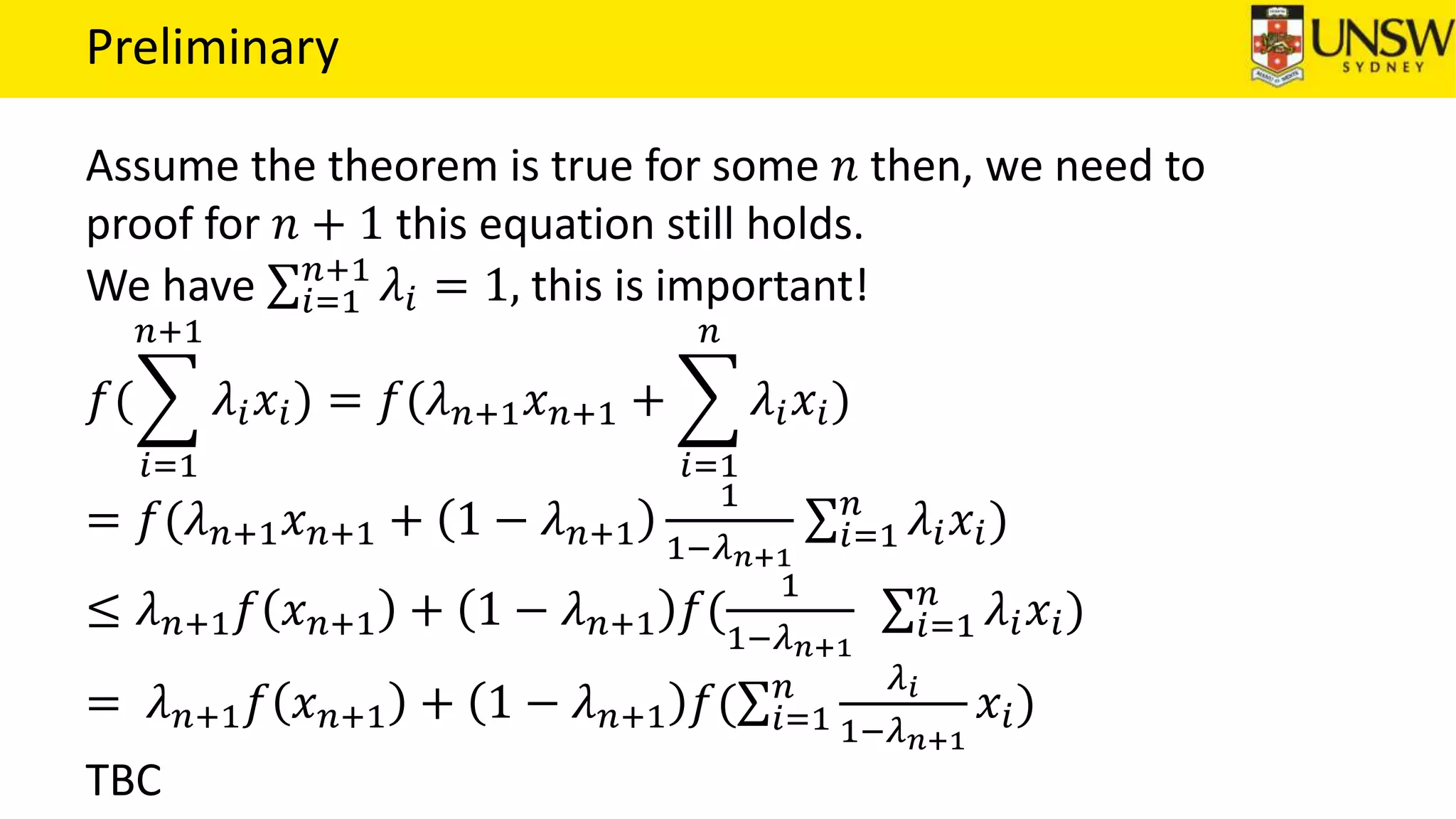
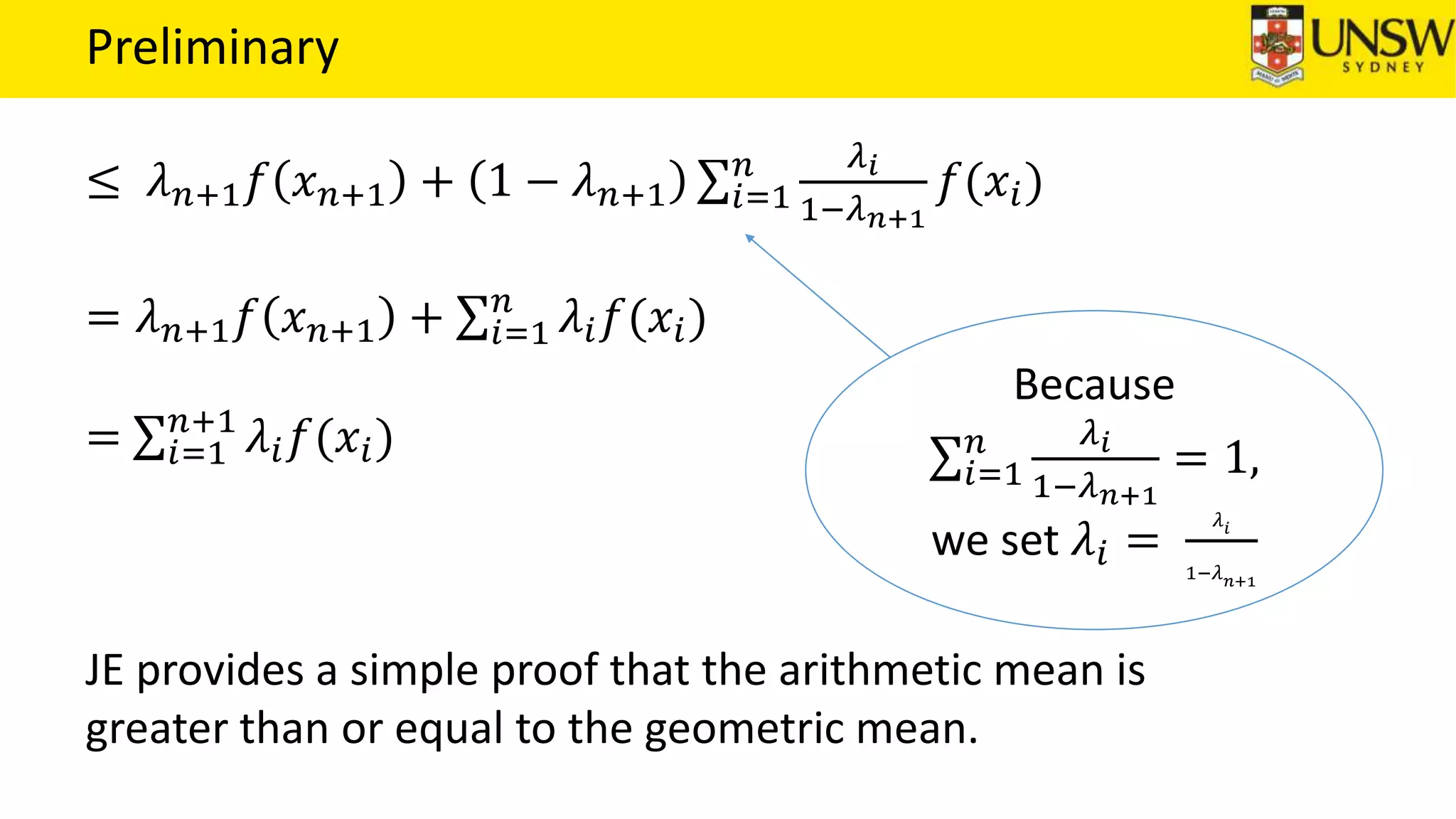
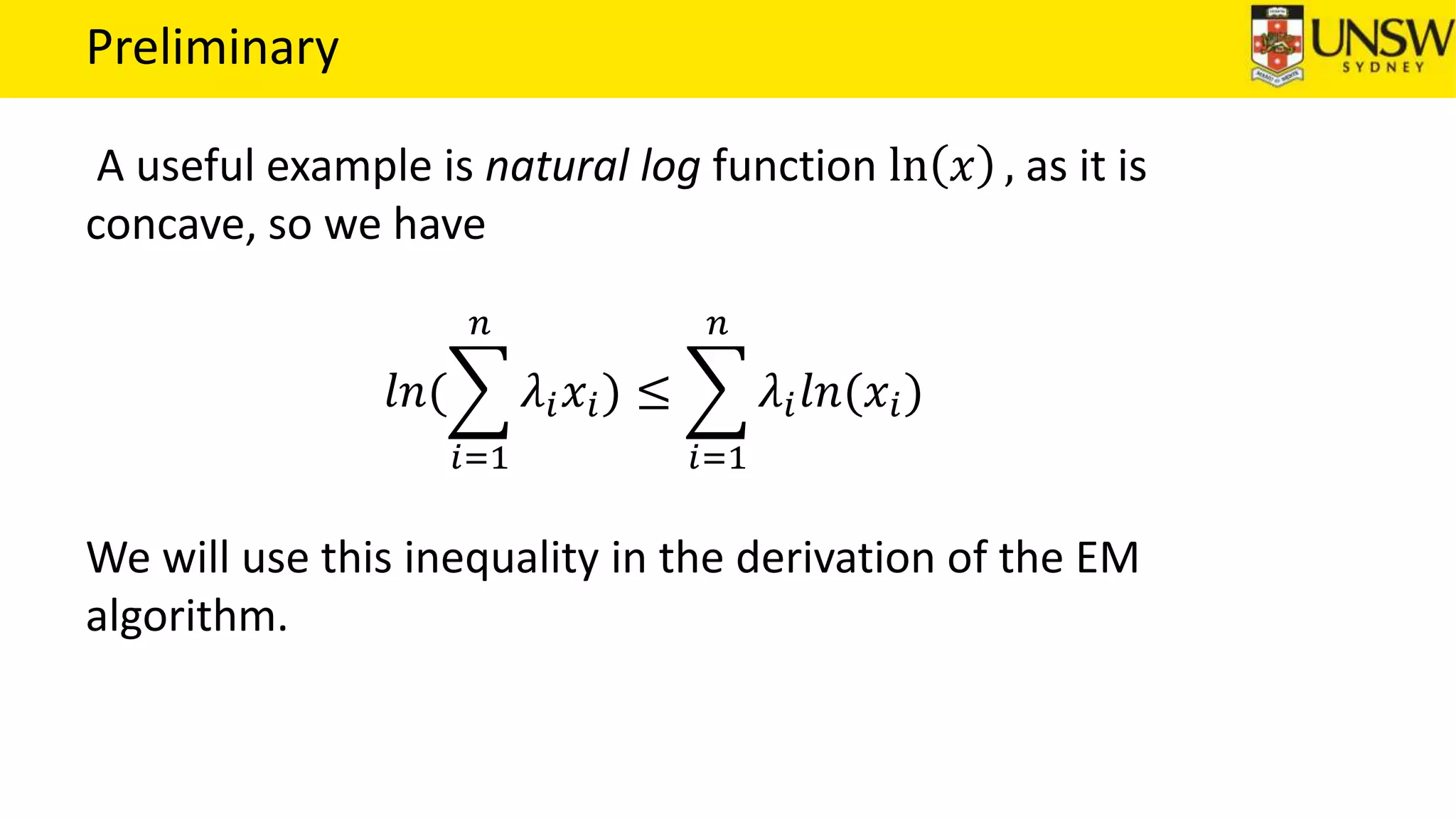
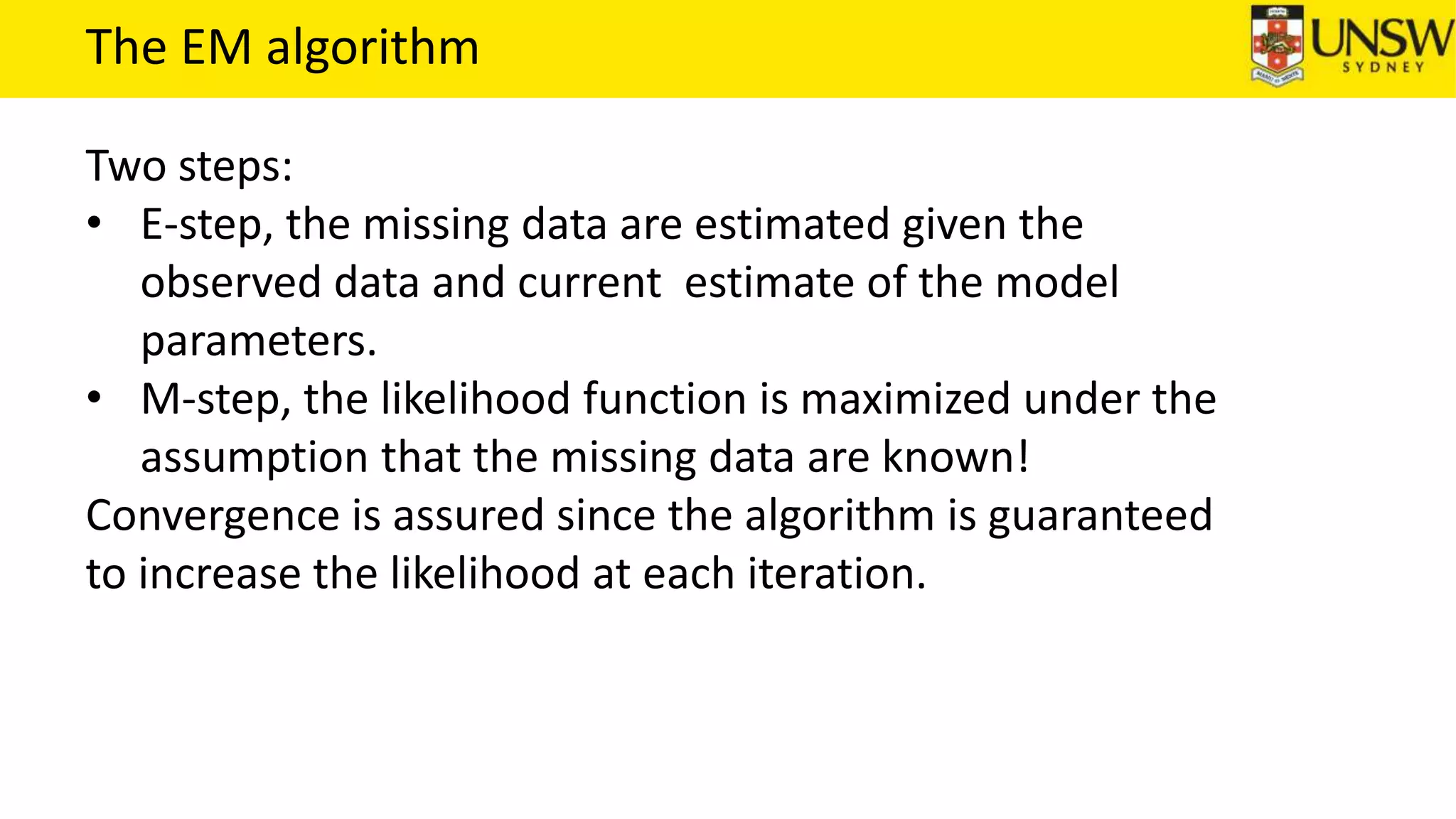
