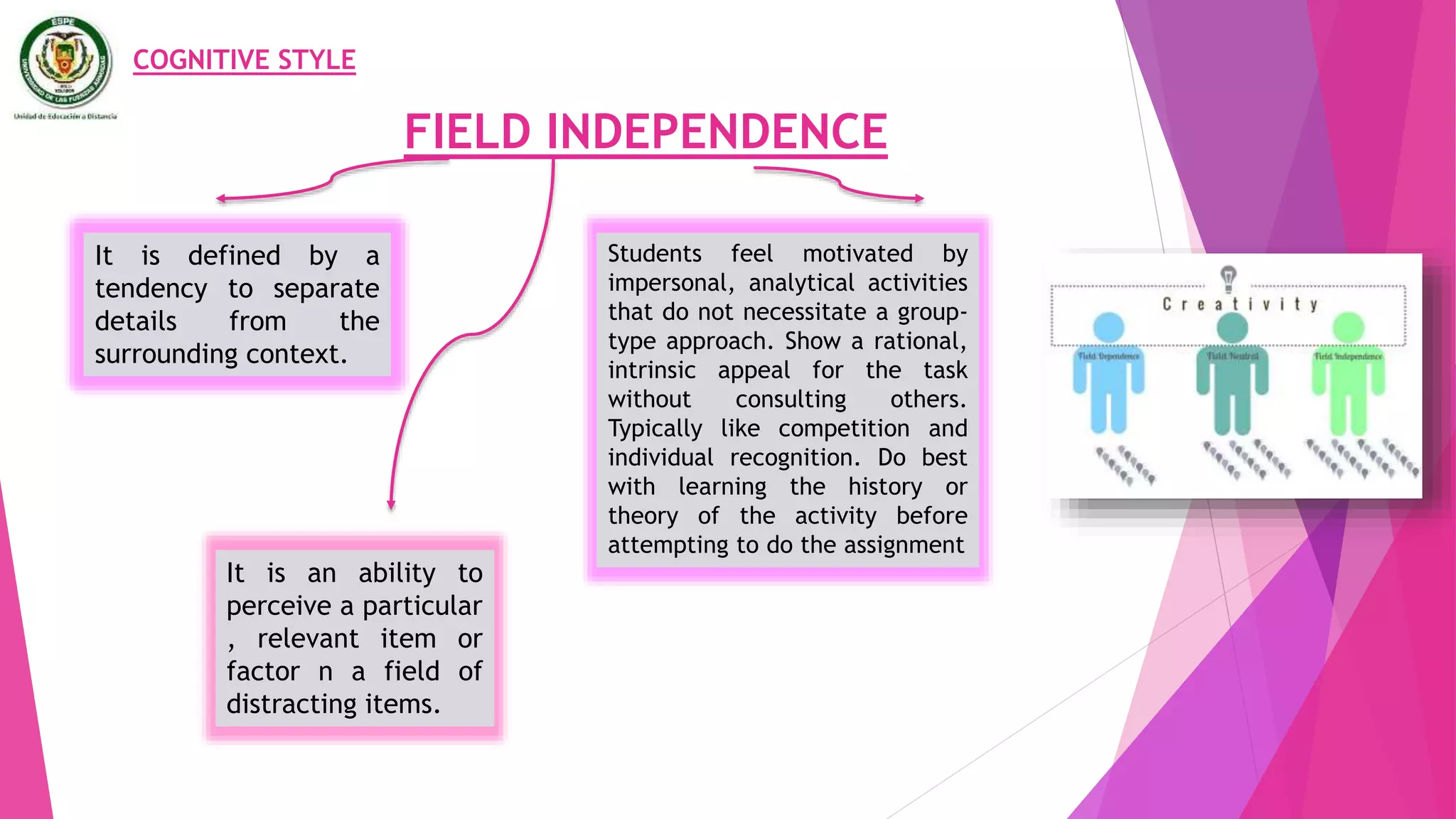
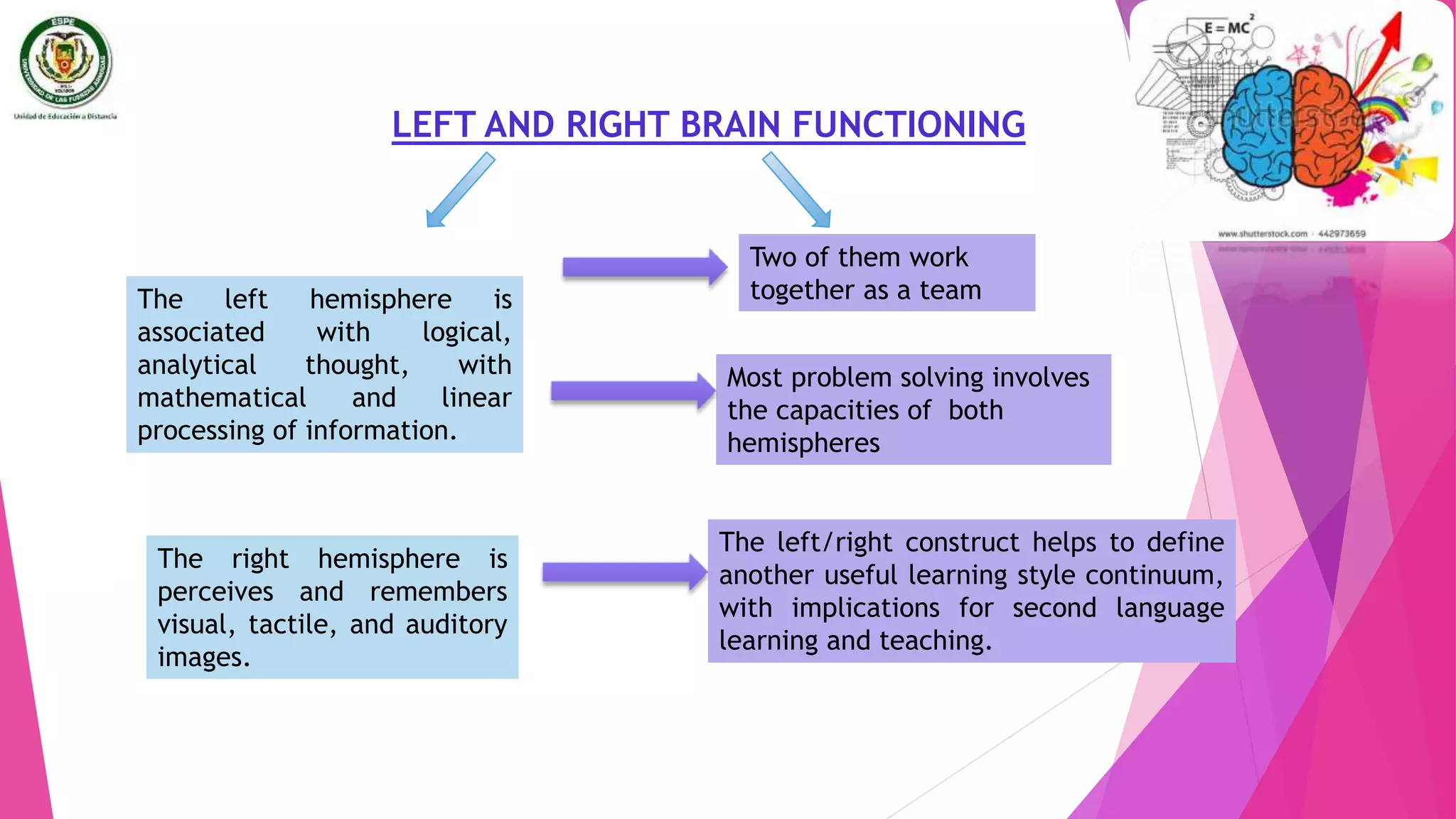
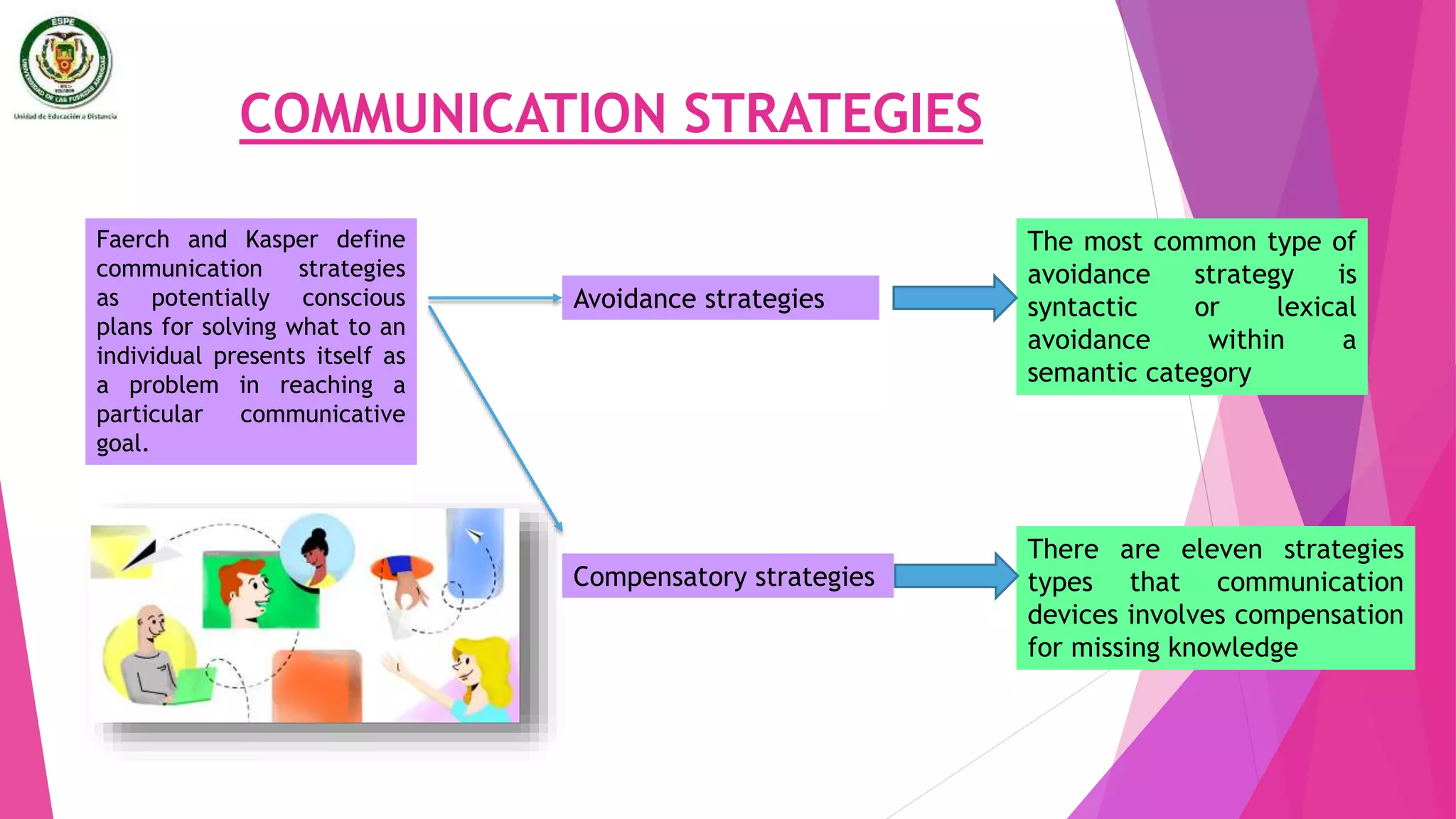
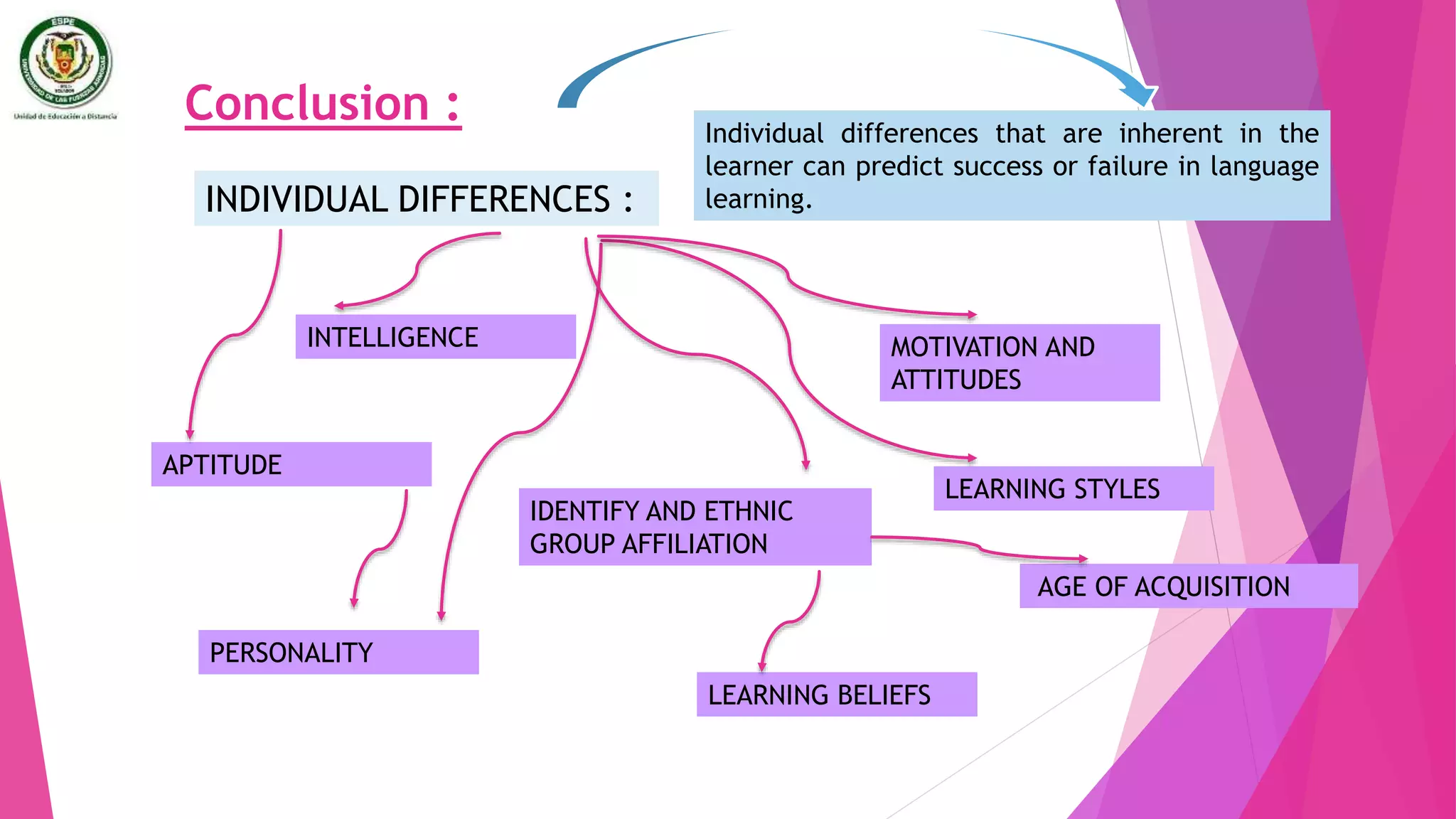
