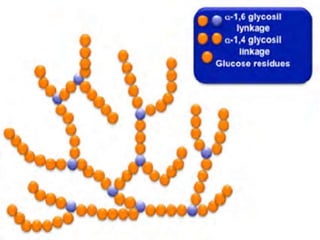
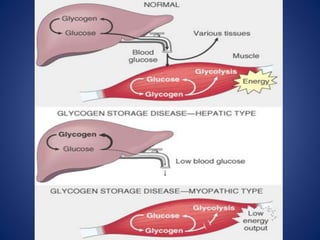
GSD is a rare inherited metabolic disorder caused by deficient or defective enzymes involved in glycogen metabolism. This leads to abnormal glycogen accumulation in tissues like the liver, heart and kidneys. There are several types of GSD based on the specific enzyme deficiency. Type I is characterized by fasting hypoglycemia, hyperlipidemia and hyperuricemia due to glucose-6-phosphatase deficiency. Type II involves alpha-glucosidase deficiency causing glycogen buildup in lysosomes. Type III features abnormal glycogen storage with short branches due to glycogen debranching enzyme deficiency.