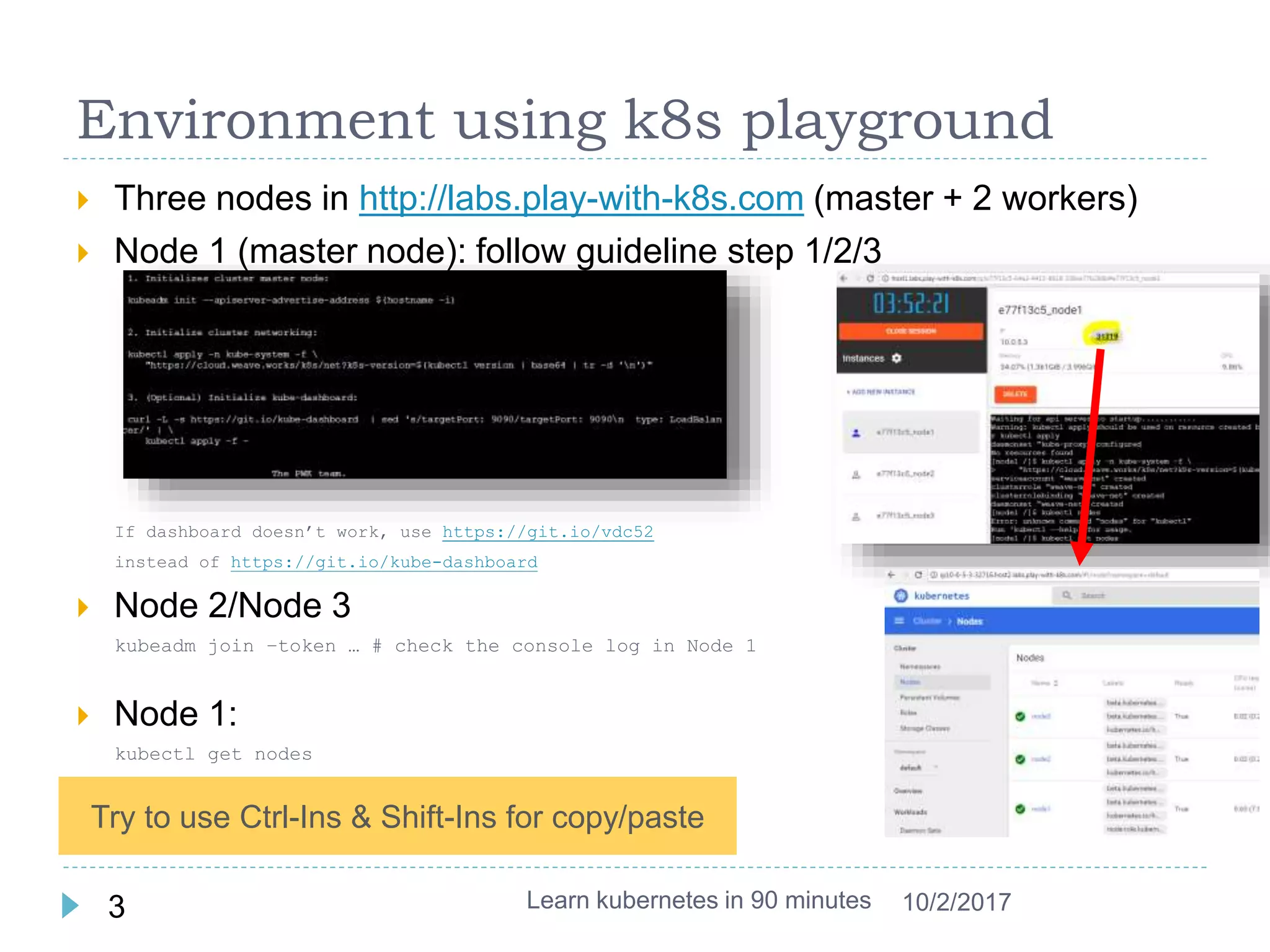
