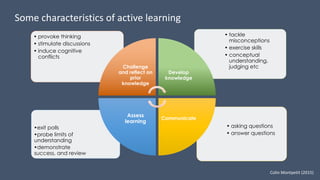
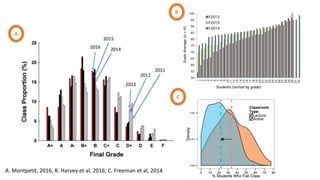
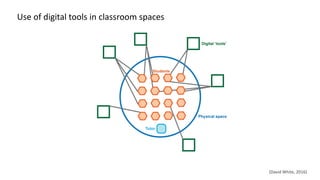
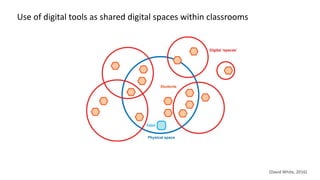
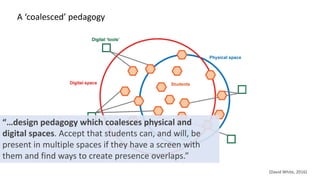
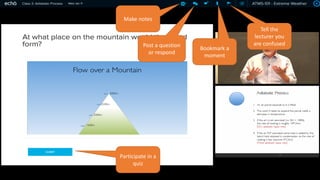
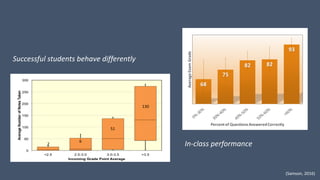
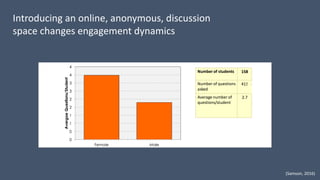
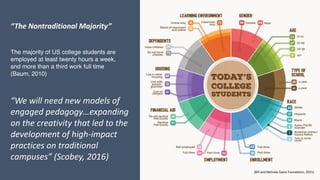
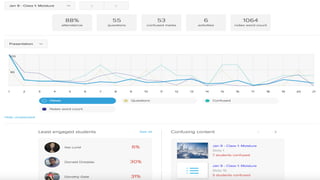
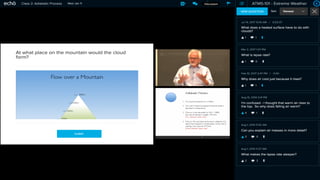
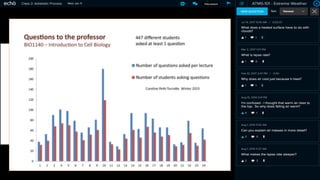
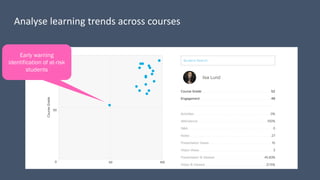
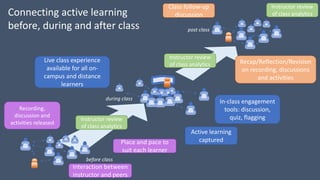
This document discusses how to transform student engagement through active learning by connecting experiences before, during, and after class. It recommends (1) blending in-class and online learning, (2) engaging students during class with tools, (3) connecting out-of-class learners, (4) providing instructors with real-time feedback, and (5) merging learning across the entire experience. This holistic approach can personalize learning, improve outcomes, and increase student satisfaction through enhanced interaction and flexibility.