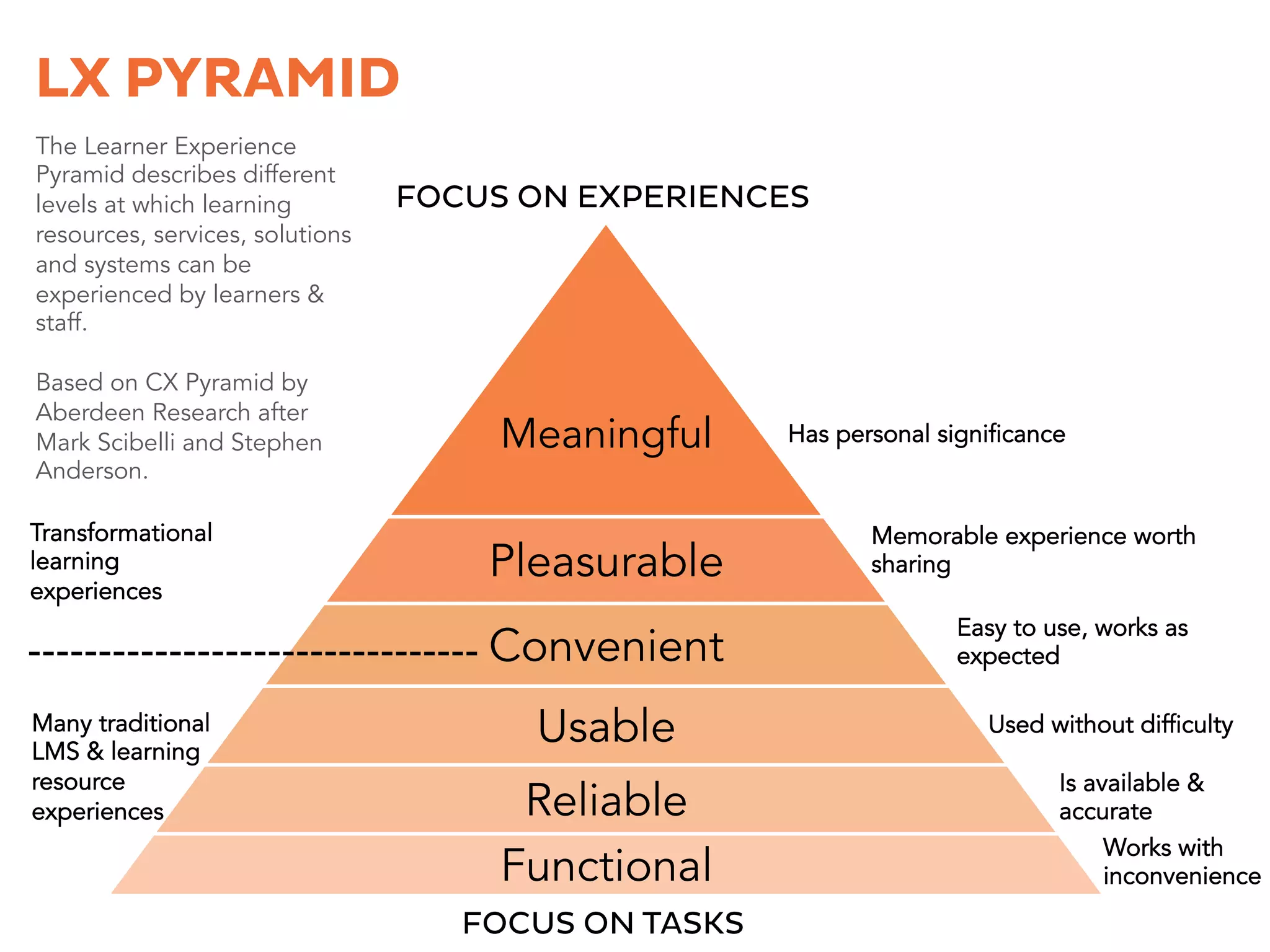
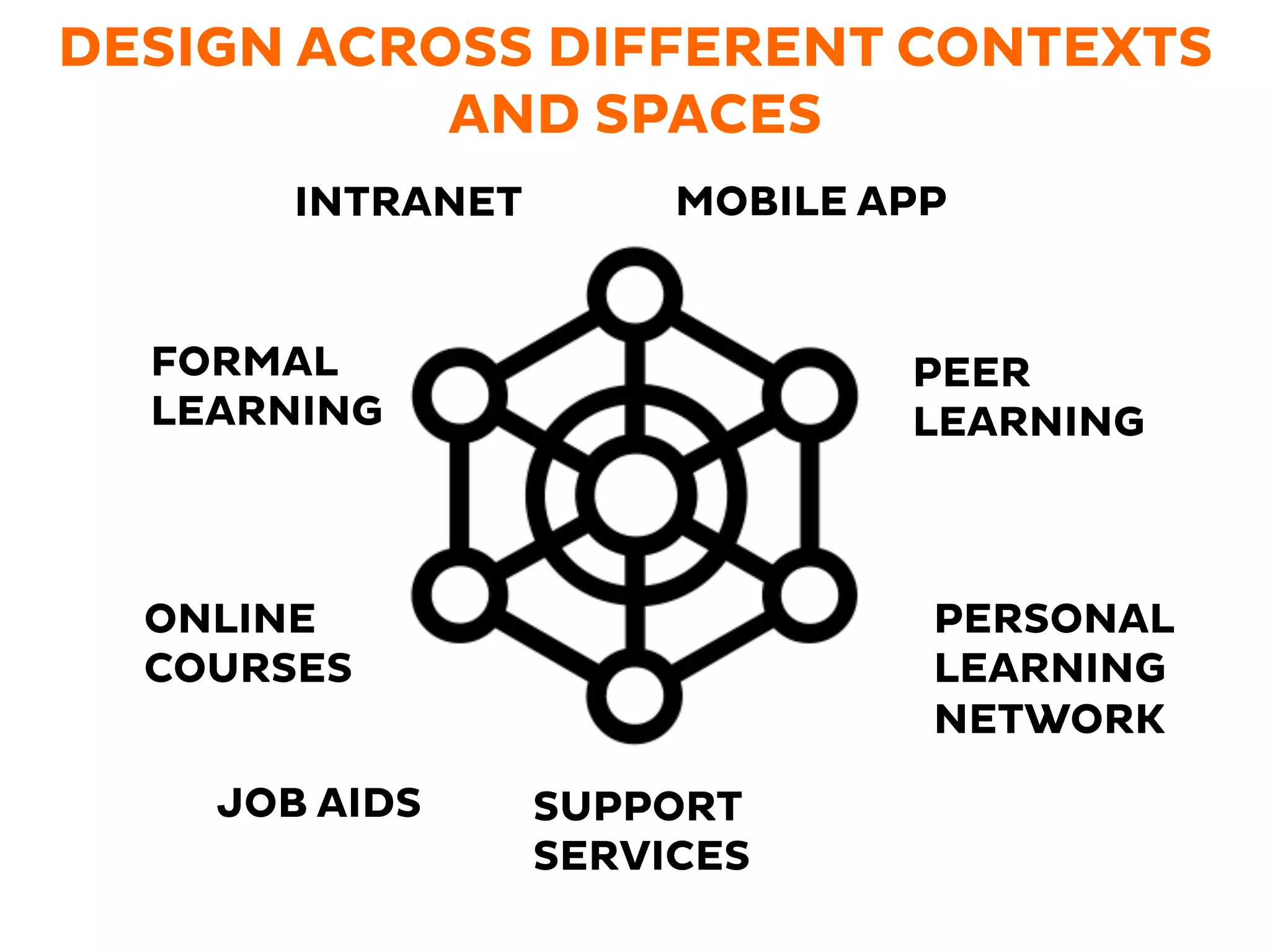
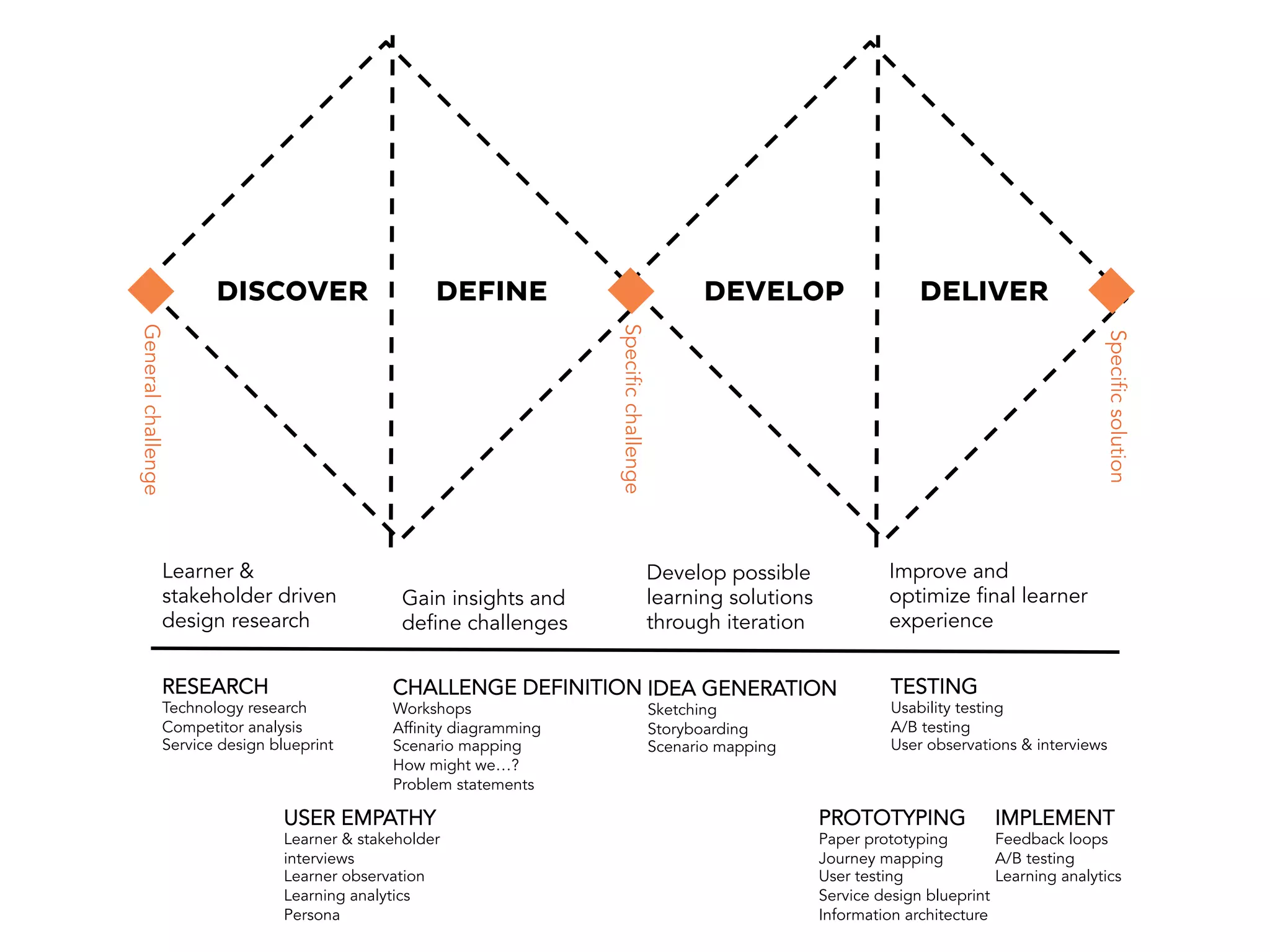