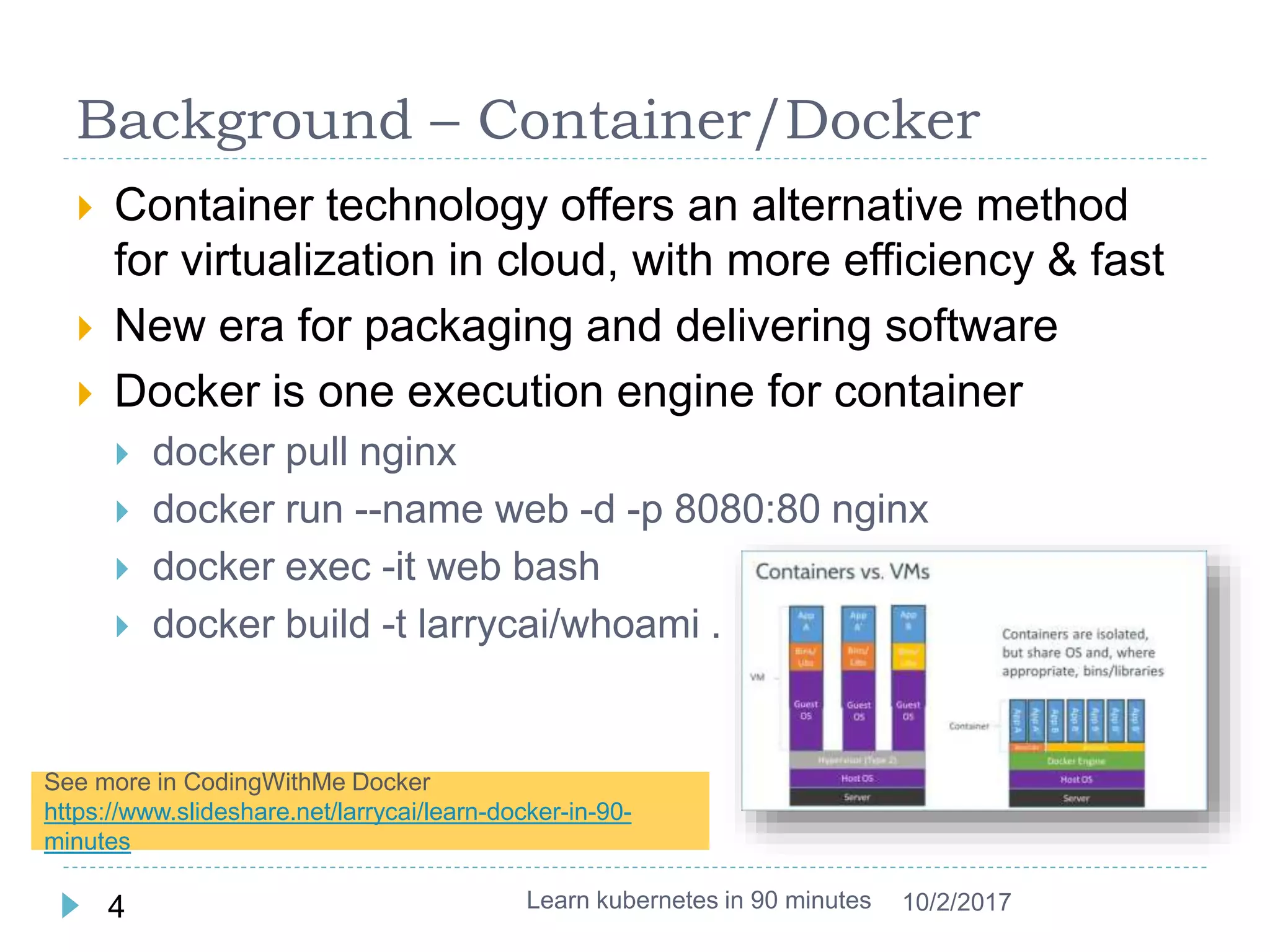
