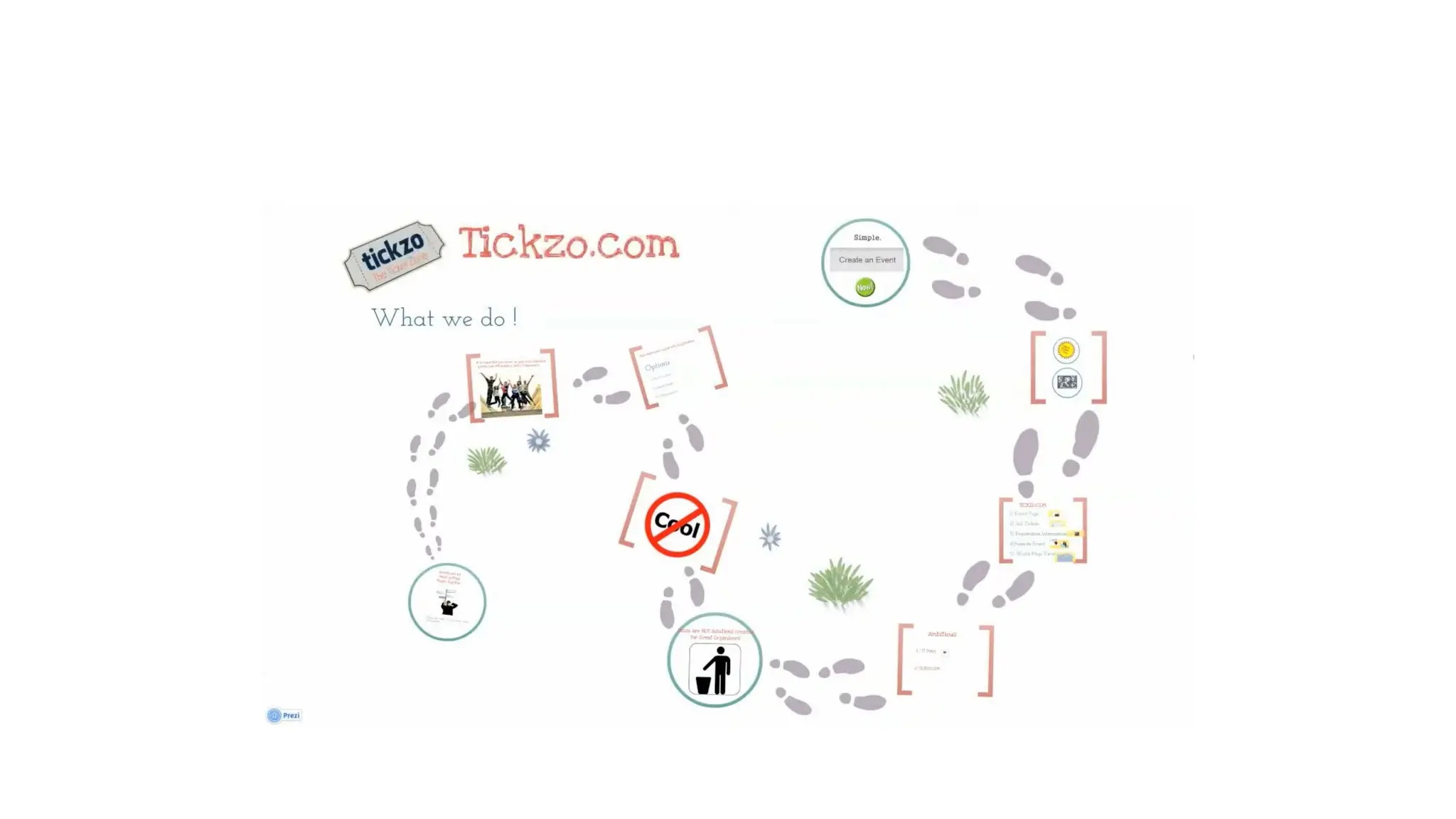
re you sitting on the next big idea but don’t know where to start?
This power-packed presentation dives deep into the art and science of ideation and product innovation — essential