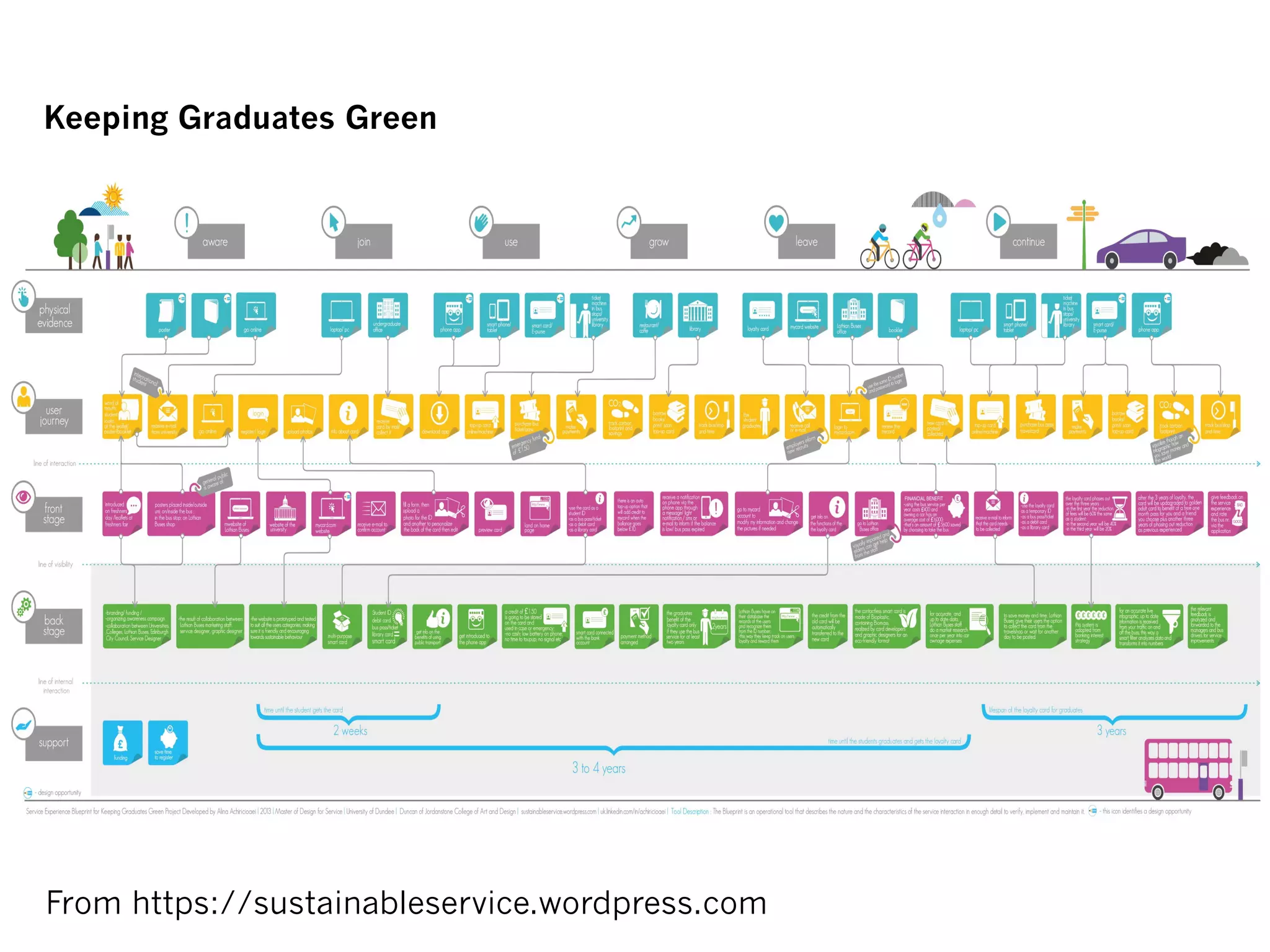
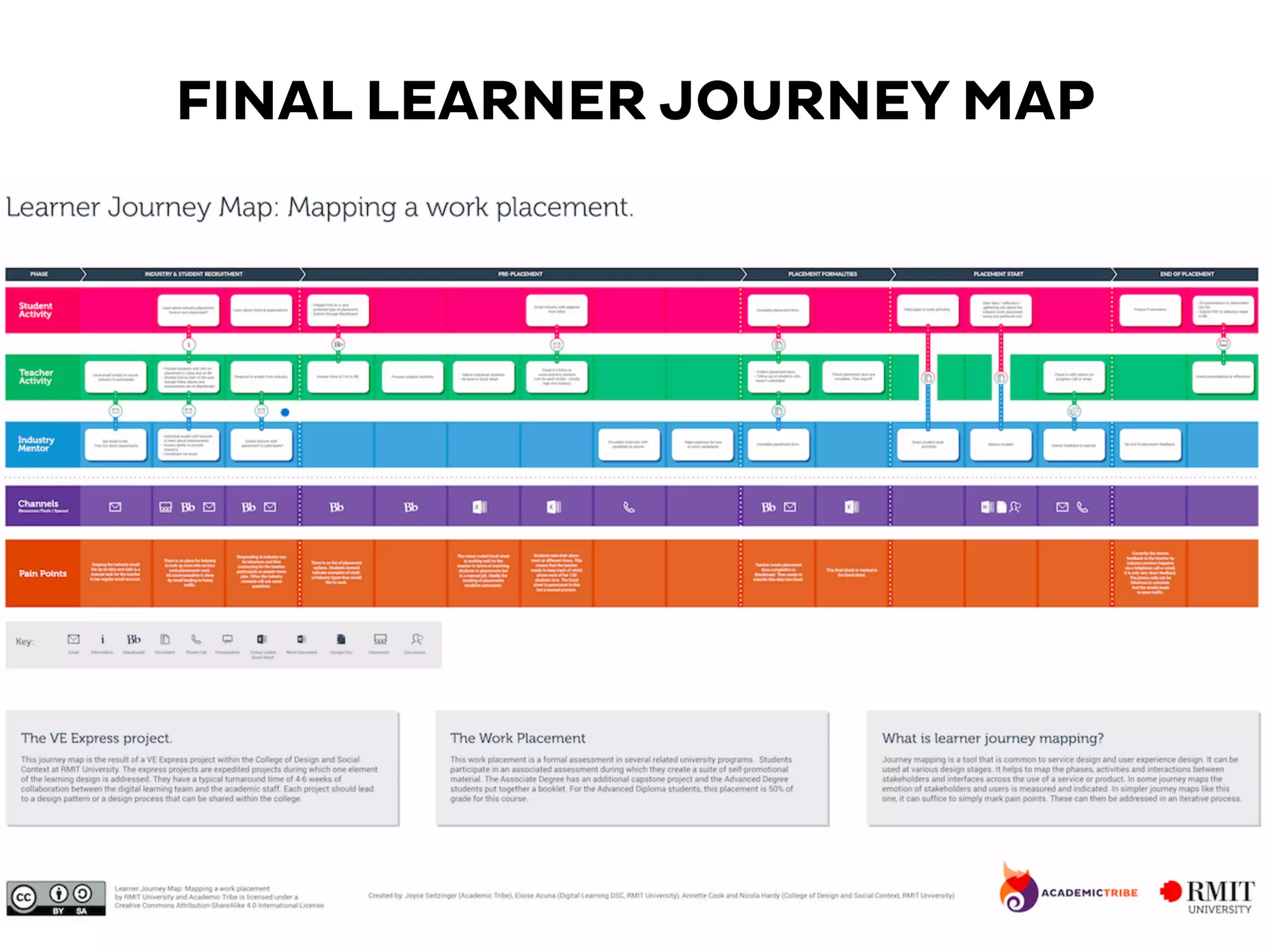