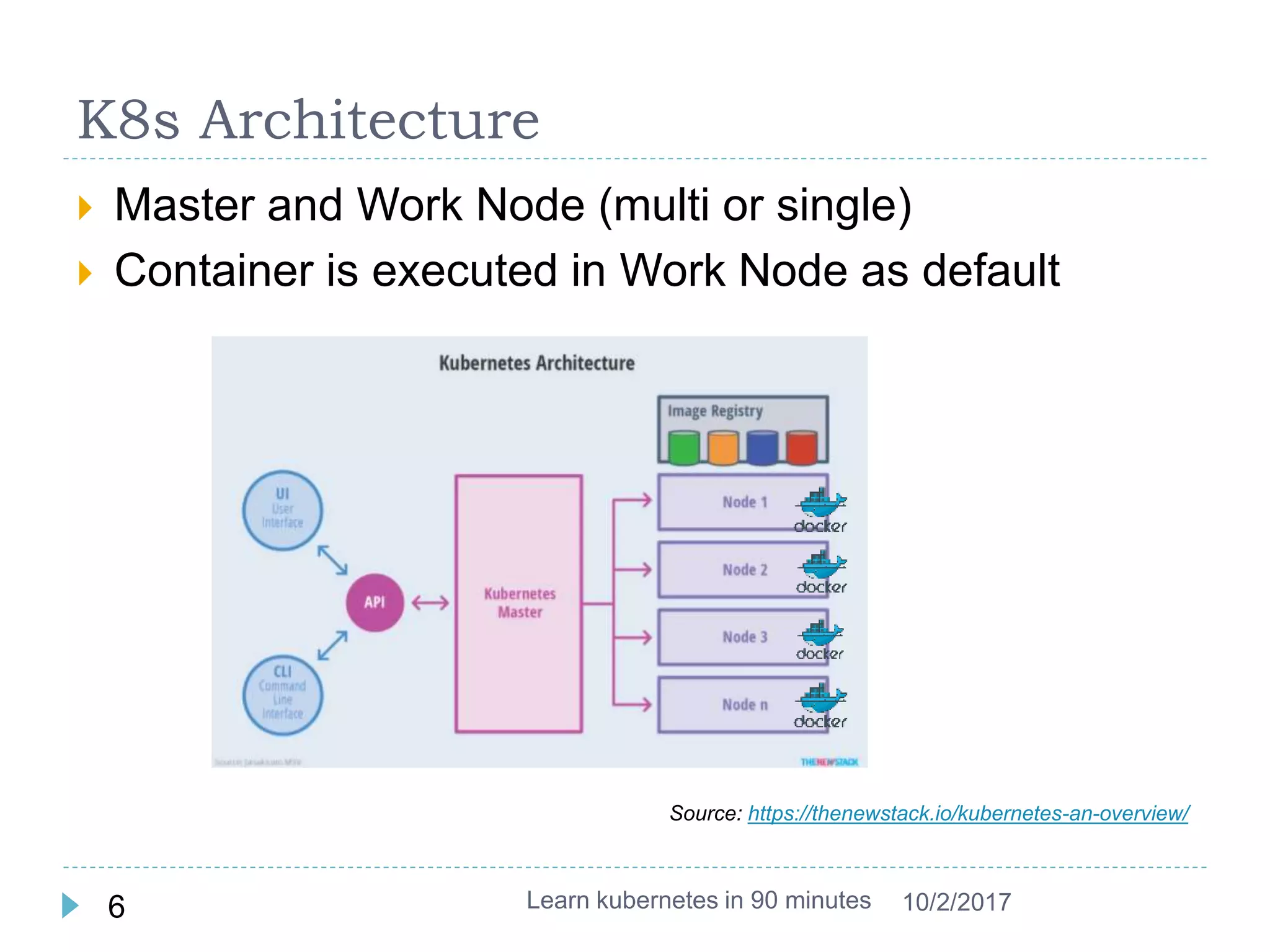
