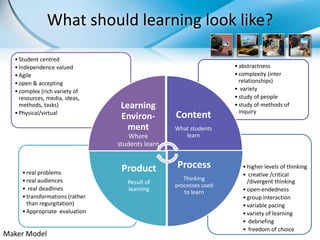
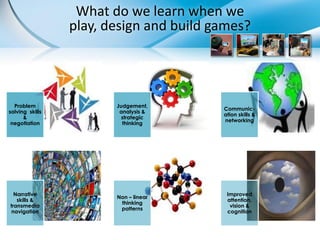
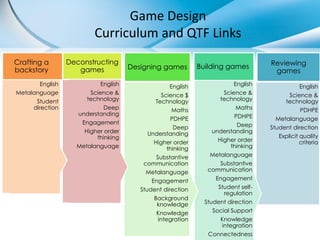
Games have the potential to transform learning by making it student-centered, complex, and intrinsically motivating. When designed well, games can engage students in solving real-world problems through interactive problem-solving and collaboration. Game-based learning approaches like project-based learning embed critical thinking, communication, and deeper learning within an authentic and engaging context. Educators are exploring how to apply game mechanics and principles of game design to better capture students' interests and promote active, self-directed, and collaborative styles of learning.