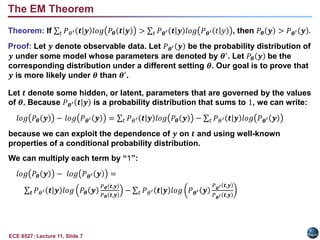
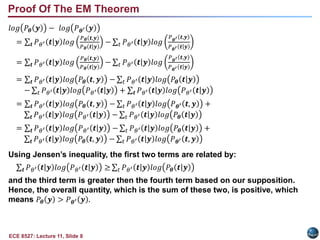
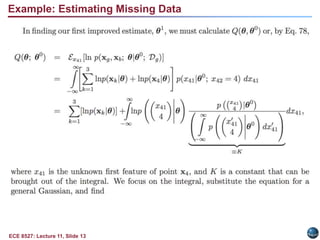
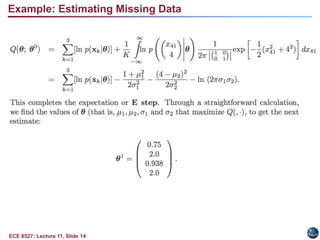
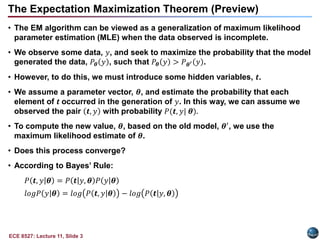
This document discusses the Expectation Maximization (EM) algorithm. EM is an iterative method used to find maximum likelihood estimates of parameters in probabilistic models. It estimates parameters given measurement data, commonly for Gaussian mixture distributions. EM alternates between an expectation (E) step, which computes the expected likelihood including latent variables, and a maximization (M) step, which computes parameter estimates maximizing the expected likelihood. The EM algorithm converges by ensuring that the expected log likelihood is increased with each iteration. Jensen's inequality and the EM theorem prove that this process will converge to a local maximum of the likelihood function.



![ECE 8527: Lecture 11, Slide 6
• Continuing in efforts to simplify:
𝑥
𝑝 𝑥 𝑙𝑜𝑔
𝑞 𝑥
𝑝 𝑥
≤
𝑥
𝑝 𝑥
𝑞 𝑥
𝑝 𝑥
− 1 =
𝑥
𝑝 𝑥
𝑞 𝑥
𝑝 𝑥
−
𝑥
𝑝 𝑥
= 𝑥 𝑝 𝑥 − 𝑥 𝑞 𝑥 = 0.
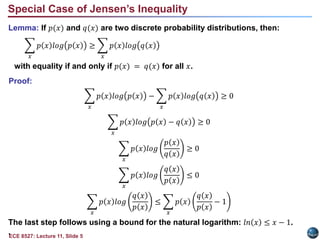
• We note that since both of these functions are probability distributions, they
must sum to 1. Therefore, the inequality holds.
• The general form of Jensen’s inequality relates a convex function of an
integral to the integral of the convex function and is used extensively in
information theory:
If 𝑔(𝑥) is a convex function on 𝑅𝑥, and 𝐸[𝑔(𝑋)] and 𝑔(𝐸[𝑋]) are finite,
then 𝐸[𝑔(𝑋)] ≥ 𝑔(𝐸[𝑋]).
• There are other forms of Jensen’s inequality such as:
If 𝑝1, 𝑝2, … , 𝑝𝑛 are positive constants that sum to 1 and 𝑓 is a real continuous
function, then:
convex: 𝑓 𝑖=1
𝑛
𝑝𝑖𝑥𝑖 ≤ 𝑖=1
𝑛
𝑝𝑖𝑓 𝑥𝑖 concave: 𝑓 𝑖=1
𝑛
𝑝𝑖𝑥𝑖 ≥ 𝑖=1
𝑛
𝑝𝑖𝑓 𝑥𝑖
Special Case of Jensen’s Inequality](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture11-221108033702-2879fb95/85/lecture_11-pptx-7-320.jpg)