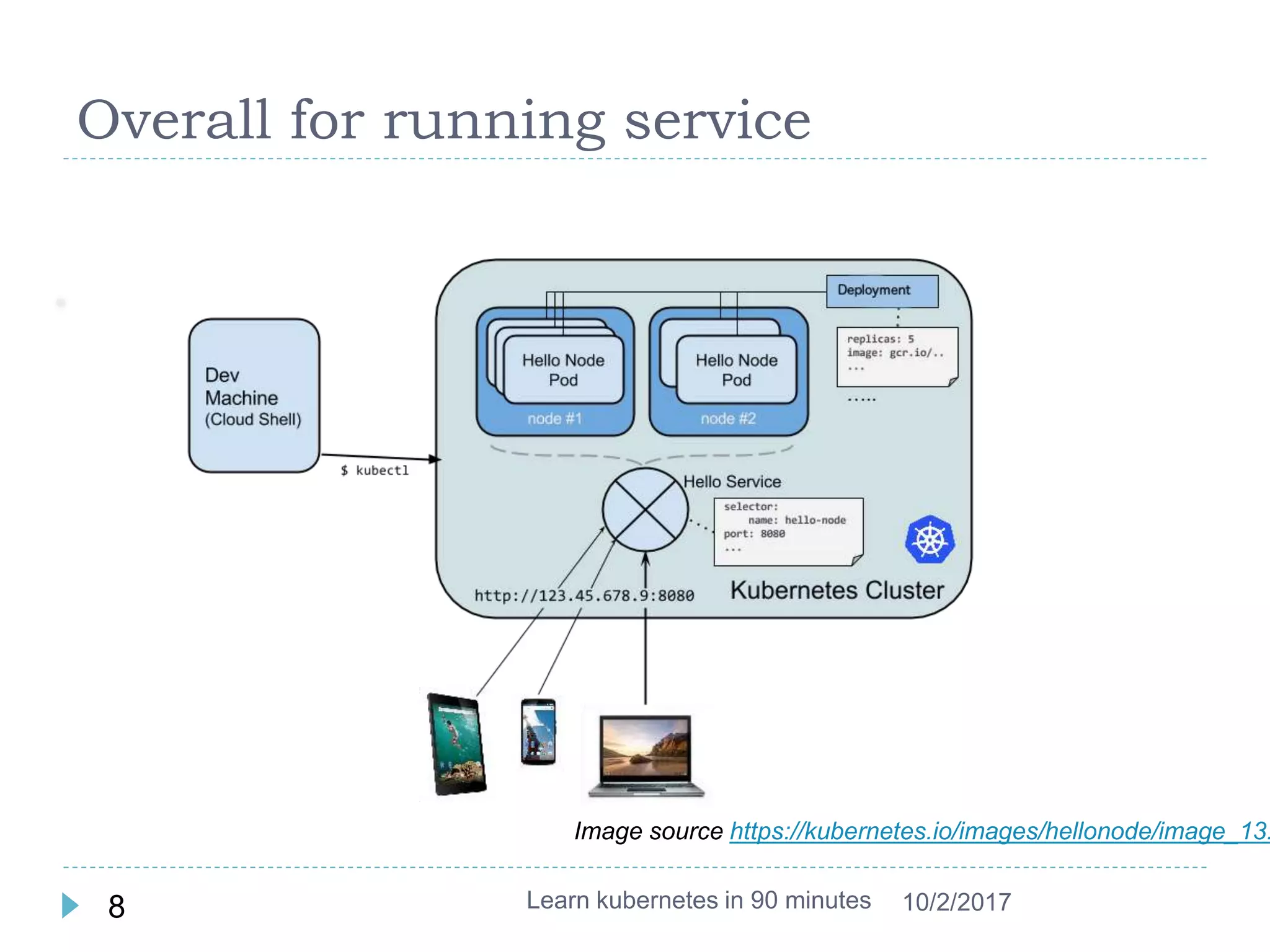