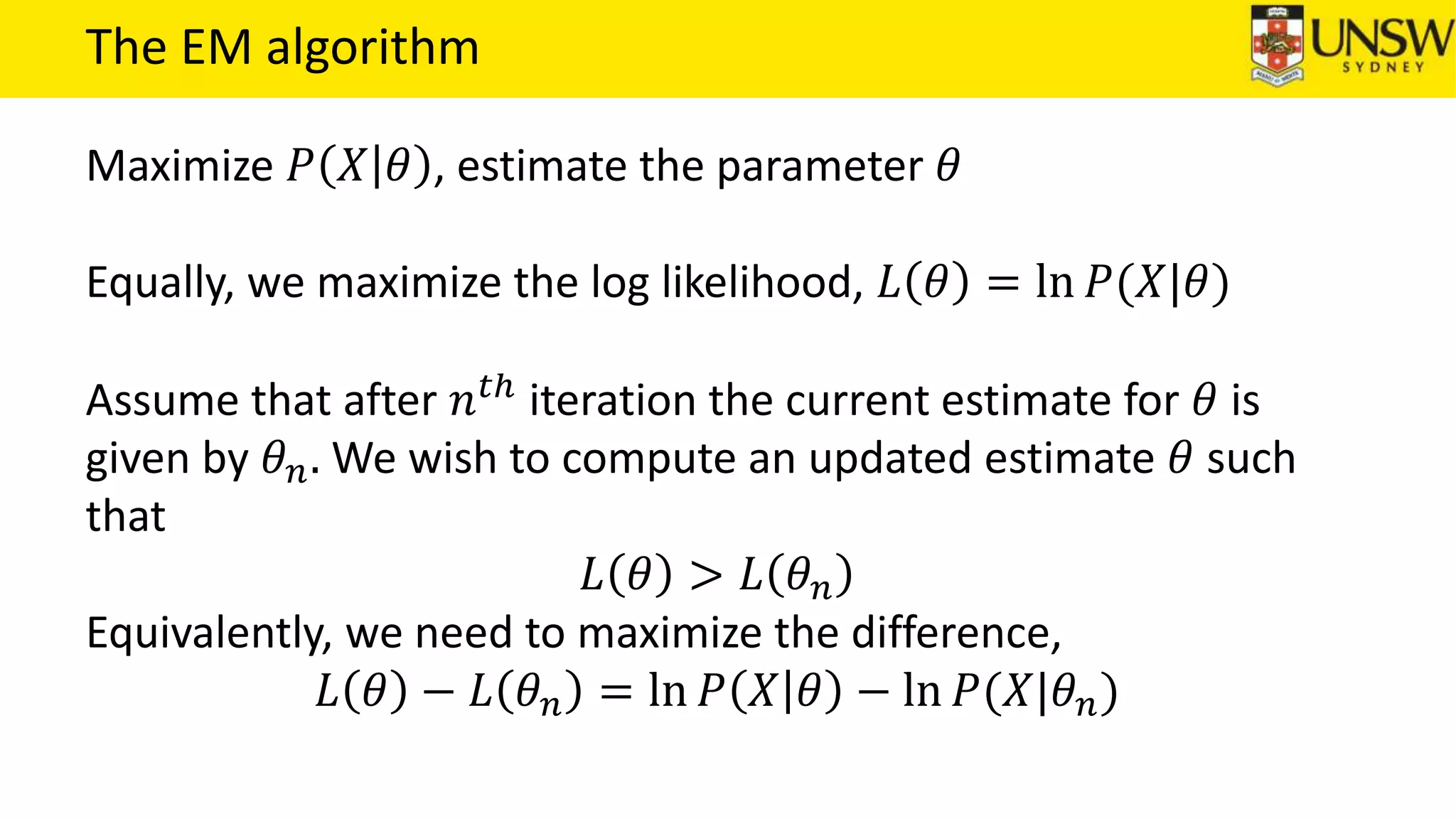
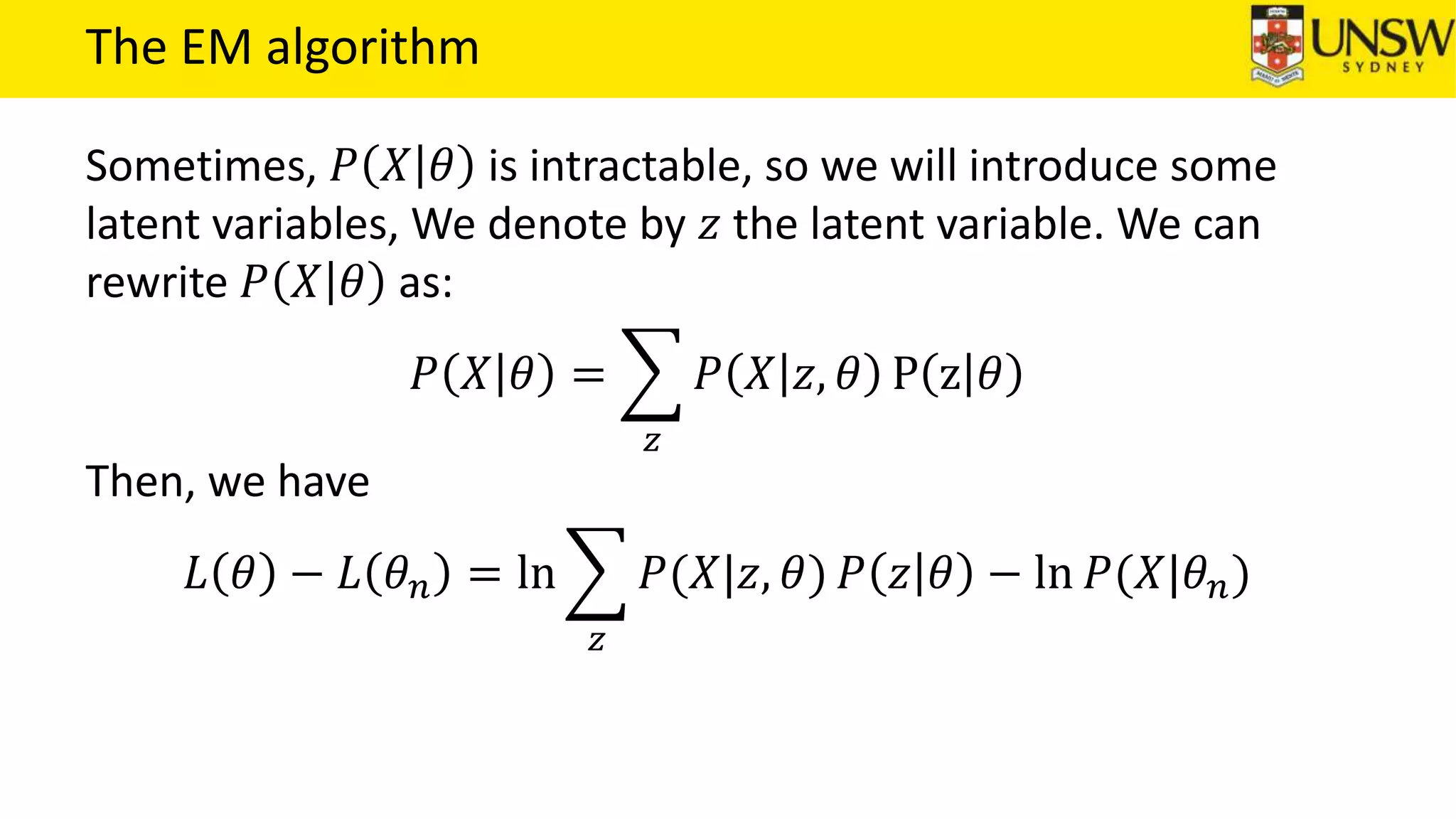
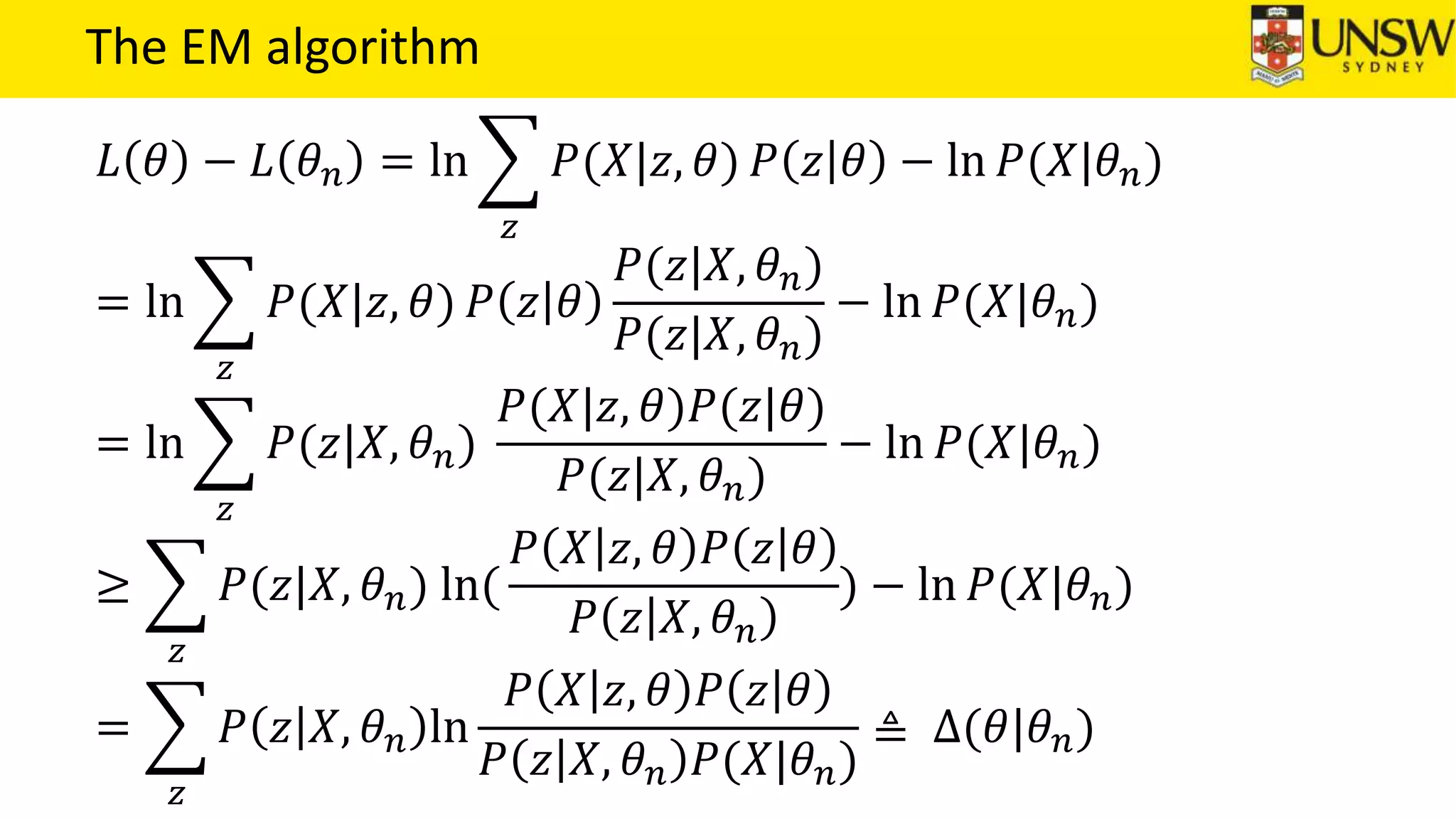
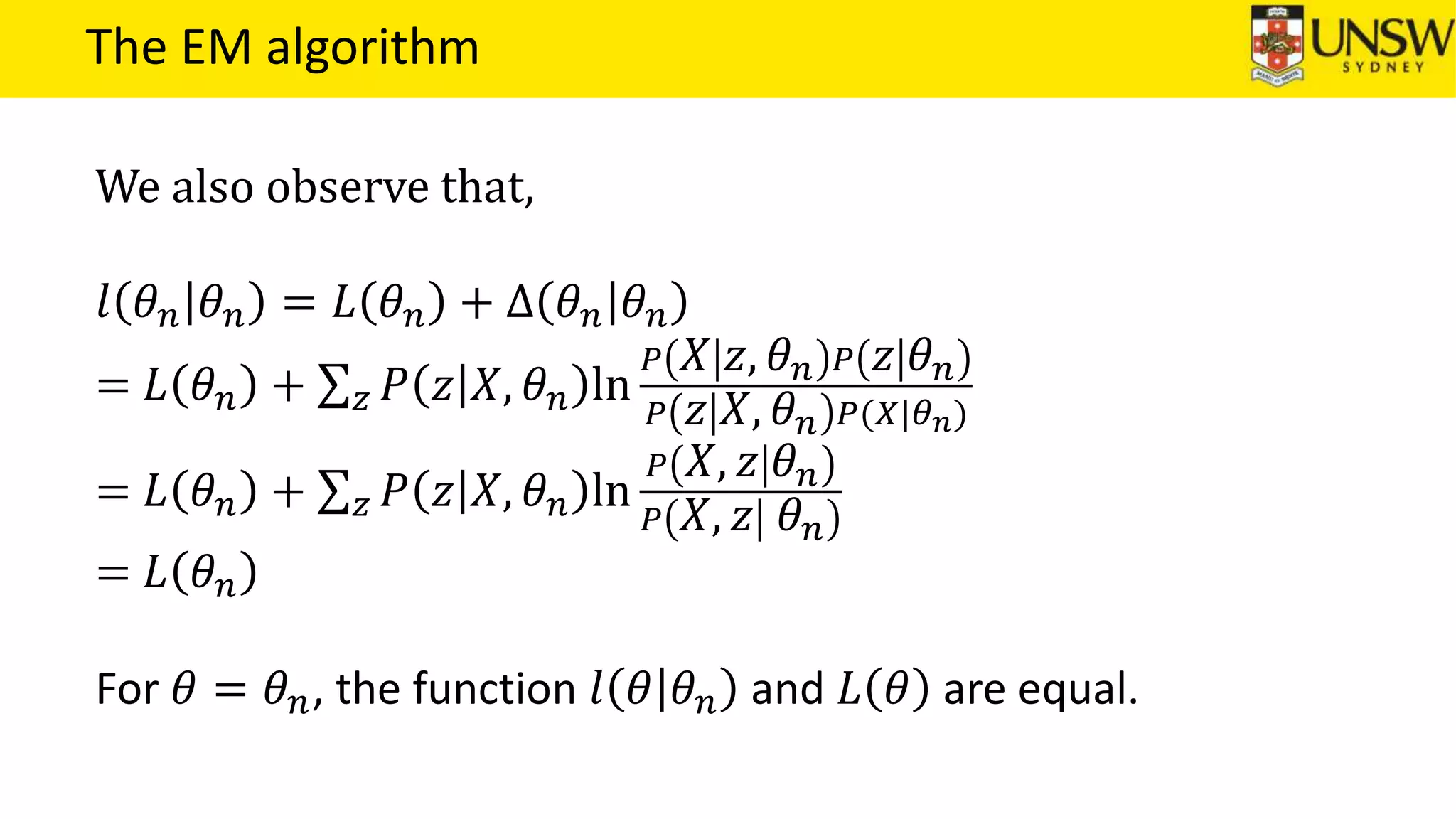