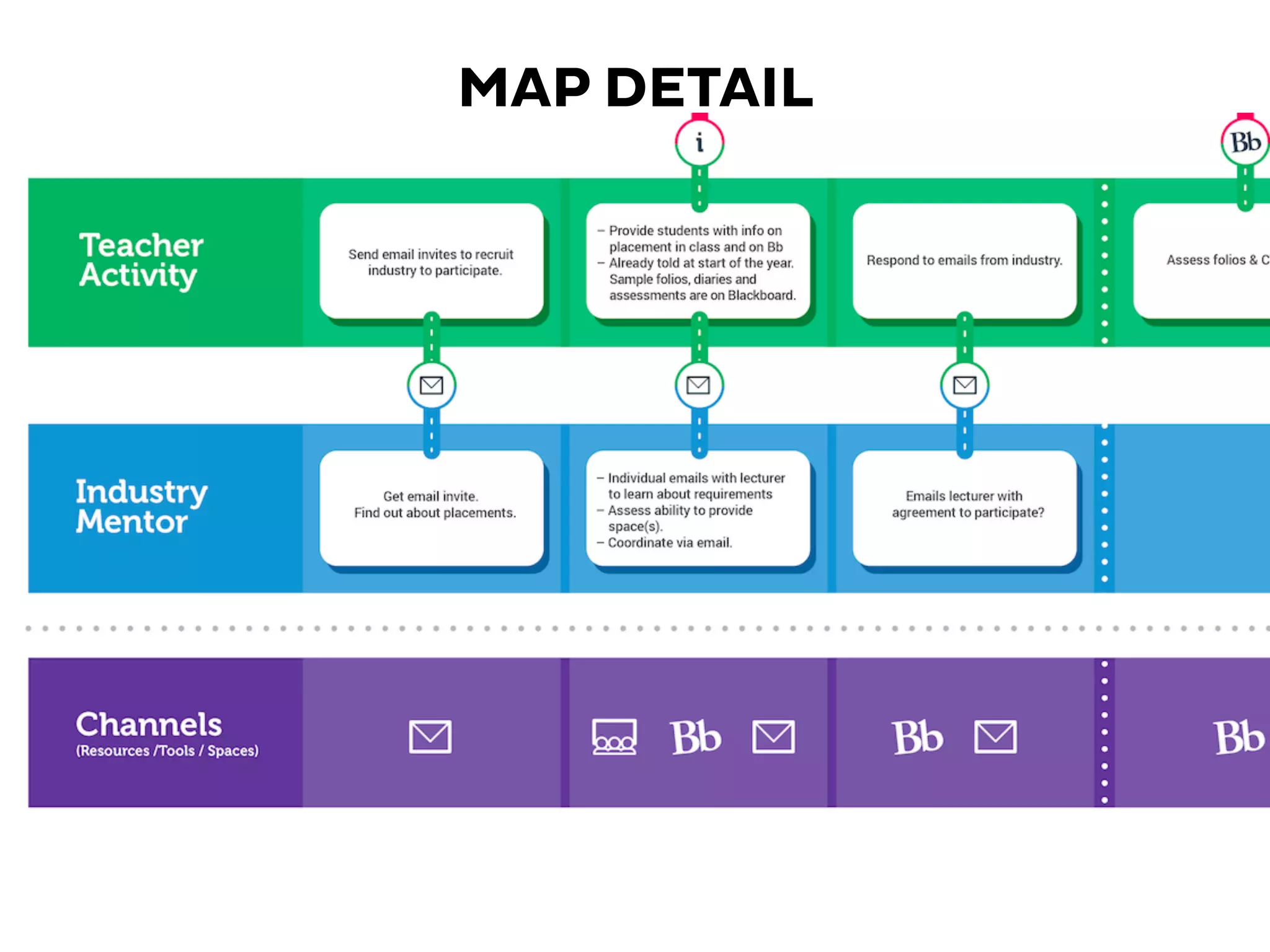
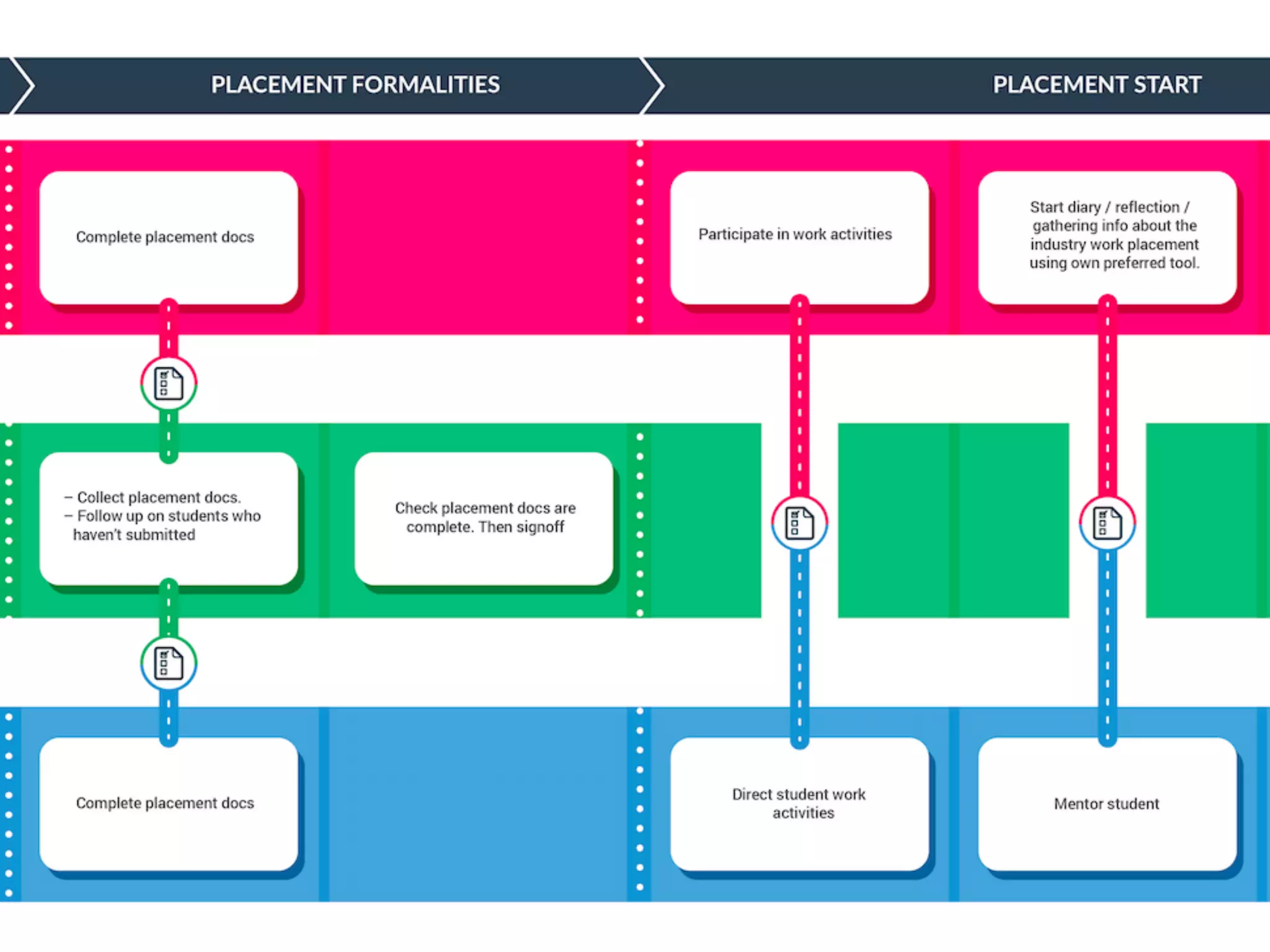
The document discusses learner experience design, emphasizing that it transcends material aspects and focuses on creating meaningful and memorable experiences. It introduces the learner experience pyramid, service design thinking, and various methodologies for the co-creation of experiences, asserting that empathy for users is essential. Additionally, it provides practical steps for mapping learner journeys and emphasizes collaboration and understanding among stakeholders in the design process.