skills for entrepreneurs, designers, engineers, and changemakers.
🔍 What you'll learn:
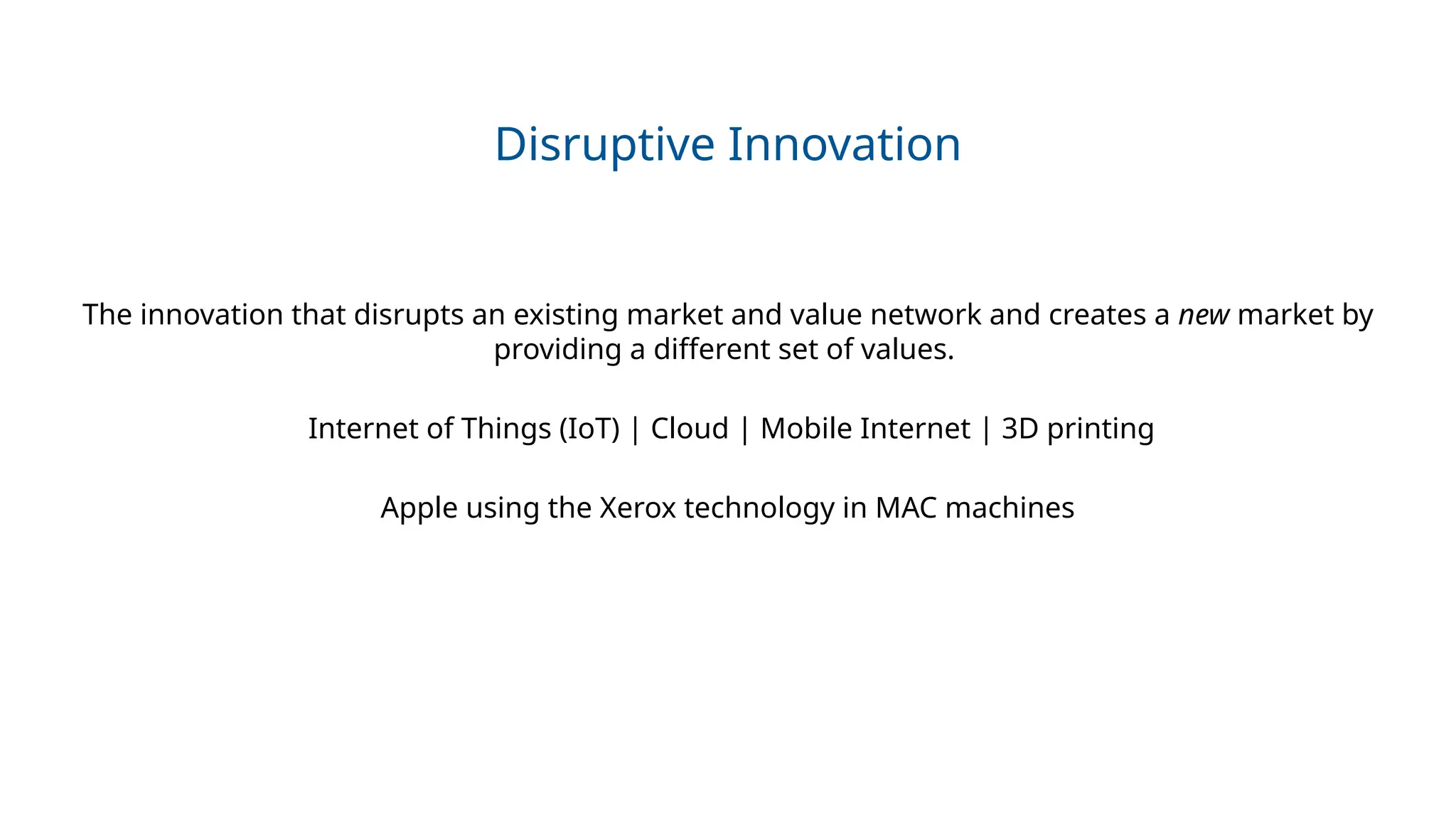
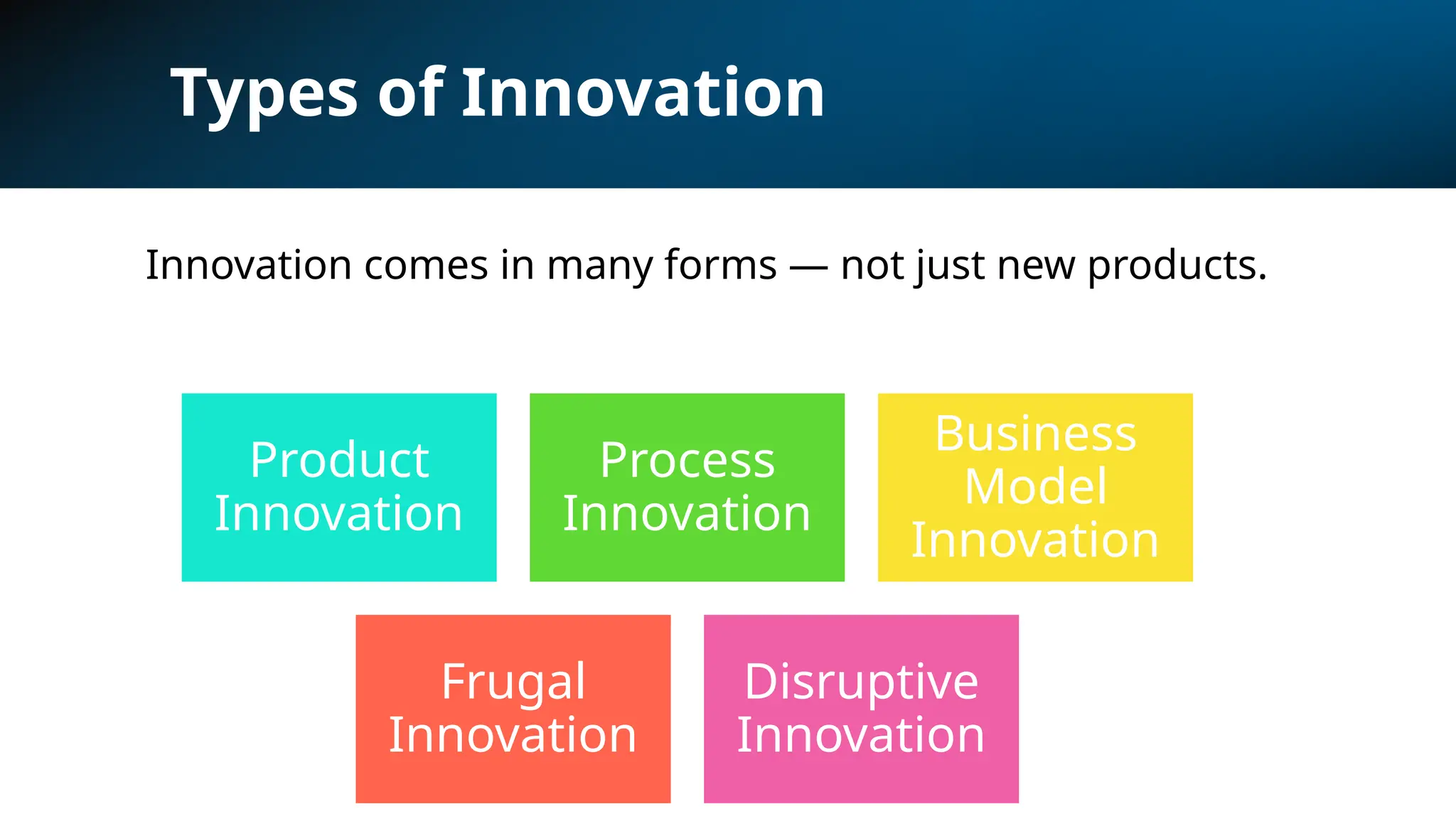
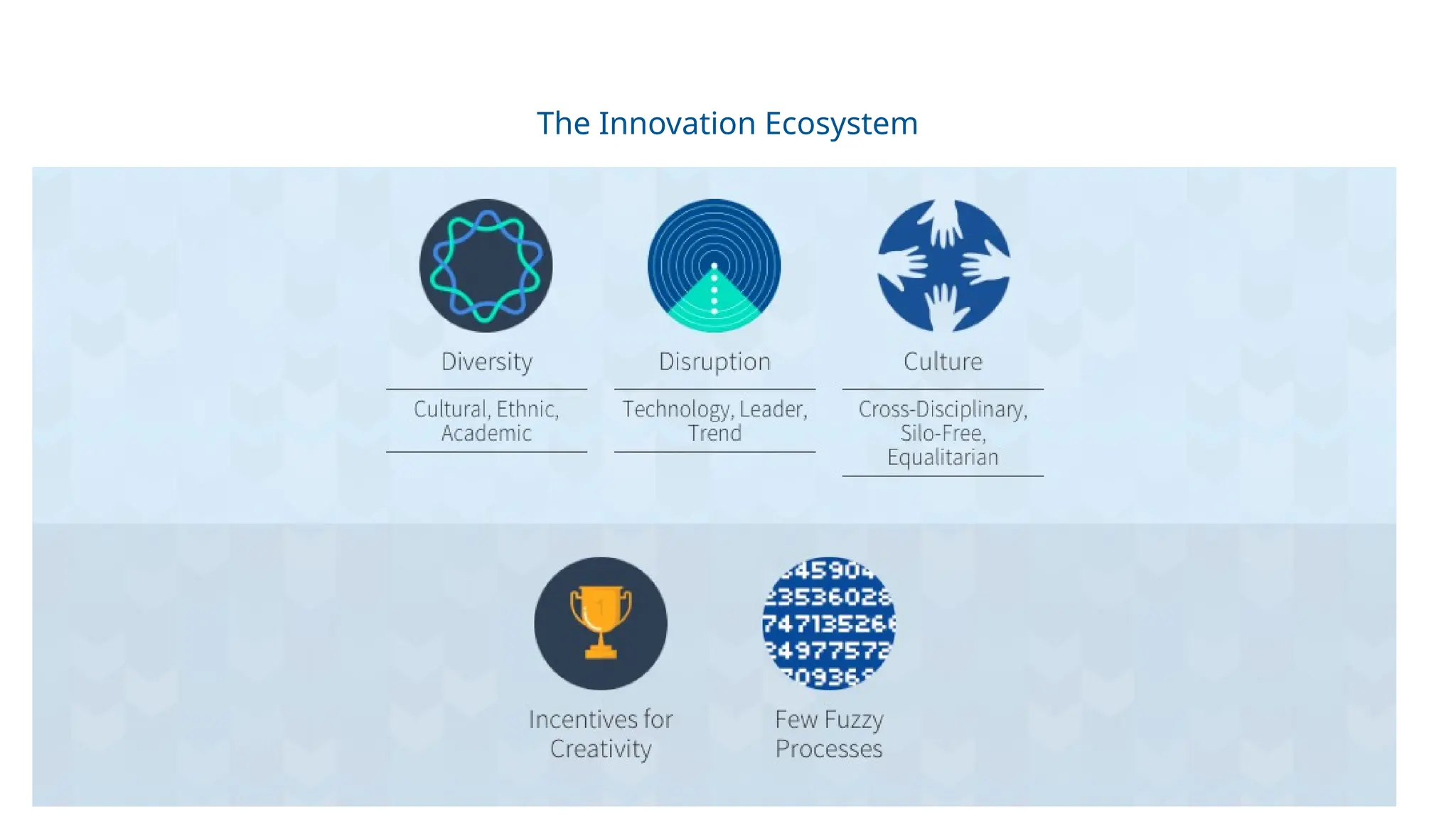
