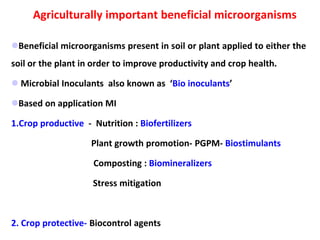
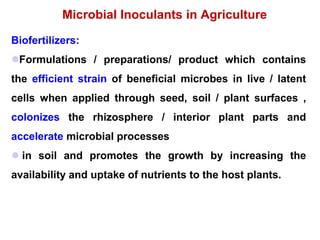
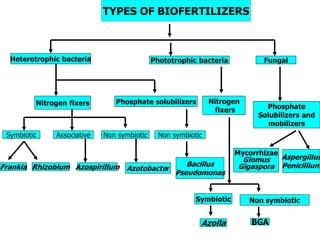
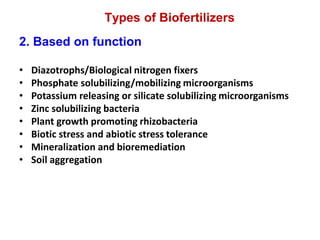
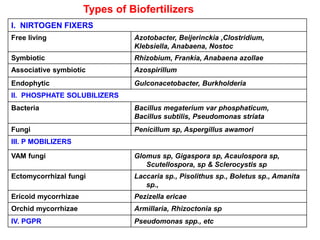
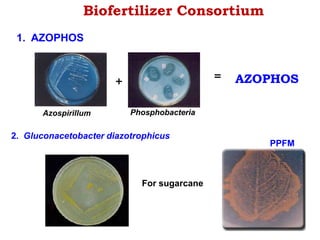
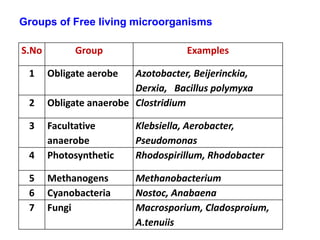
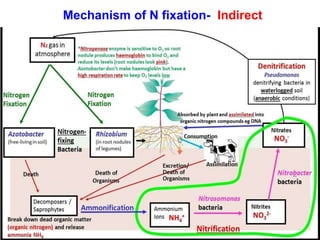
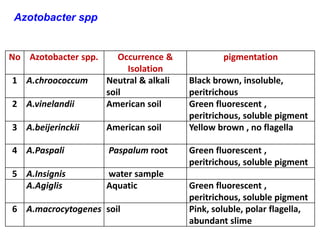
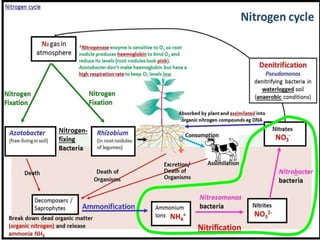
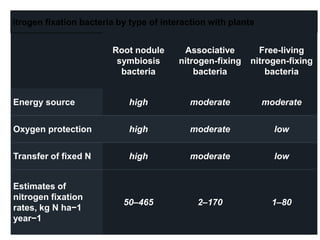
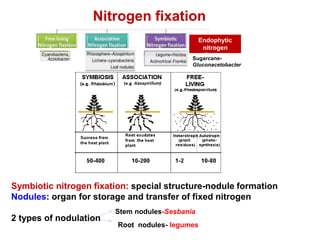
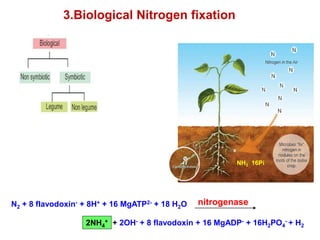
This document provides information about biofertilizers and microbial inoculants used in agriculture. It defines biofertilizers as formulations containing beneficial microbes that colonize plant roots or soil to increase nutrient availability and promote plant growth. The document discusses different types of biofertilizers classified by microorganism (bacteria, fungi, algae) and function (nitrogen fixers, phosphate solubilizers). Key nitrogen-fixing bacteria discussed include Azotobacter, Rhizobium, and Frankia. The document emphasizes the benefits of biofertilizers like increased fertilizer use efficiency, supplementing soil nutrients, and reducing environmental pollution.