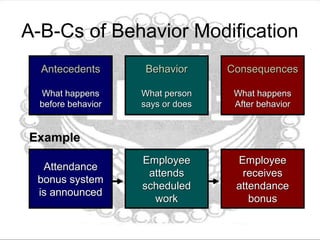
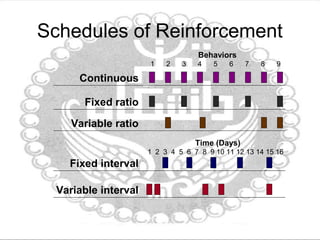
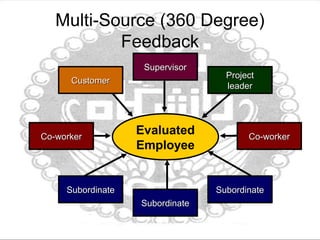
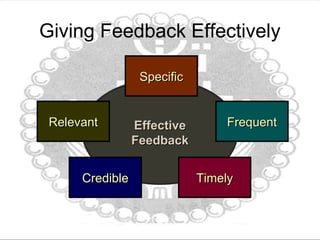
This document discusses organizational behavior and learning through behavior modification. It defines learning as a relatively permanent change in behavior resulting from interaction with the environment. It outlines several theories of learning, including classical and operant conditioning. It describes the antecedents, behavior, and consequences (A-B-C) model of behavior modification. It also discusses shaping behavior through positive and negative reinforcement or punishment, different schedules of reinforcement, and using behavior modification for job performance. The document emphasizes the importance of feedback for learning and improving performance through clarification of roles, correction, and motivation. It notes characteristics of effective feedback and evaluating feedback from multiple sources.