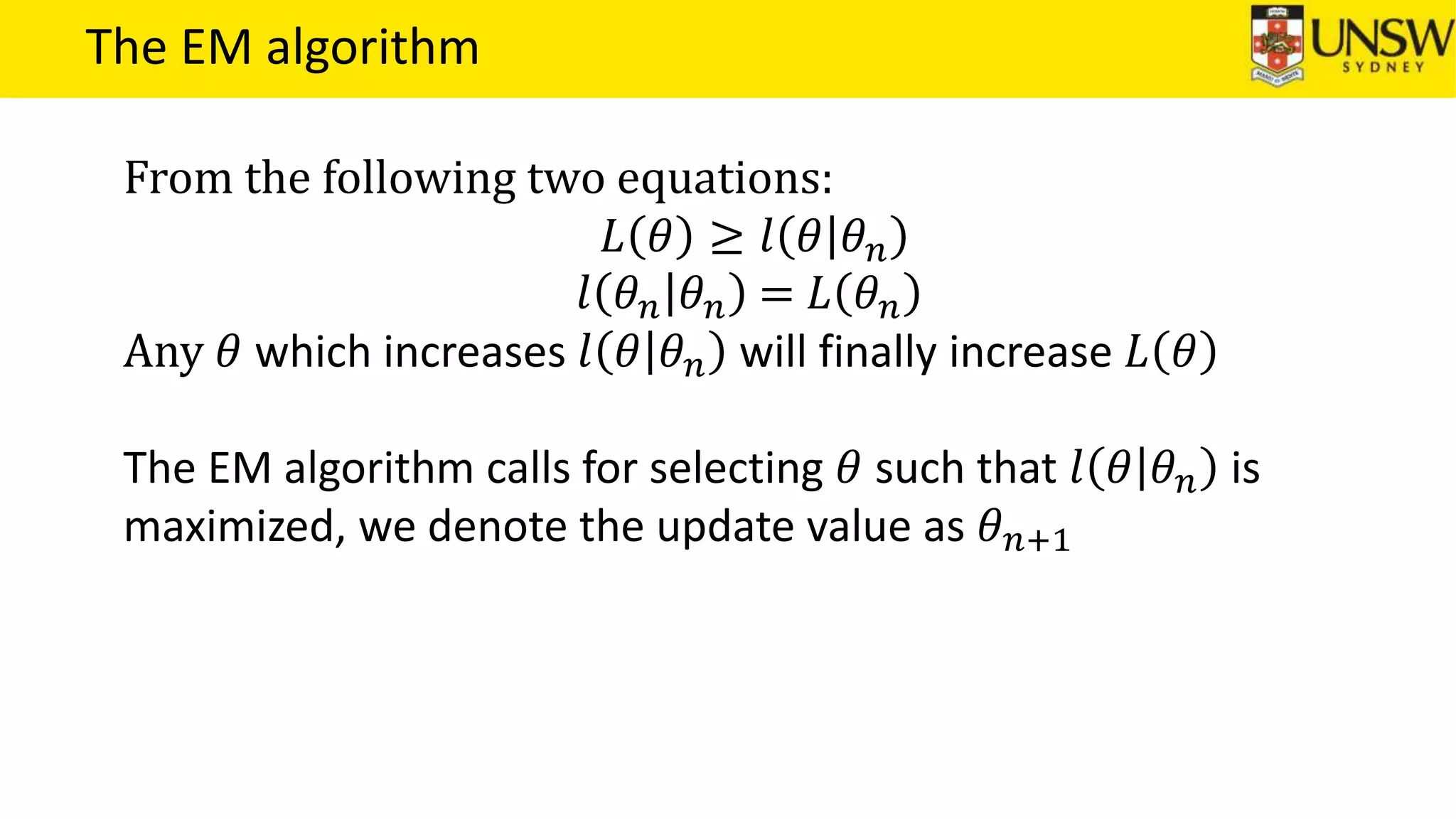
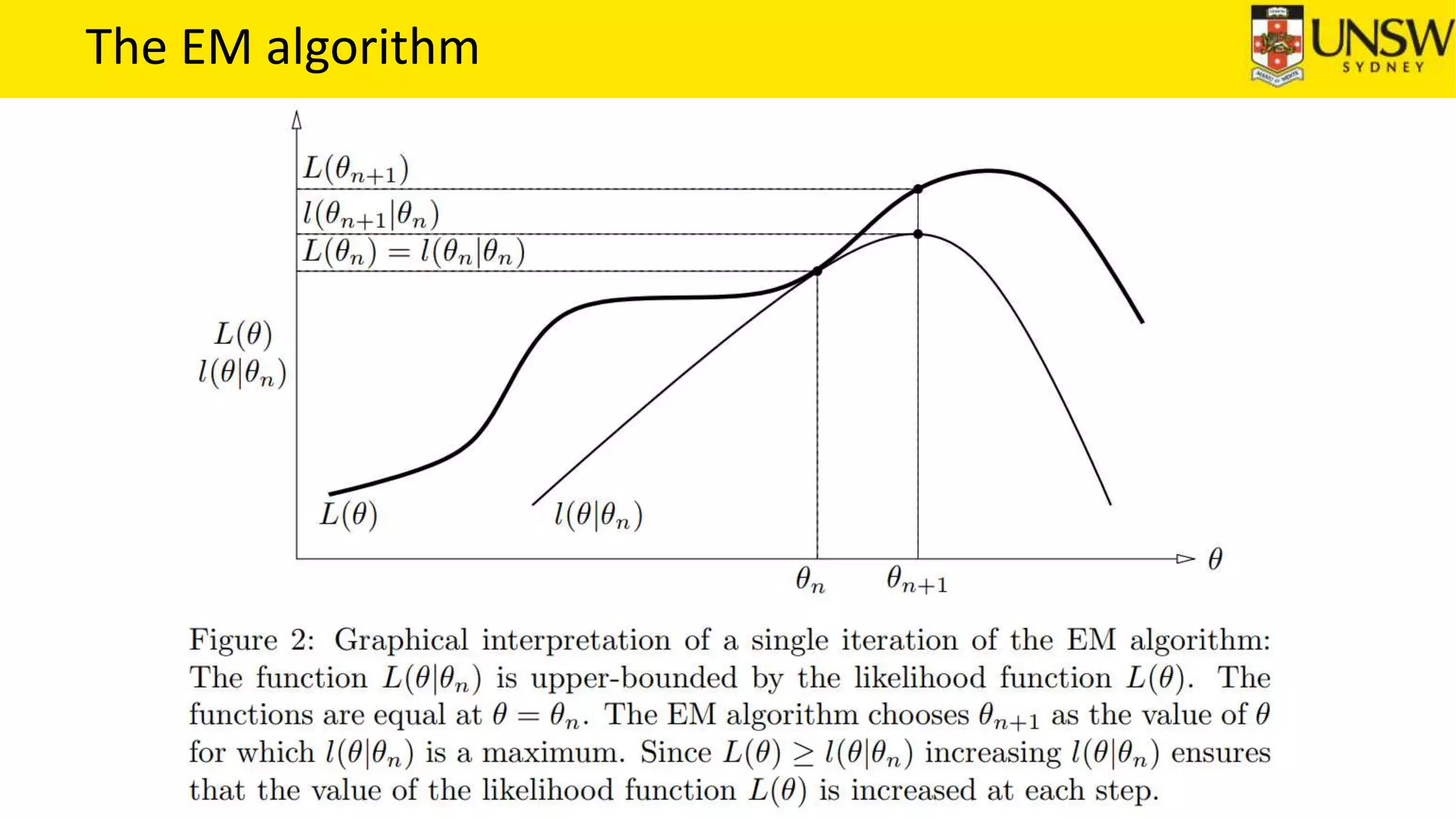
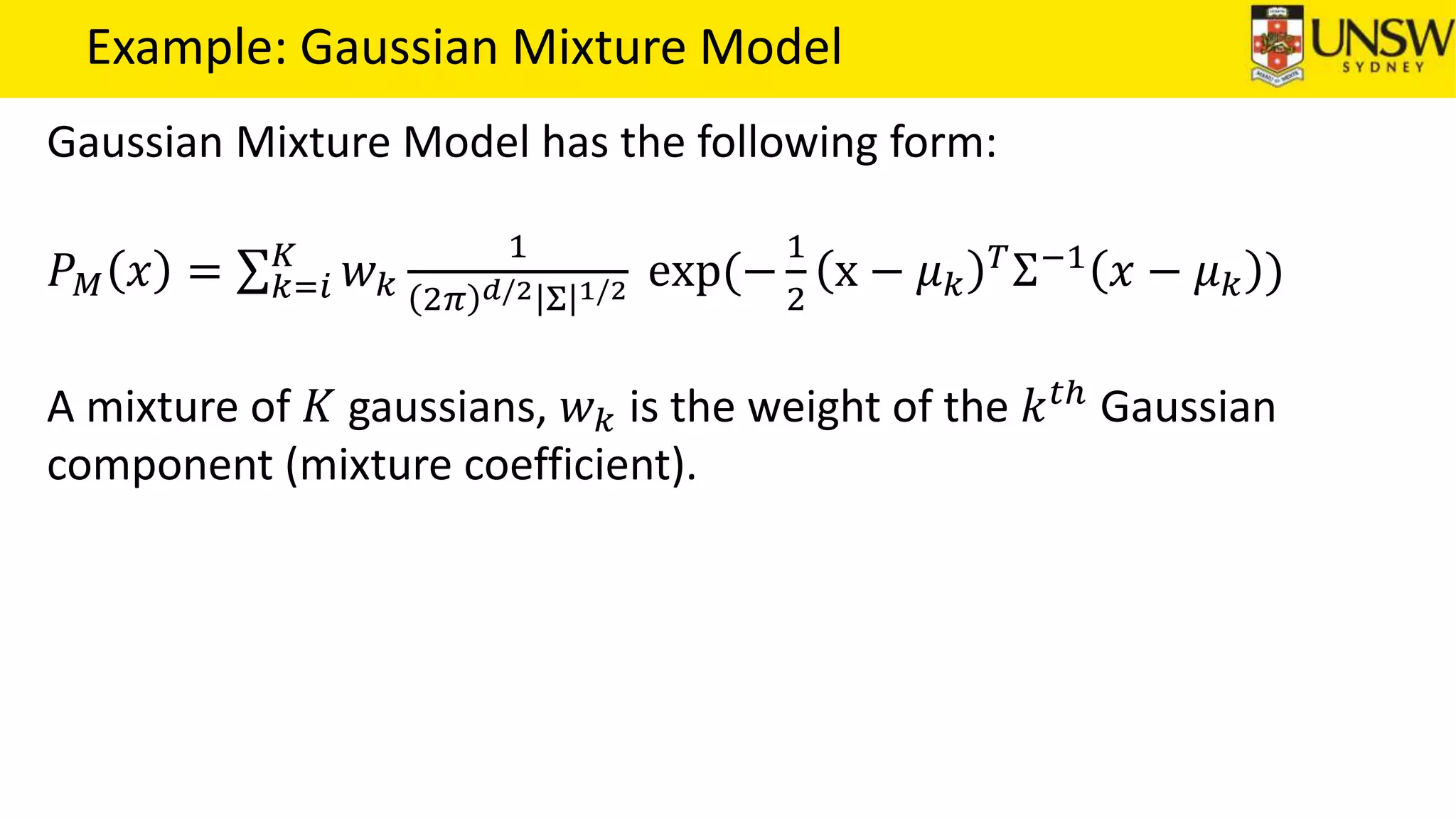
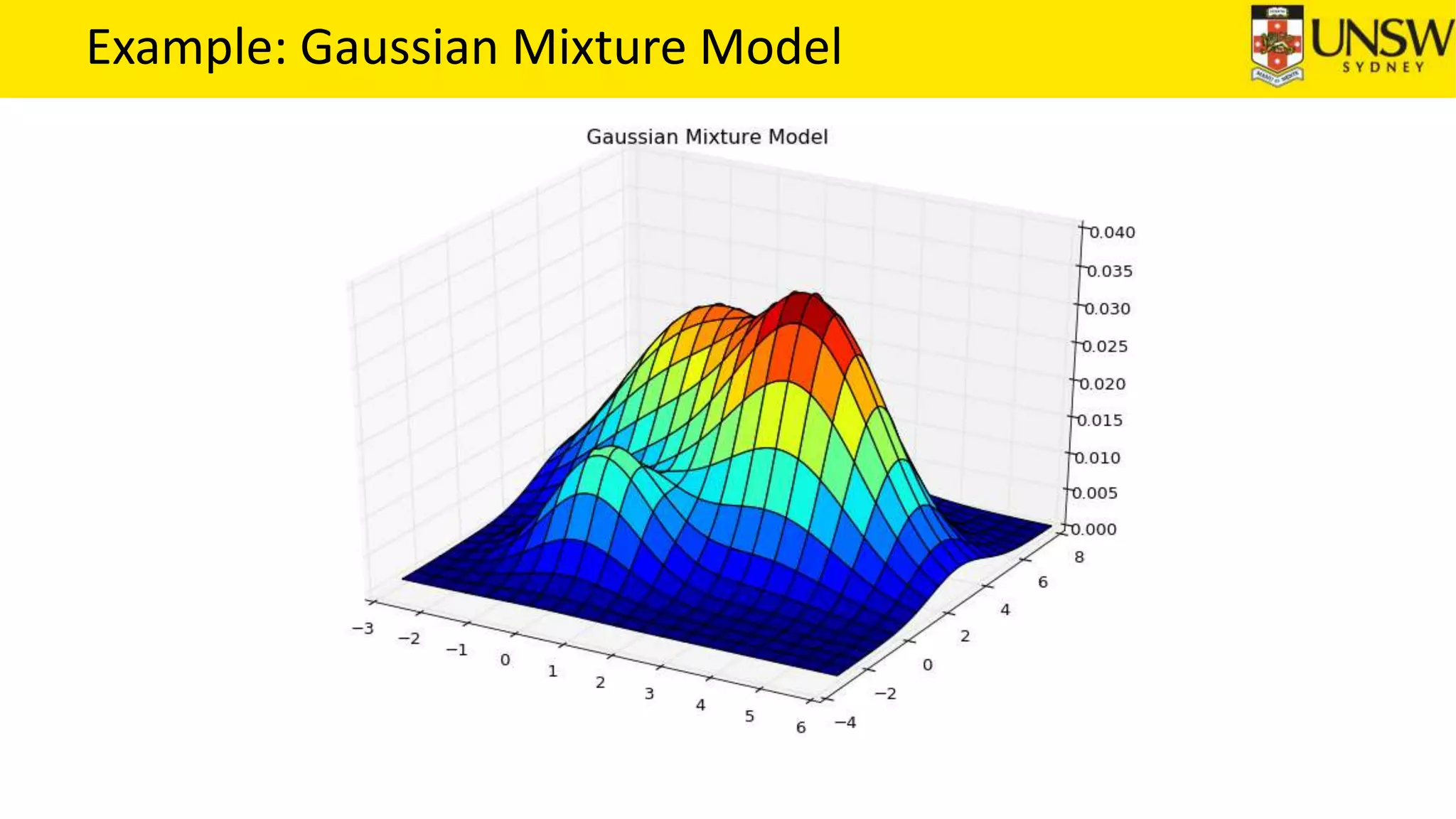
