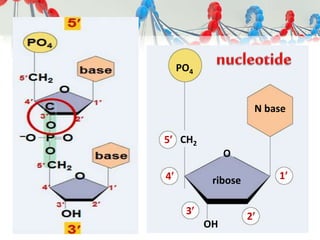
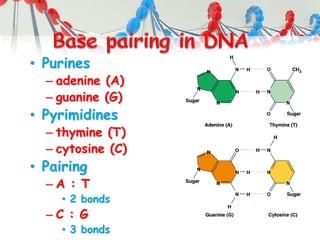
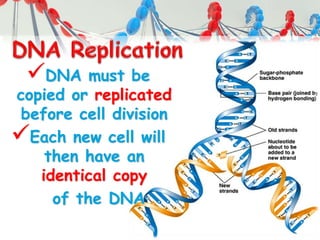
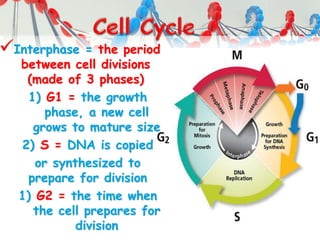
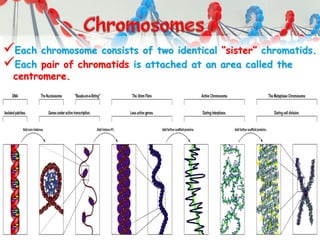
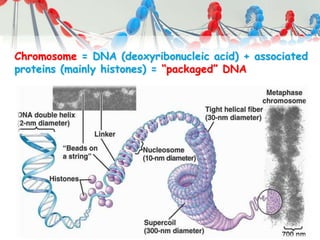
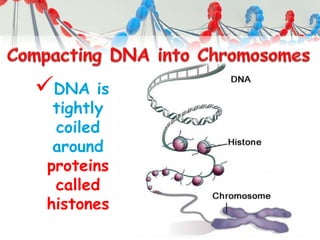
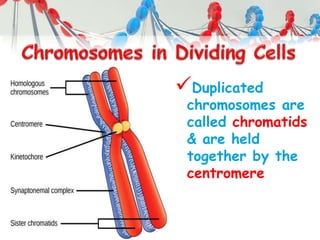
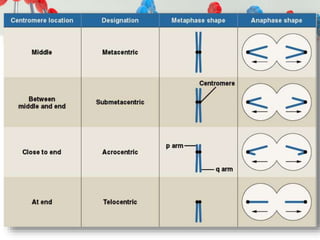
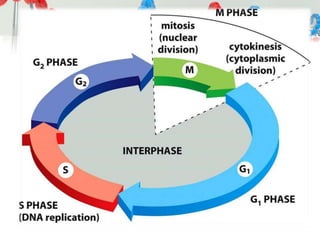
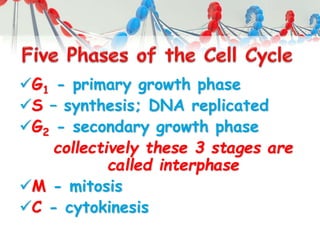
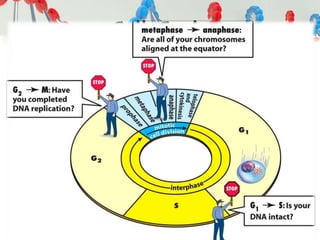
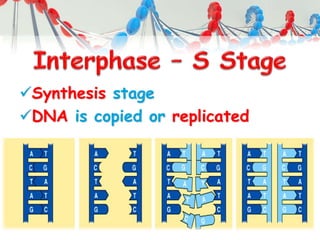
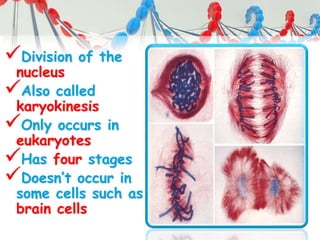
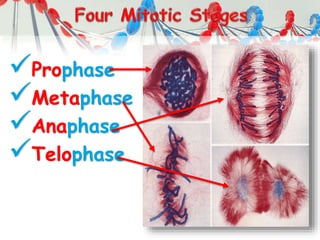
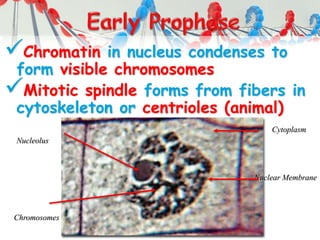
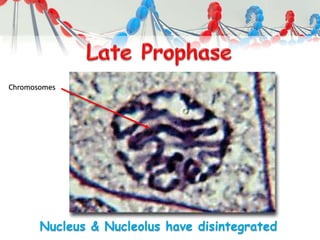
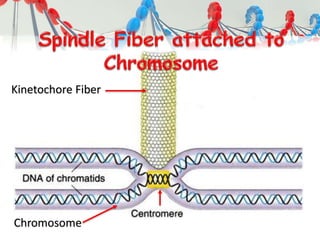
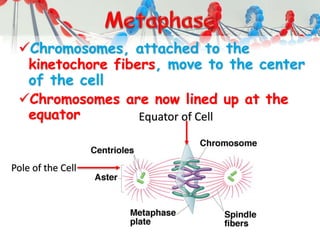
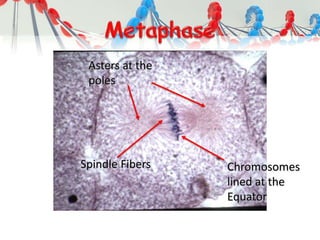
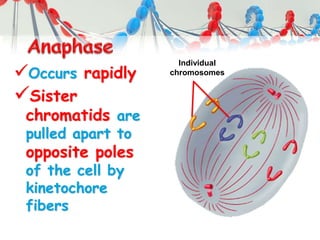
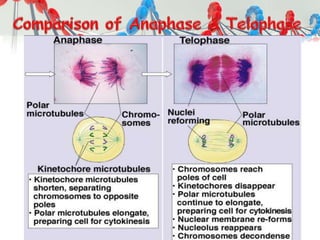
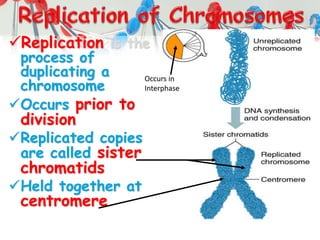
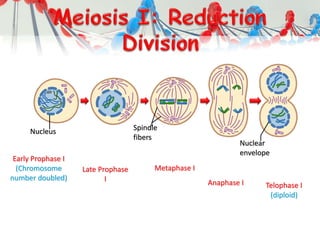
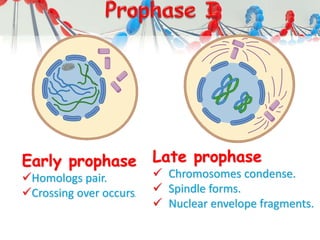
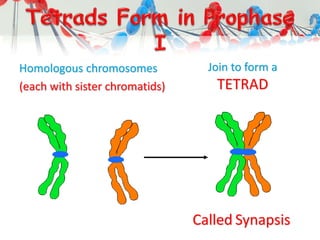