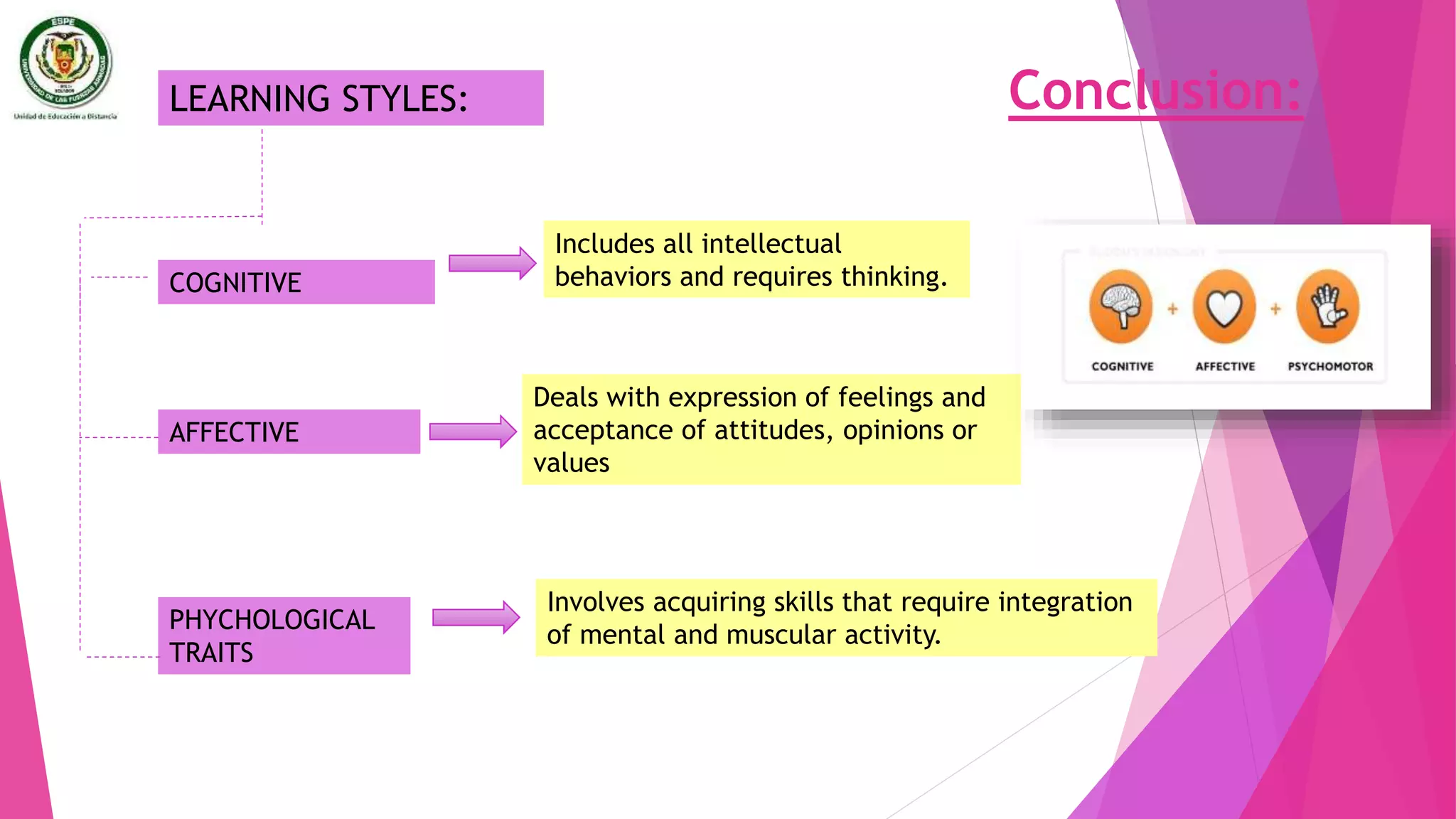
The document discusses individual differences in language learning, including learning styles, strategies, and intelligence. It describes various learning styles like field independence, left and right brain functioning, ambiguity tolerance, and visual vs auditory styles. Strategies discussed include cognitive strategies, socioaffective strategies, communication strategies, and strategies based instruction. The conclusion emphasizes that understanding individual learner differences in styles and traits can help predict language learning success, and teachers should develop instructional strategies that match students' preferred learning preferences.