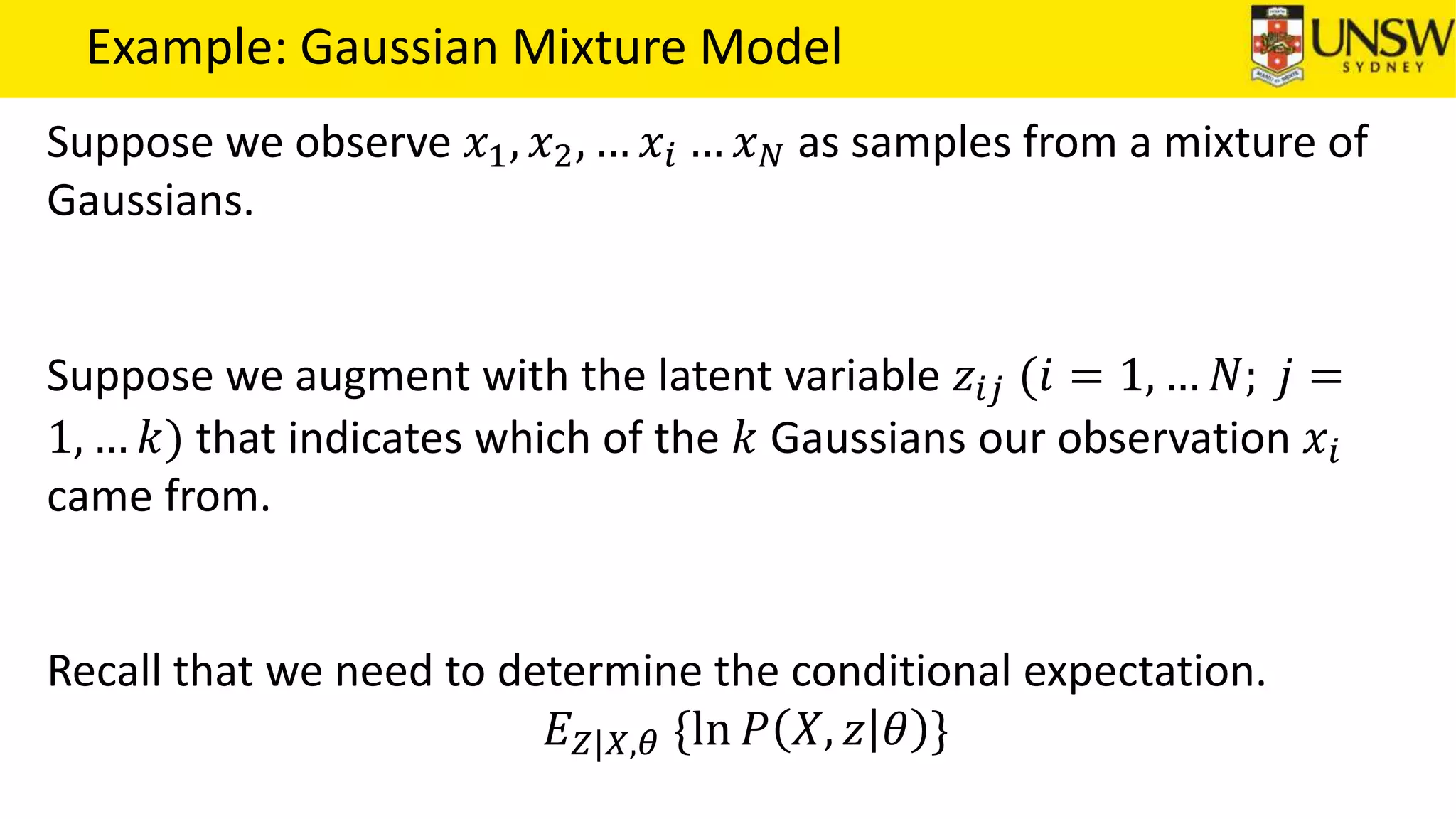
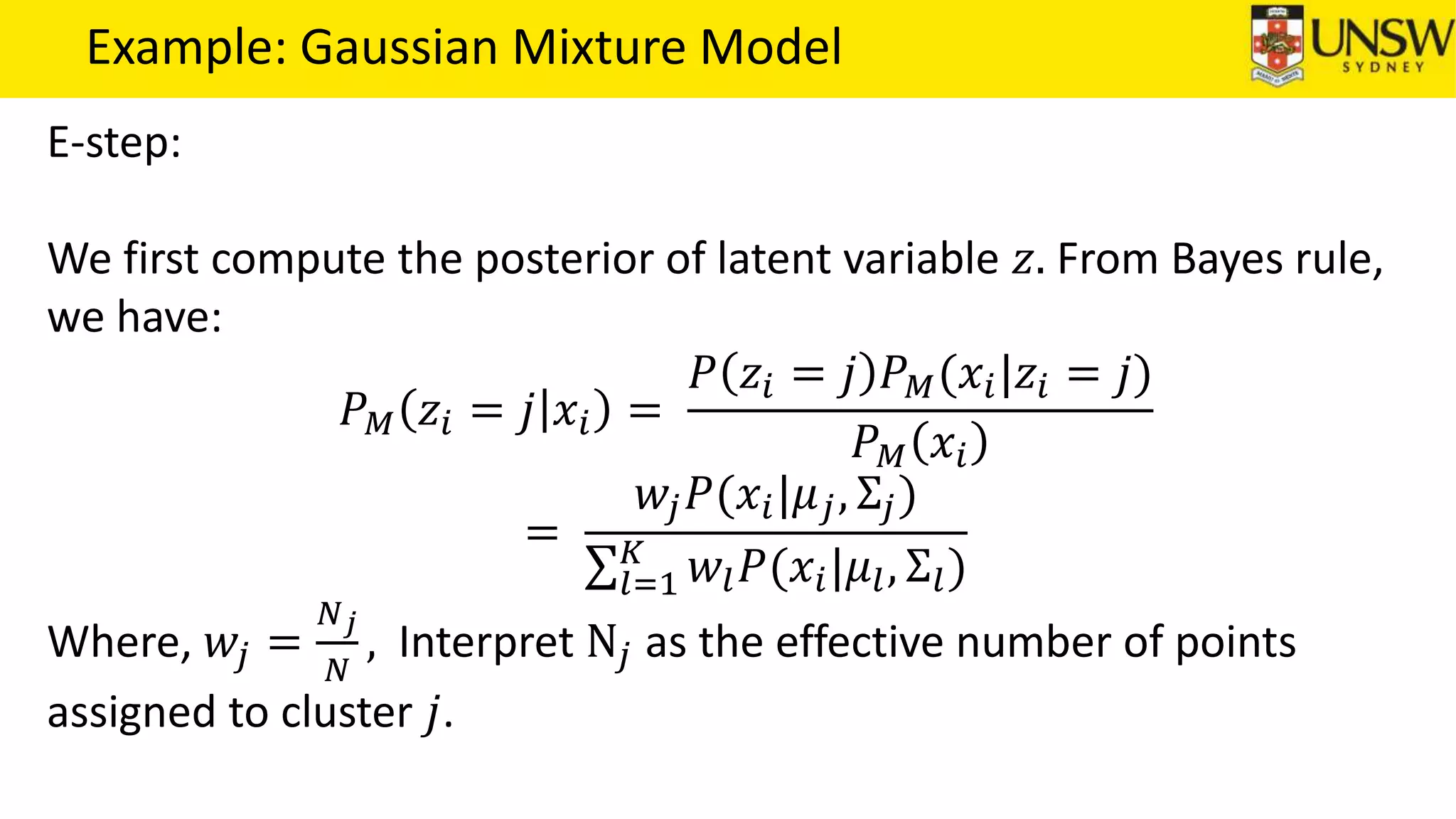
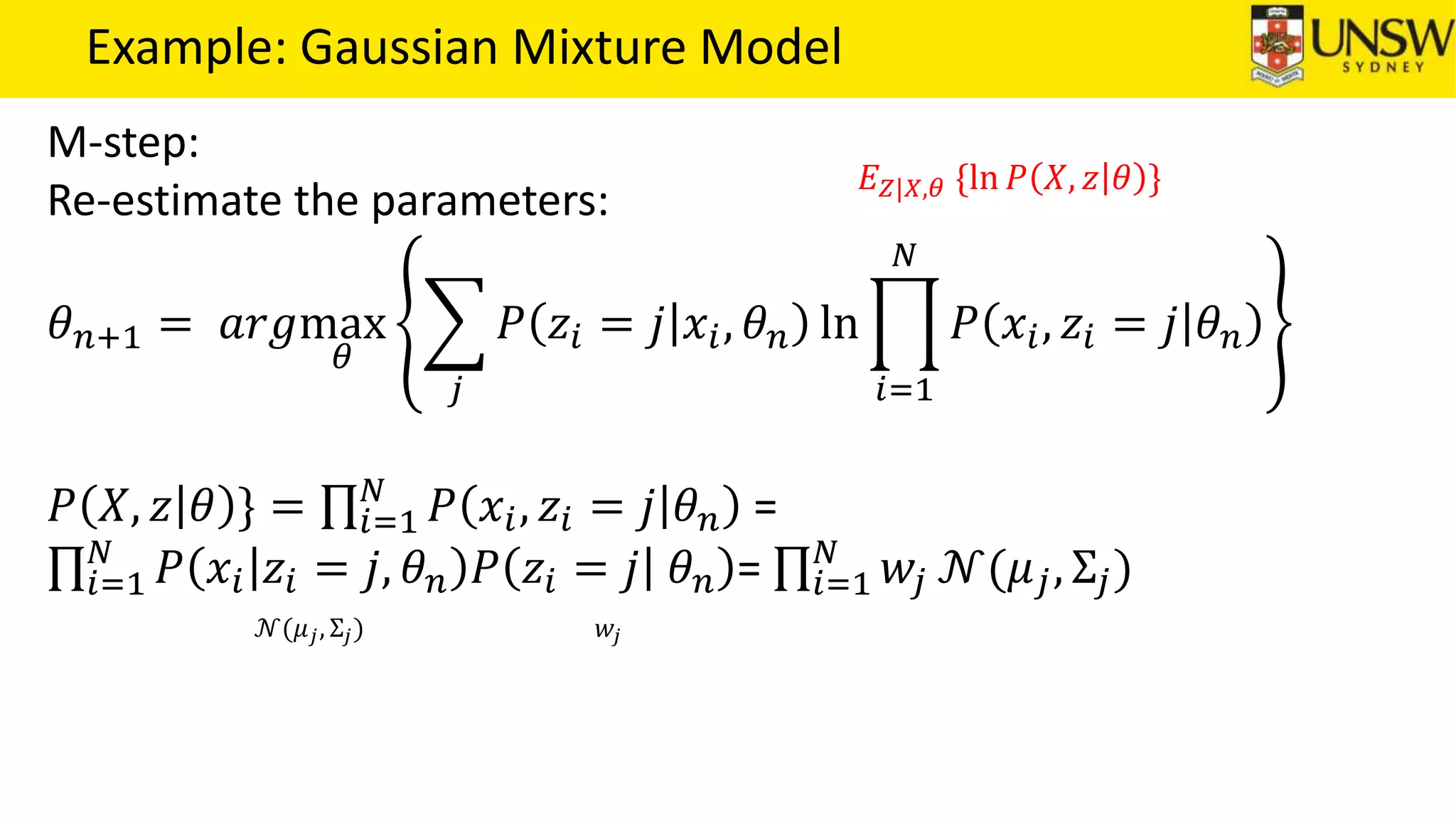
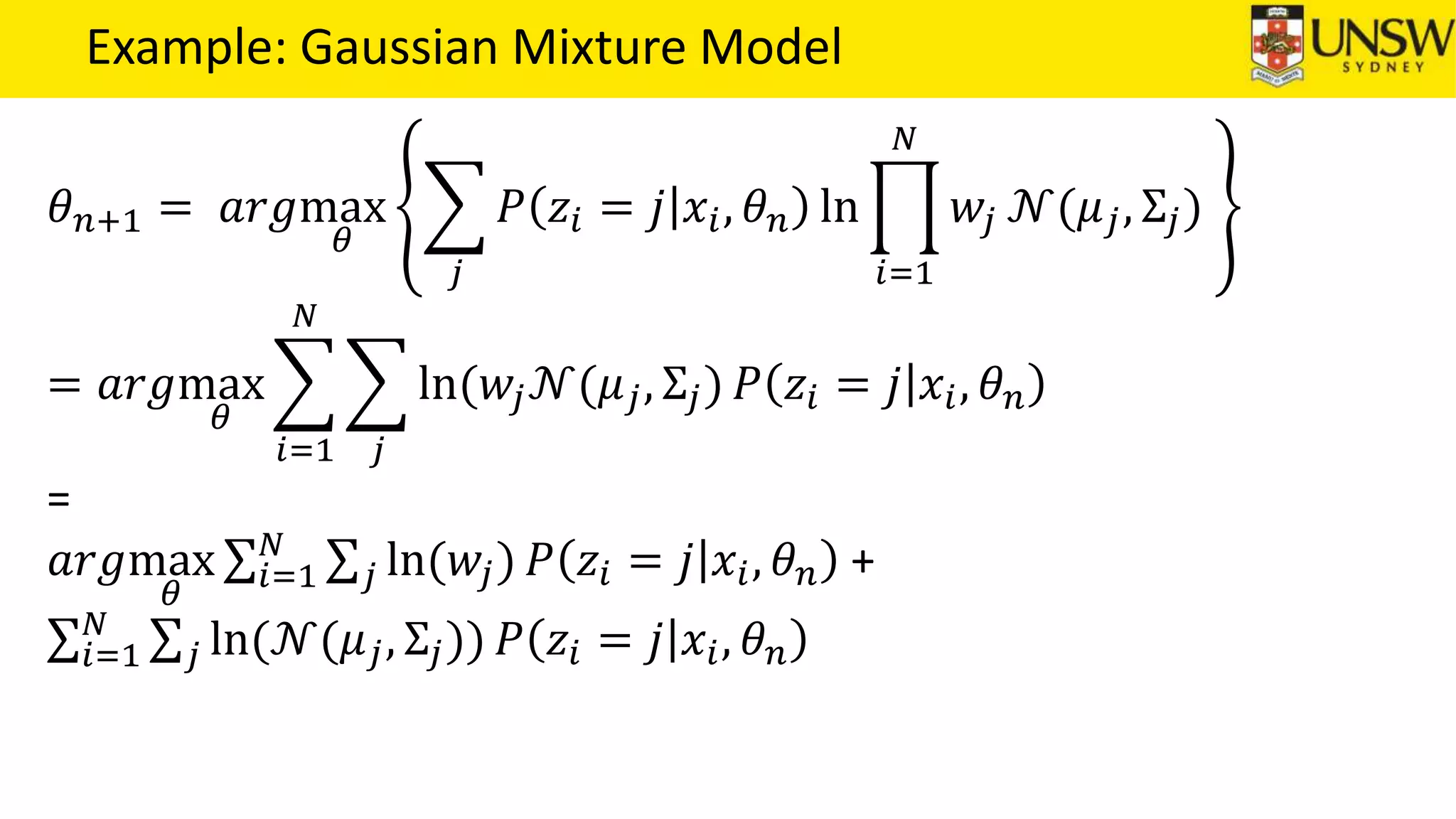
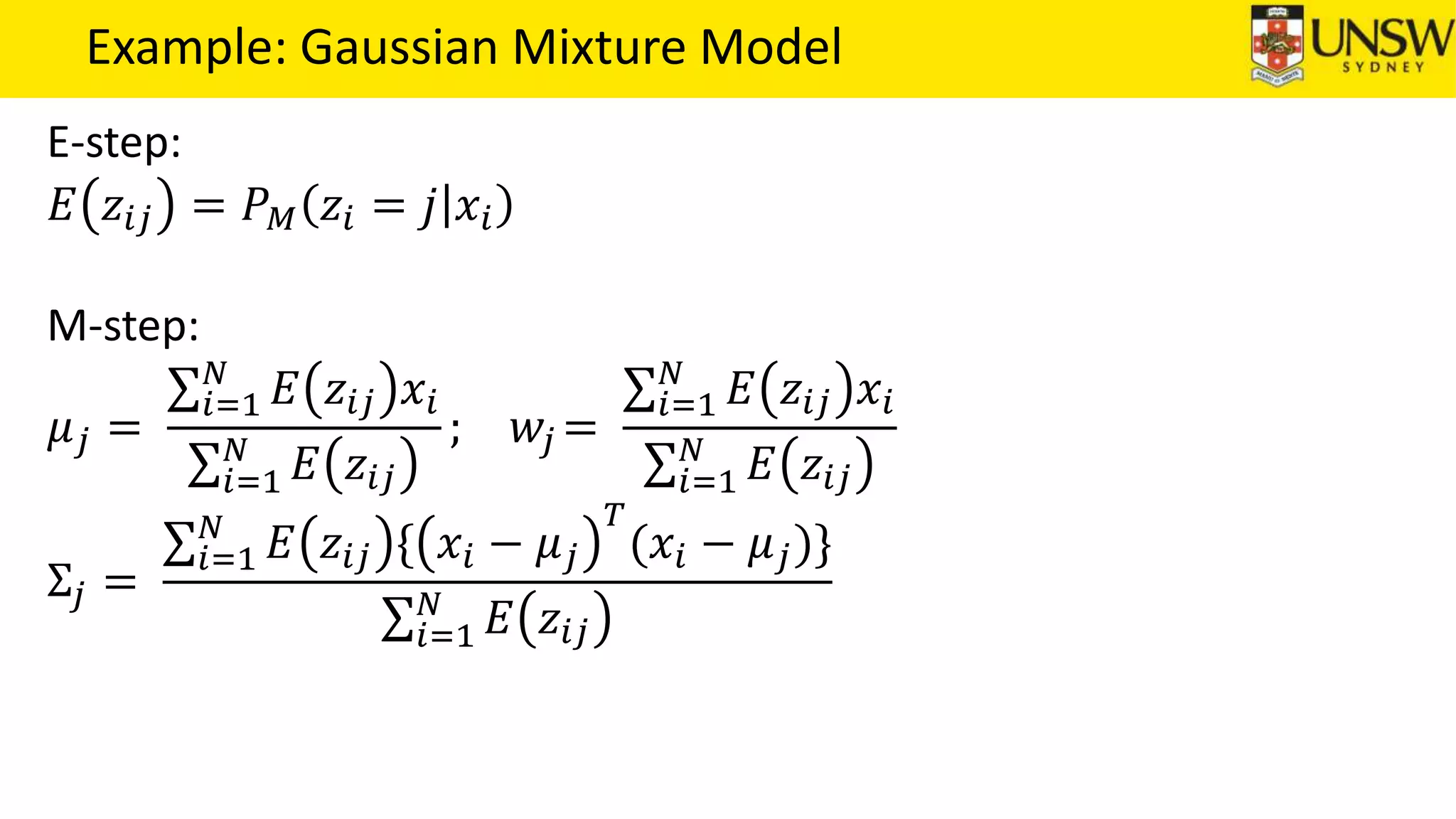