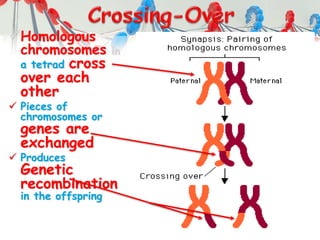
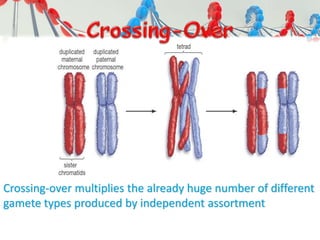
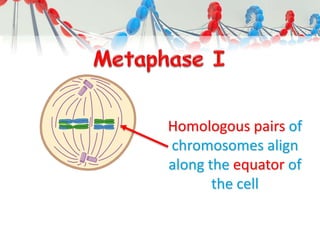
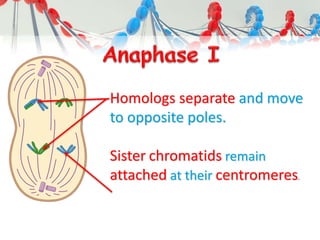
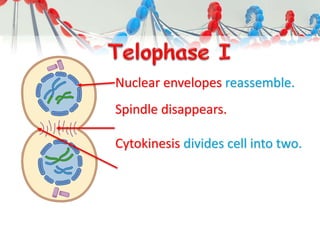
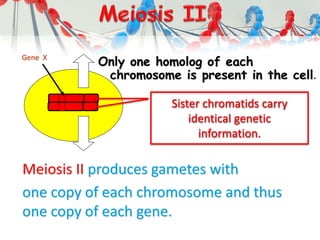
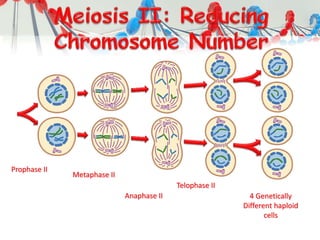
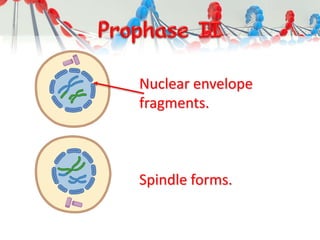
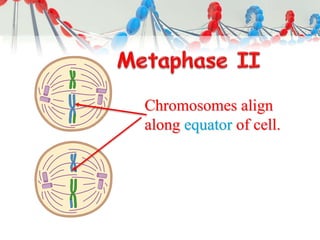
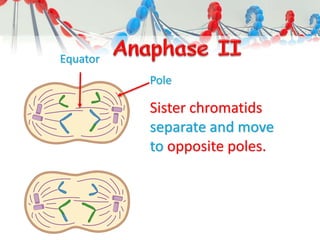
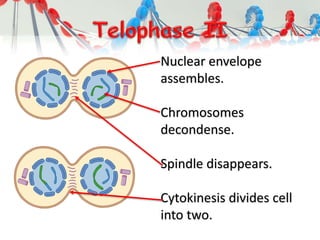
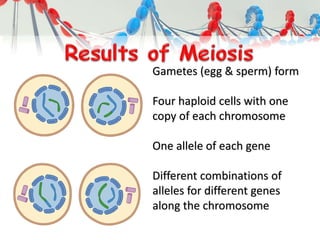
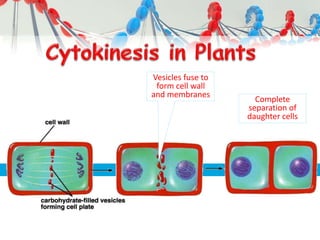
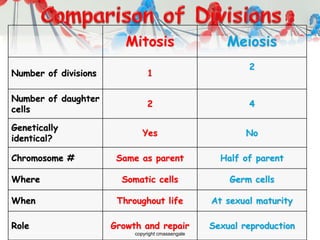
DNA is replicated before cell division so each new cell receives a complete copy. The cell cycle consists of interphase, where the cell grows and DNA replicates, and mitosis, where the cell divides. During mitosis, the nucleus divides into two identical nuclei, each containing the full set of chromosomes. Meiosis produces gametes through two cell divisions, resulting in four cells each with half the number of chromosomes as the original cell. This allows for genetic variation in offspring.