The 5 types of innovation: Product, Process, Business Model, Frugal, Disruptive
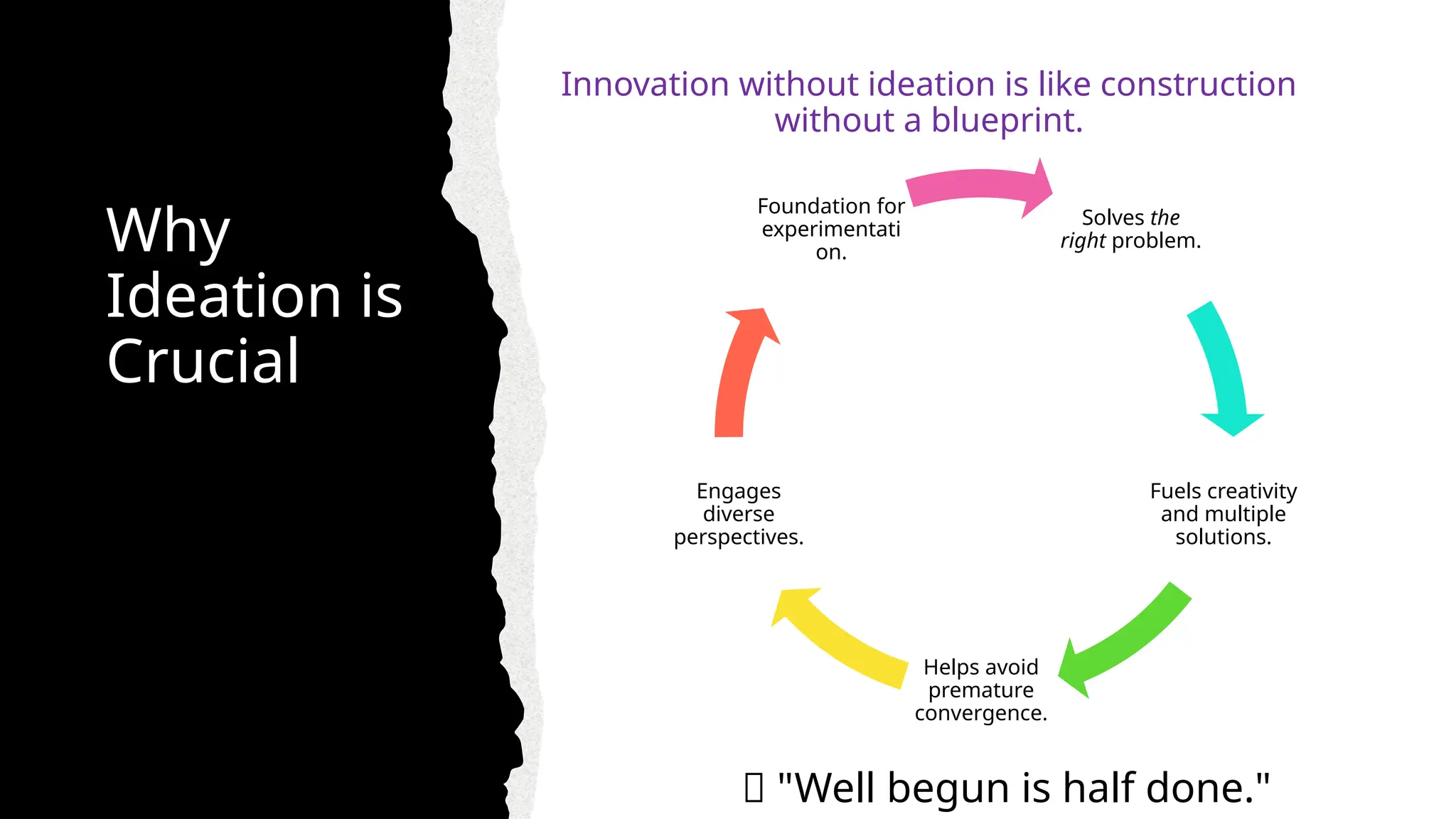
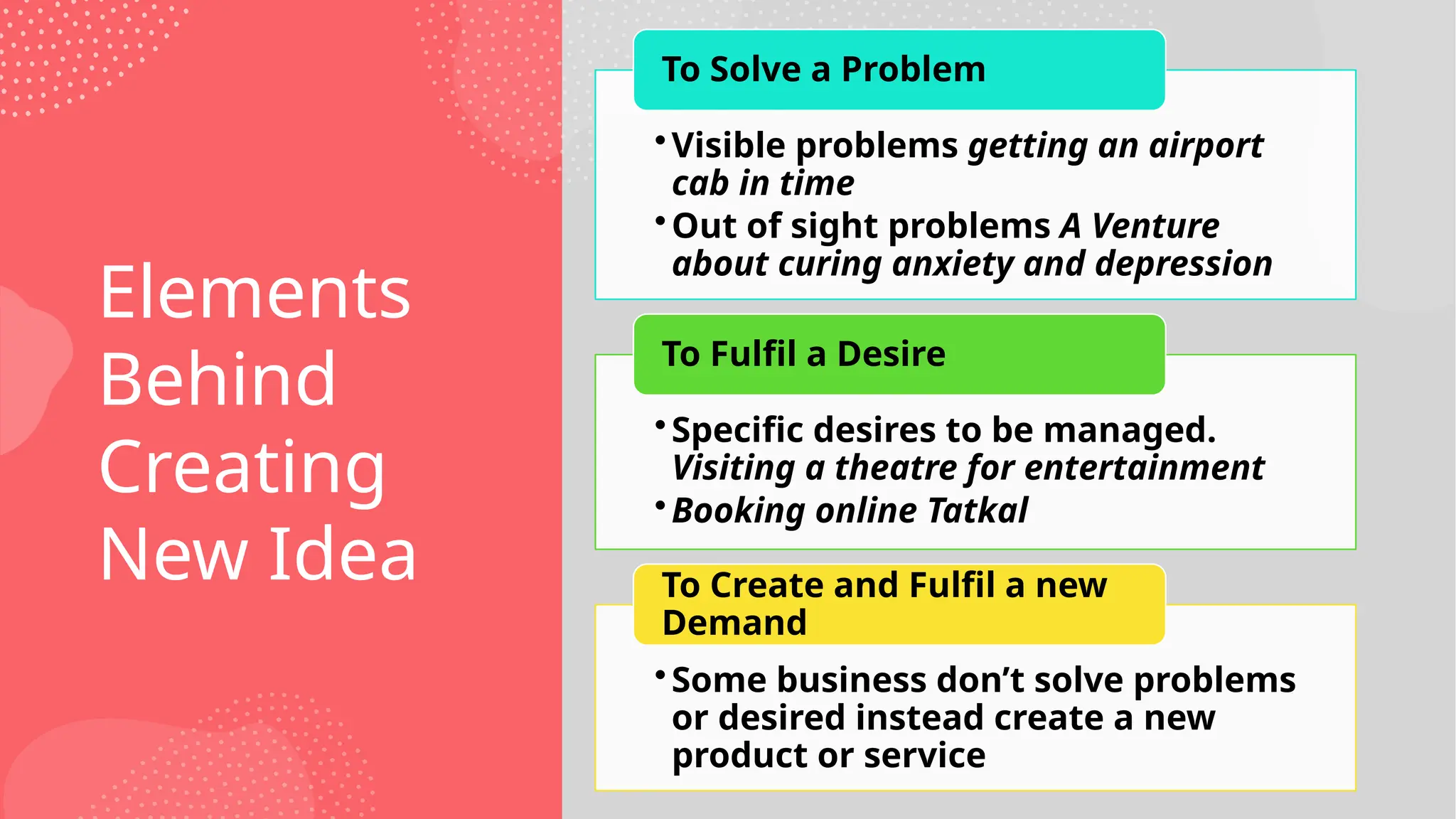
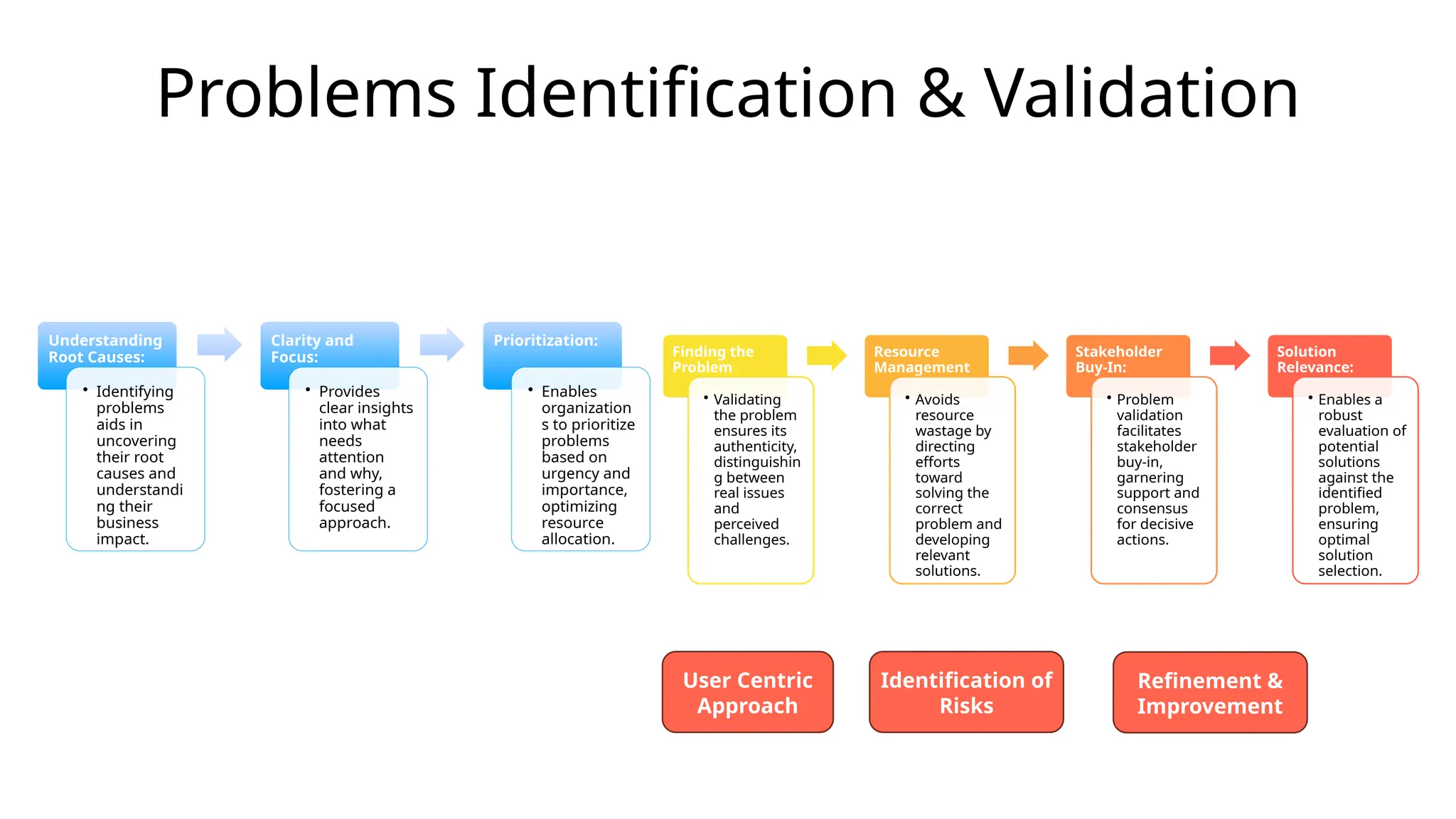
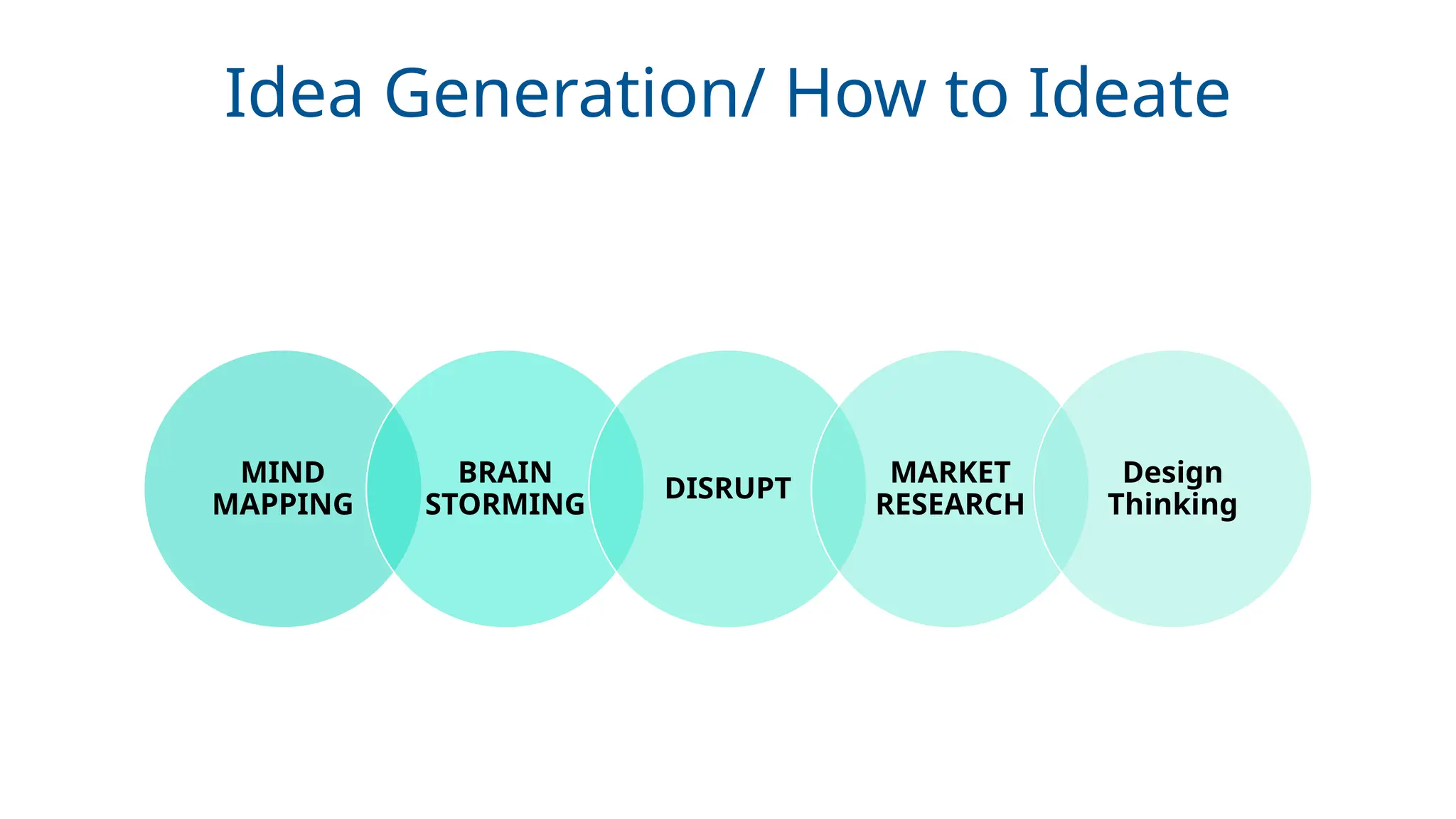