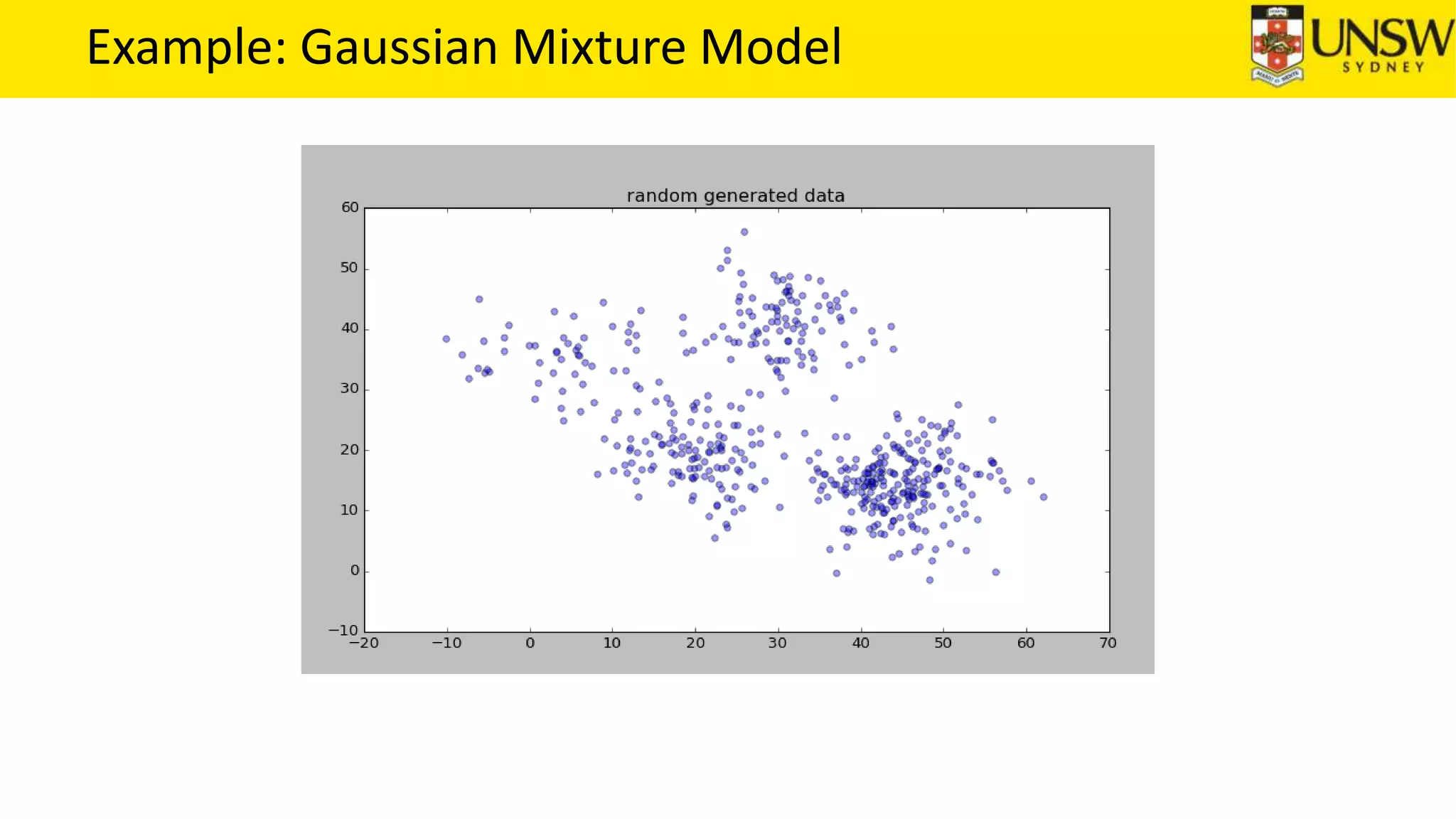
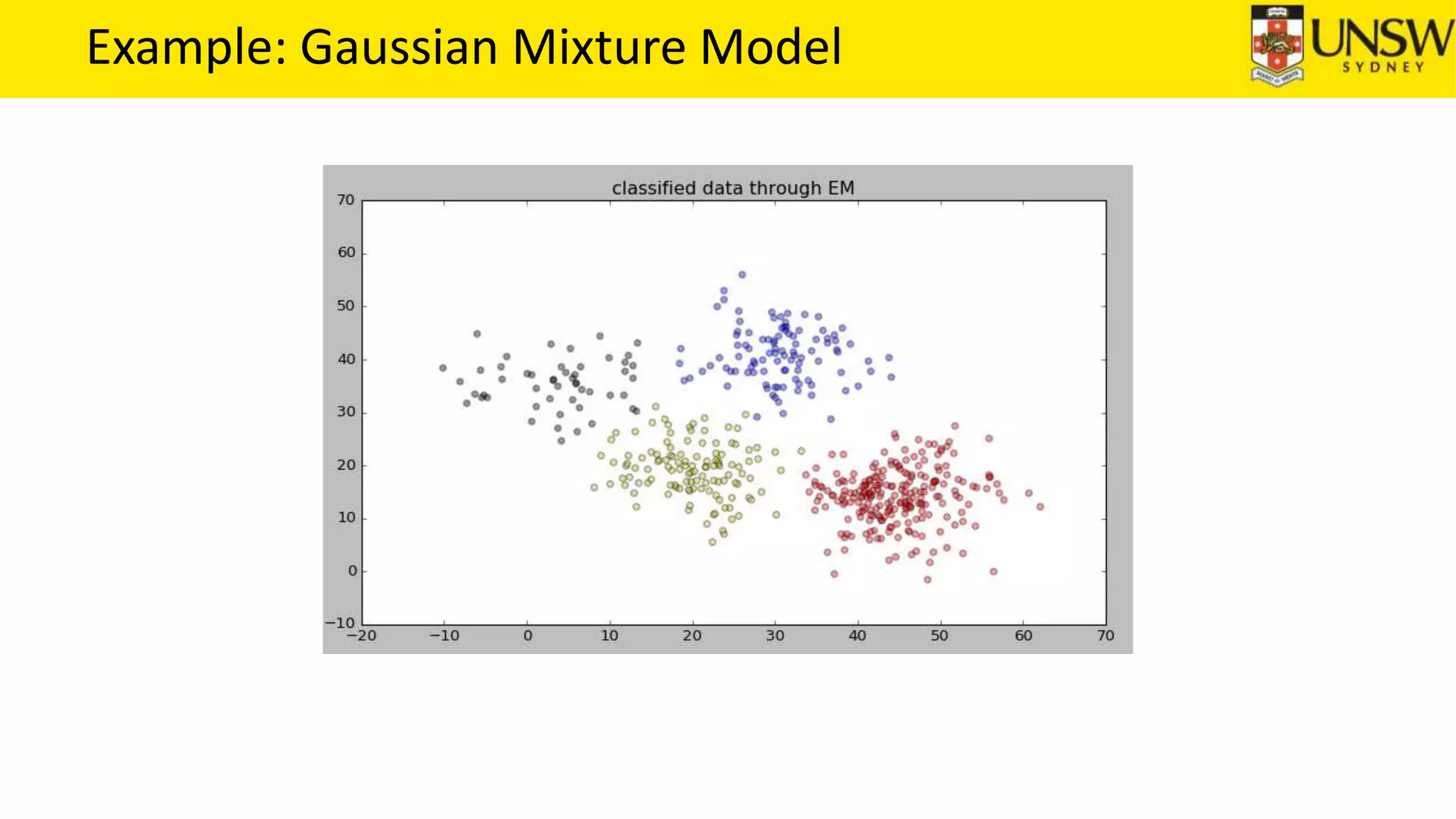
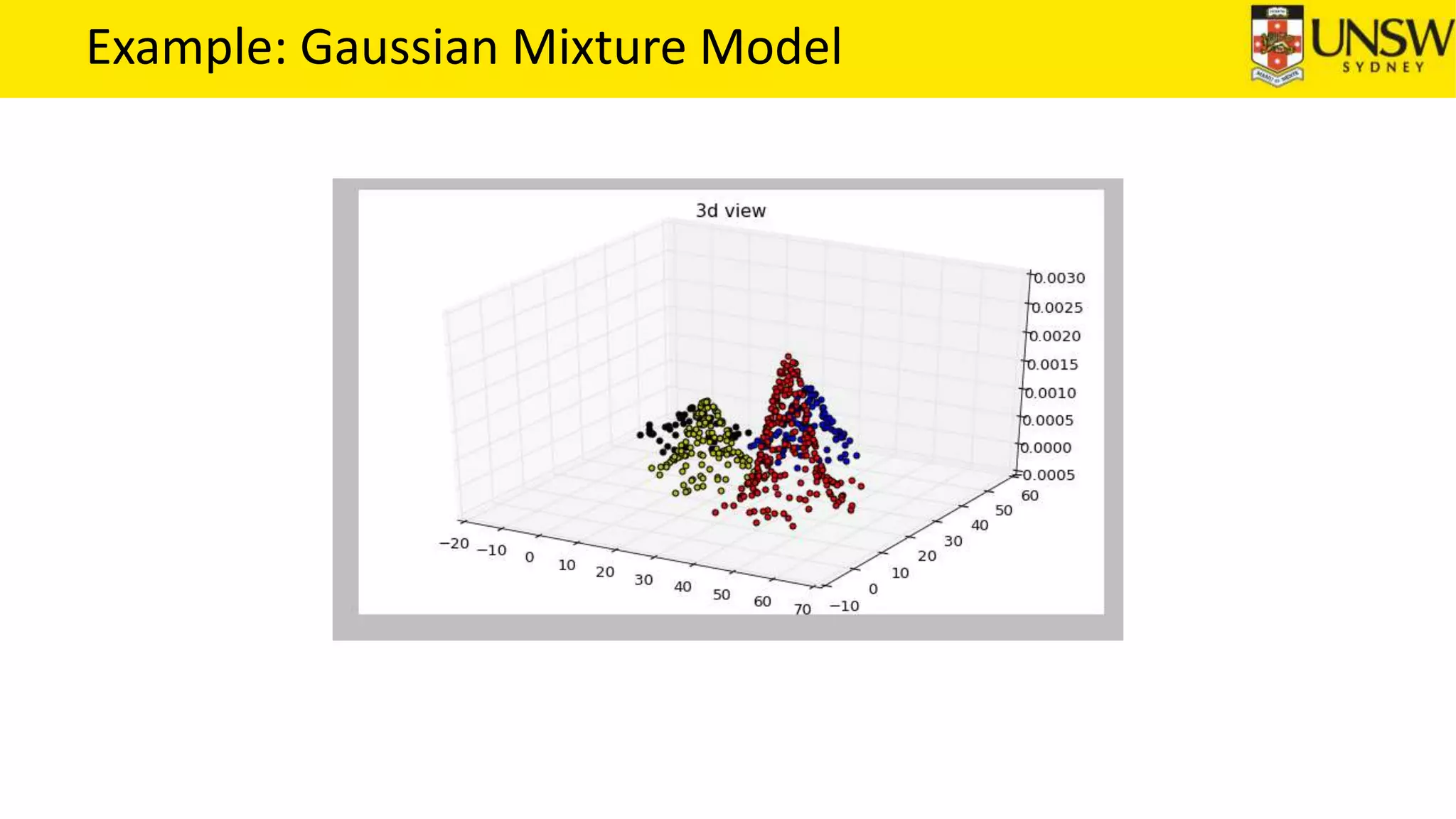
The EM algorithm is an iterative method to find maximum likelihood estimates of parameters in probabilistic models with latent variables. It has two steps: E-step, where expectations of the latent variables are computed based on current estimates, and M-step, where parameters are re-estimated to maximize the expected complete-data log-likelihood found in the E-step. As an example, the EM algorithm is applied to estimate the parameters of a Gaussian mixture model, where the latent variables indicate component membership of each data point.