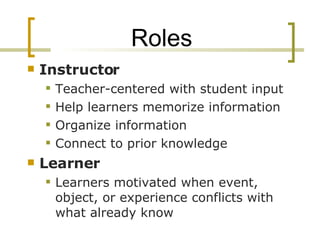
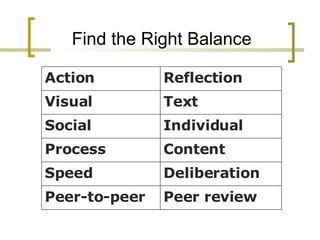
The document discusses learning theories and how the needs of the "Net Generation" have shifted paradigms in education. It contrasts behavioral, cognitive, and constructivist learning theories with the newer connectivist theory, which acknowledges the impact of technology and the need to know how to access information. The Net Generation prefers interactive, experiential, visual, social, and peer-based learning centered around authentic contexts and information literacy. Educators must adapt instruction to these preferences through balancing action and reflection, visual and text, social and individual approaches, and process versus content.