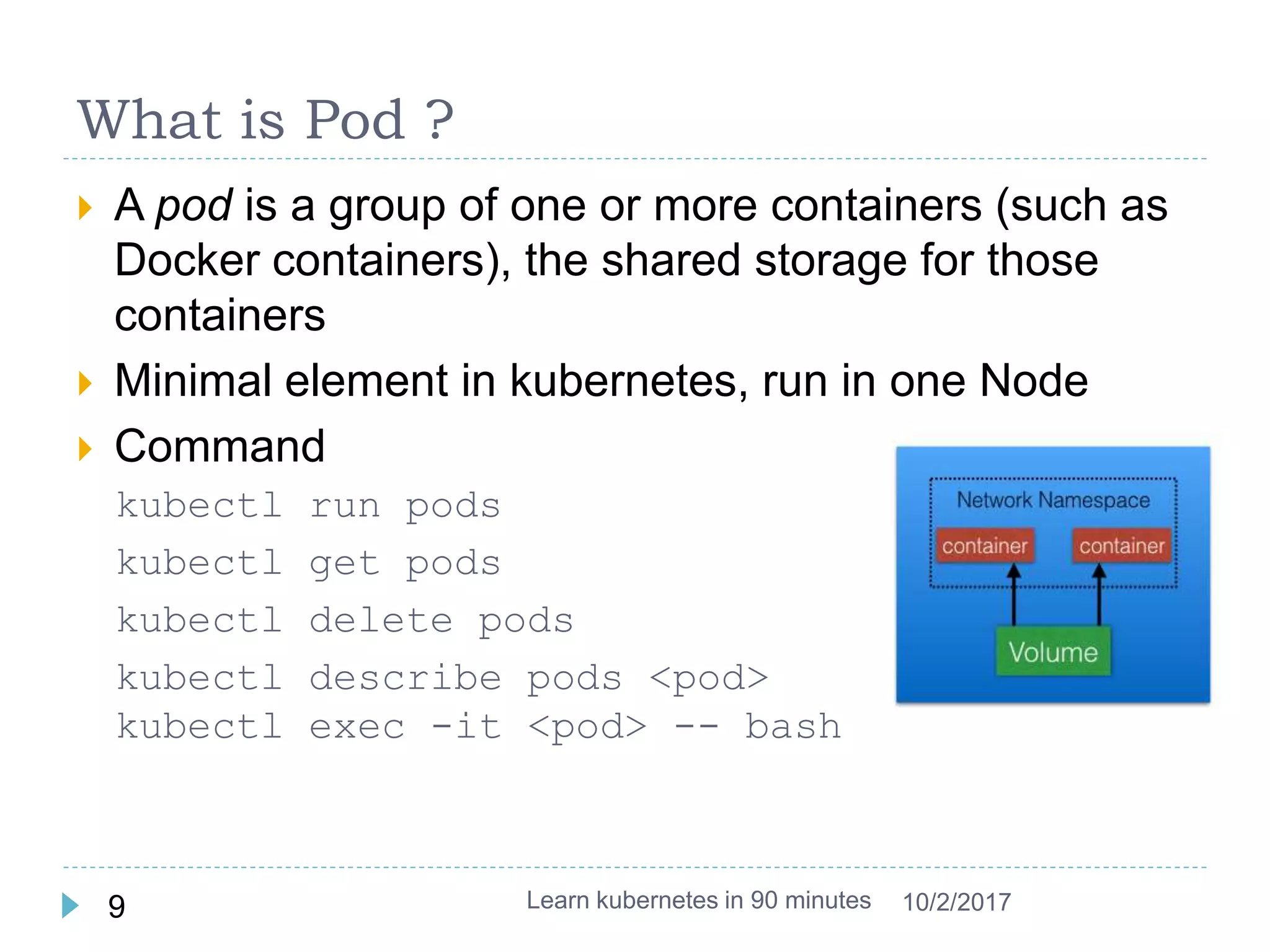