Why ideation is the most critical step in building innovative solutions
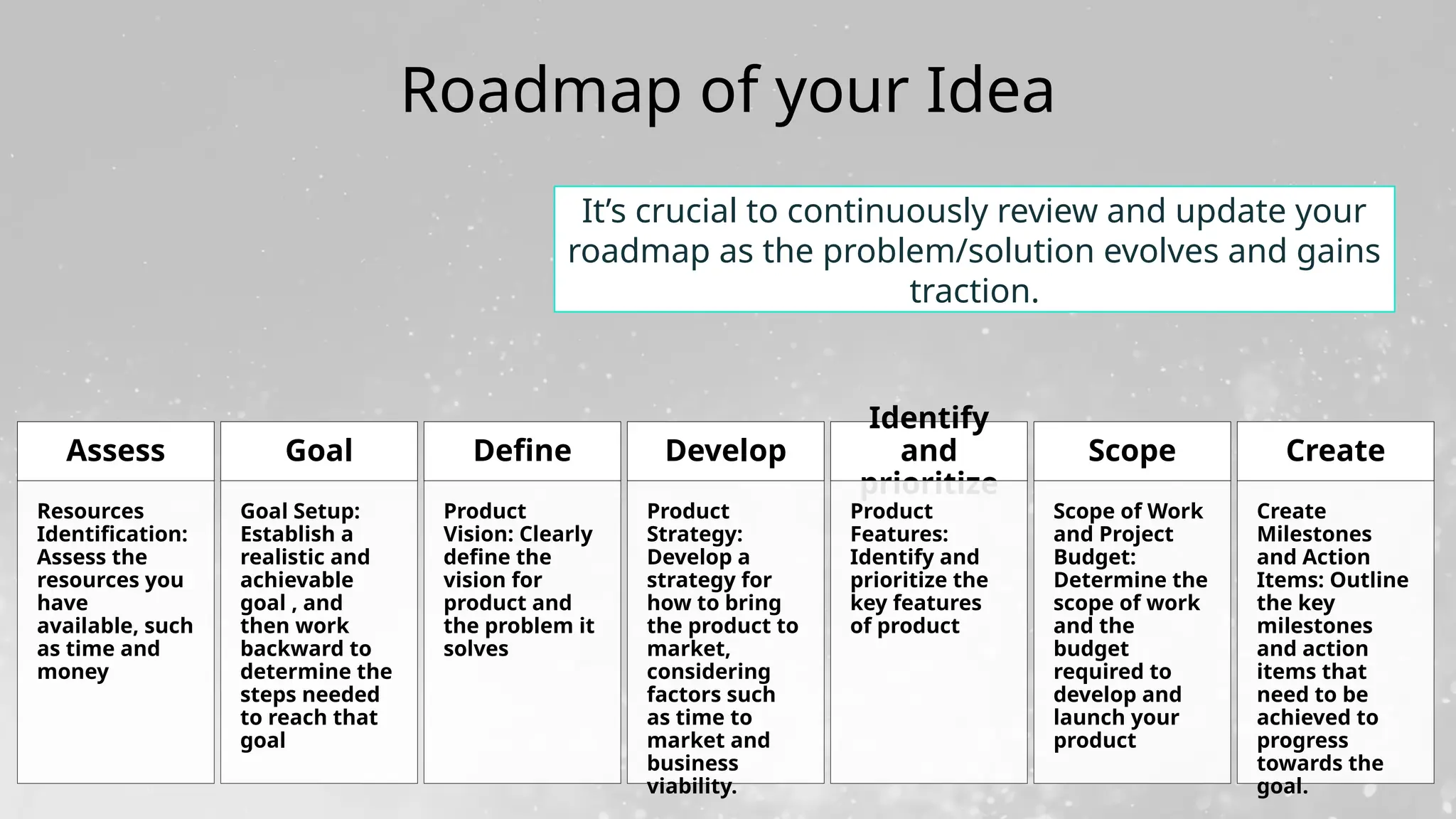
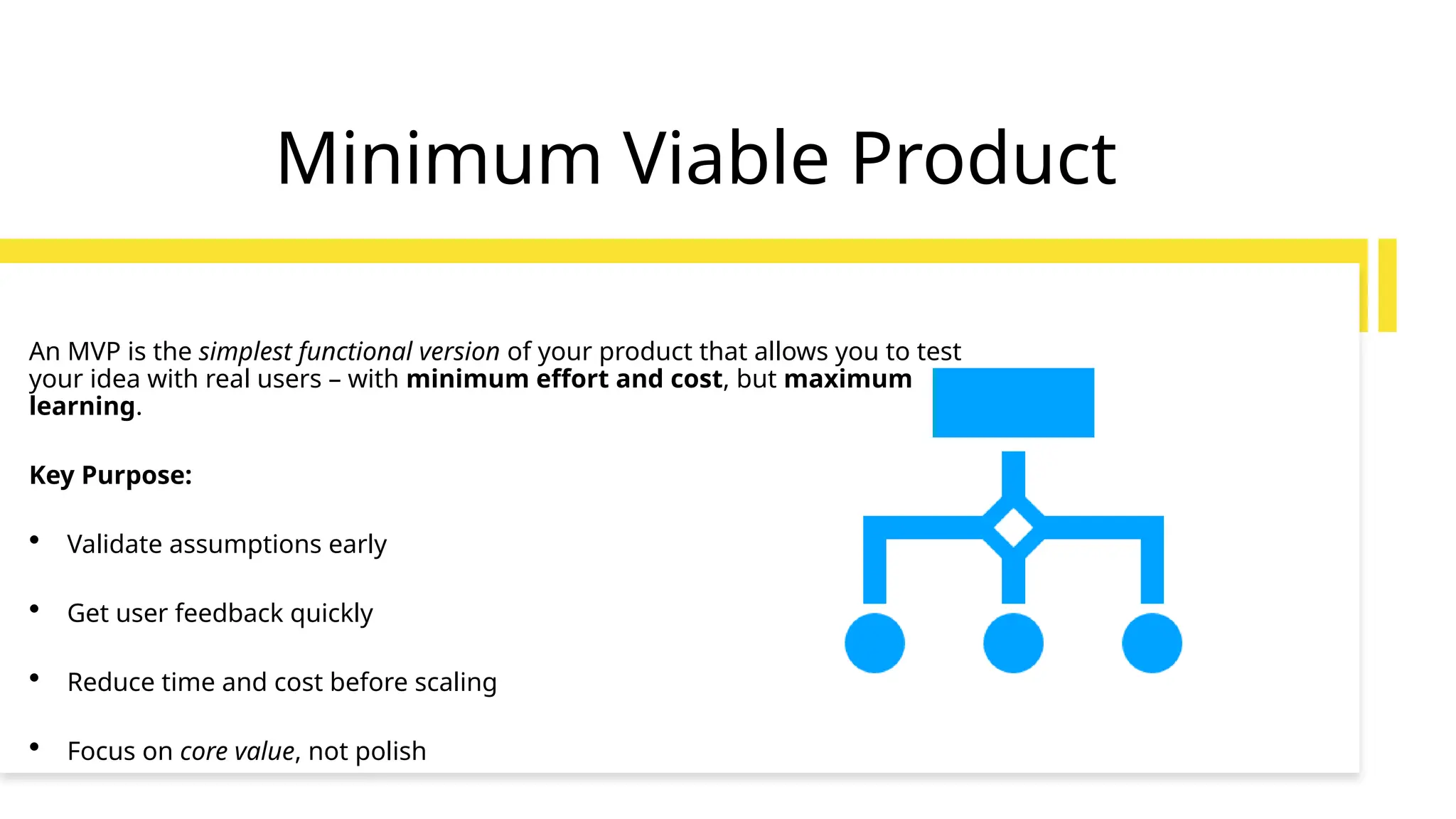
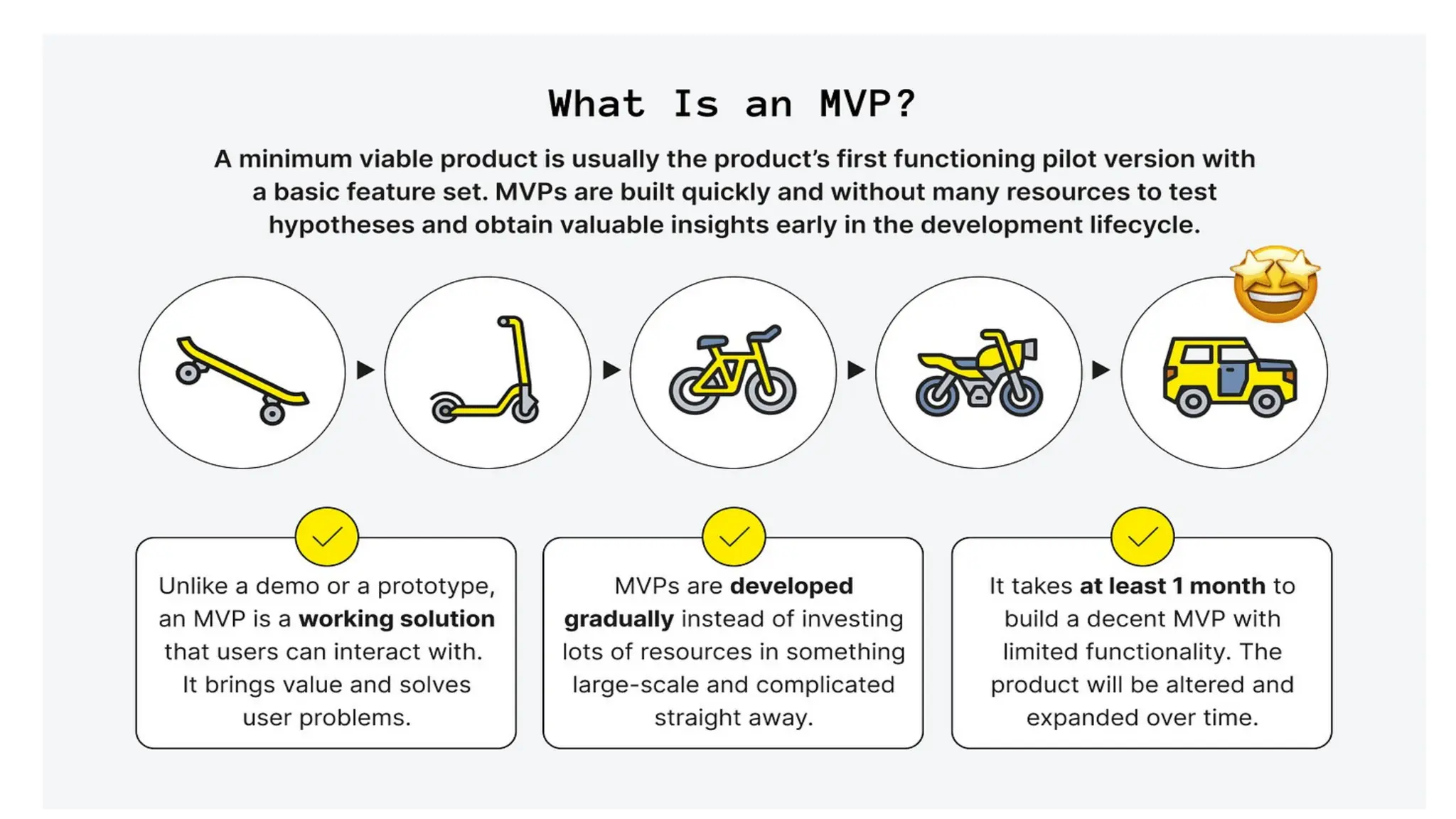
