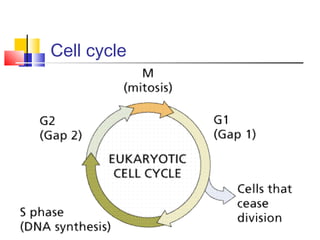
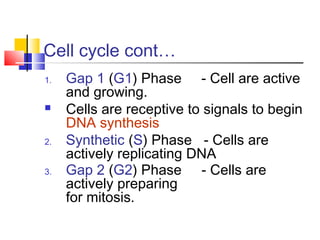
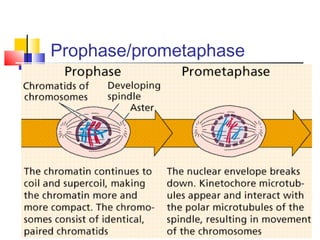
The cell cycle involves four main phases - G1, S, G2, and M. In M phase (mitosis), the cell undergoes nuclear division to form two identical daughter cells each with a full copy of the genome. Mitosis is divided into prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase where the chromosomes are aligned and separated between the two cells. Cytokinesis then divides the cytoplasm and cell membrane, completing cell division to form two daughter cells.