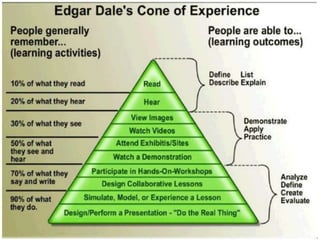
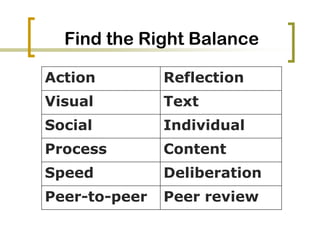
The document outlines a framework for course design that emphasizes understanding learners and creating an effective learning environment through iterative steps. It highlights the importance of integrating 21st-century skills and digital engagement while addressing the varied cognitive styles of students. Furthermore, it discusses the impact of technology and collaborative strategies on enhancing student motivation and learning outcomes.