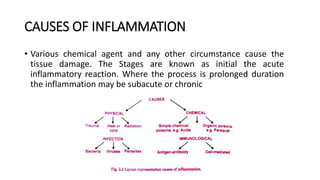
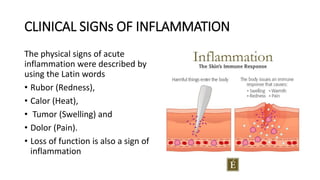
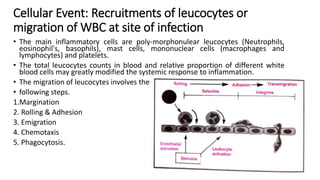
This document discusses inflammation and wound healing. It begins by defining inflammation as the body's protective response to tissue injury. The causes of inflammation include microbial infections, hypersensitivity reactions, physical trauma, chemicals, and tissue necrosis. The signs of acute inflammation are redness, heat, swelling, pain, and loss of function. Mediators of inflammation such as histamine, prostaglandins, and complement proteins are released in response to injury and stimulate the inflammatory response. This includes increased blood flow, vascular permeability, and recruitment of immune cells to the injured site to clear infection and initiate repair. Both acute and chronic inflammation aim to remove harmful stimuli and initiate healing, though chronic inflammation can lead to fibrosis and tissue damage if the stimulus