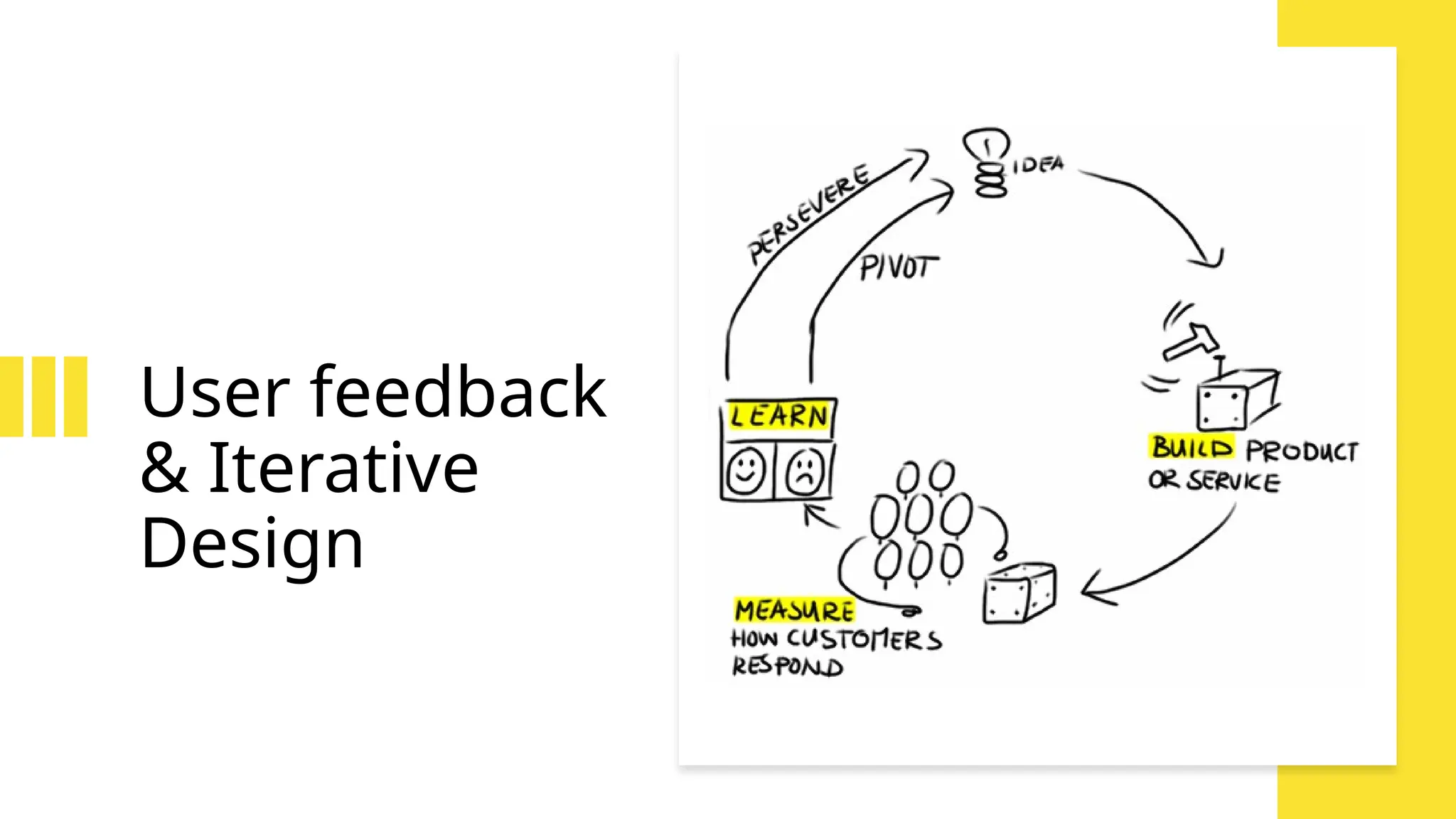
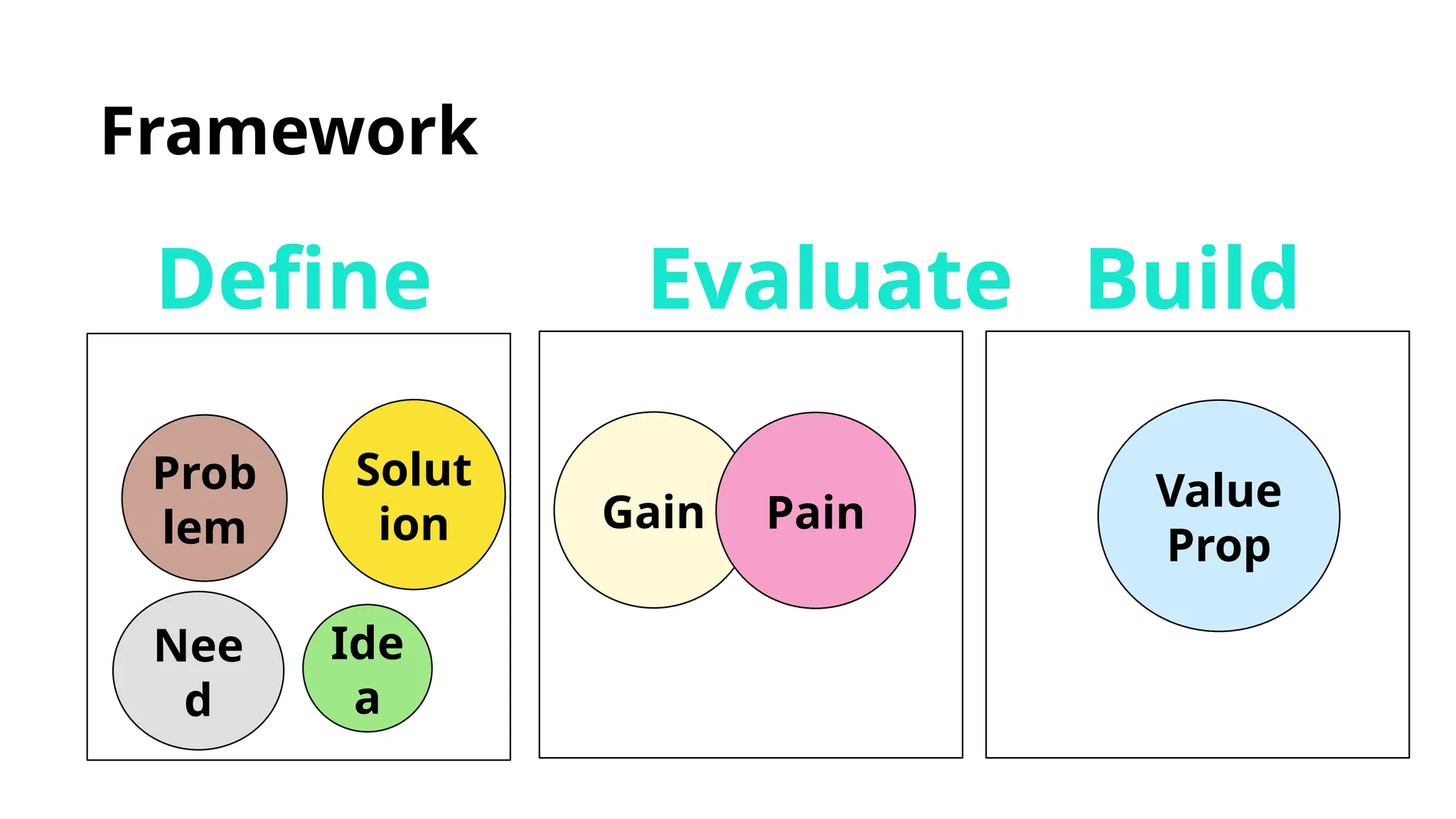
Frameworks like SCAMPER, Design Thinking, and MVP development
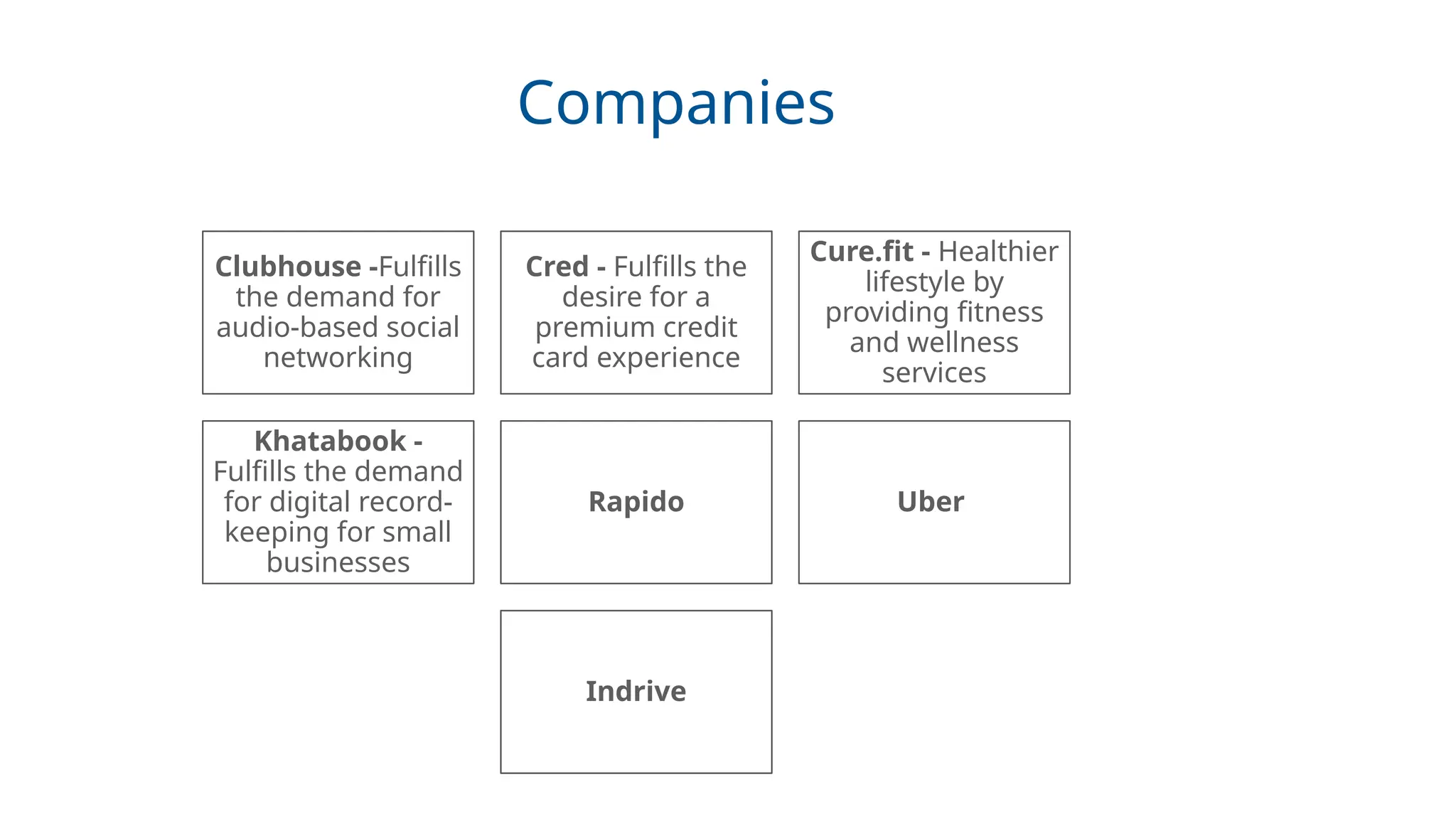
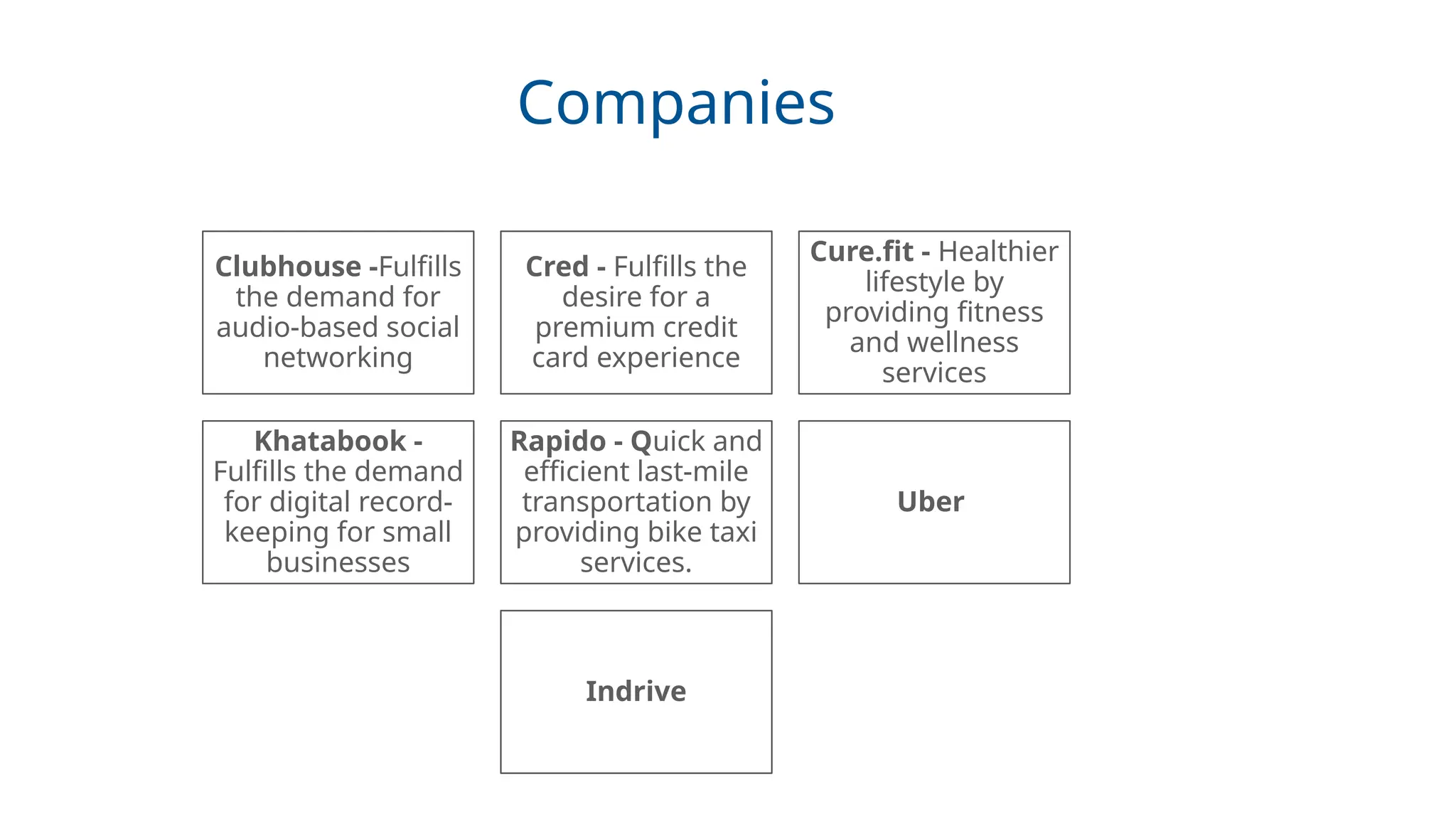
Real-world case studies: Apple, Swiggy, ToiFI, TickZo
A hands-on group activity to generate, evaluate, and pitch breakthrough ideas
🎯 Whether you're launching a startup, solving campus problems, or building your first prototype, this deck gives you a practical roadmap to turn ideas into real-world impact.
✅ Ideal for:
Innovation Workshops
Hackathons
Incubation Programs
Startup Bootcamps
University Entrepreneurship Courses
✨ Let’s build the future — one idea at a time.
🔁 Like | Share | Comment if this helped spark your next big idea!
#Innovation #ProductDesign #Ideation #Startups #DesignThinking #Entrepreneurship #MVP #SlideShare #SCAMPER #FrugalInnovation #DisruptiveTech