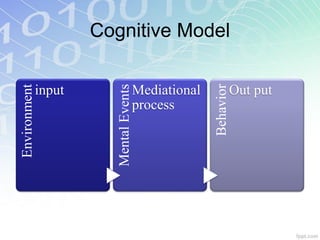
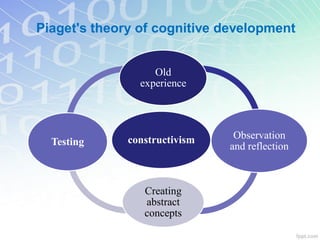
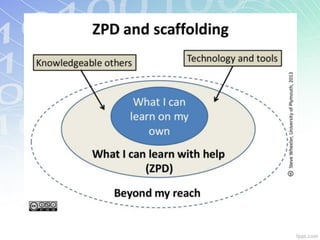
The document outlines key learning theories including behaviorism, cognitivism, and constructivism, emphasizing their implications for education technology and 21st-century learning. It highlights the importance of understanding learners' characteristics, including their engagement with technology and social interactions, to create effective instructional strategies. Additionally, it discusses the roles of teachers in facilitating learning experiences that cater to diverse learning styles and leverage technology for enhanced educational outcomes.