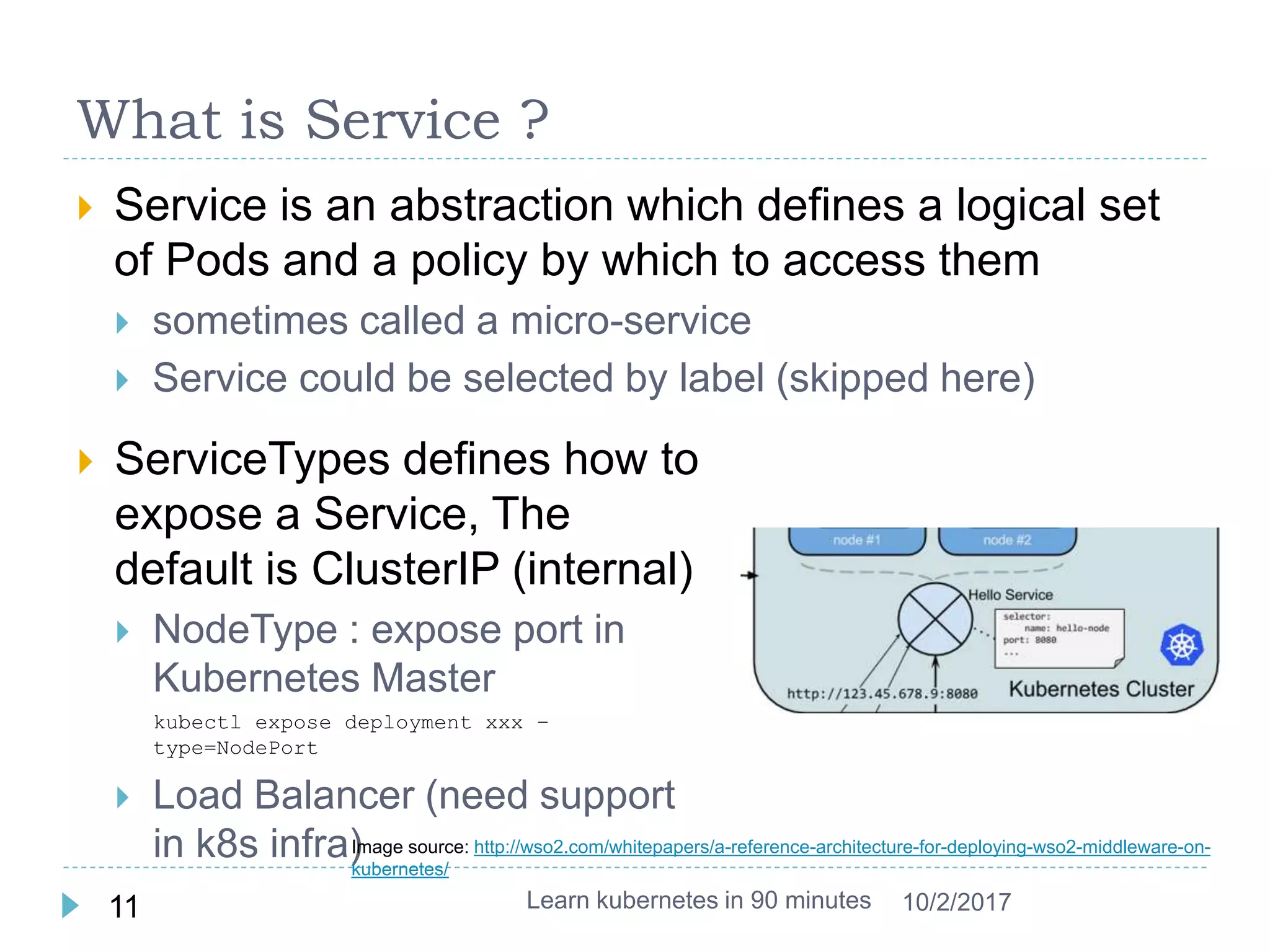
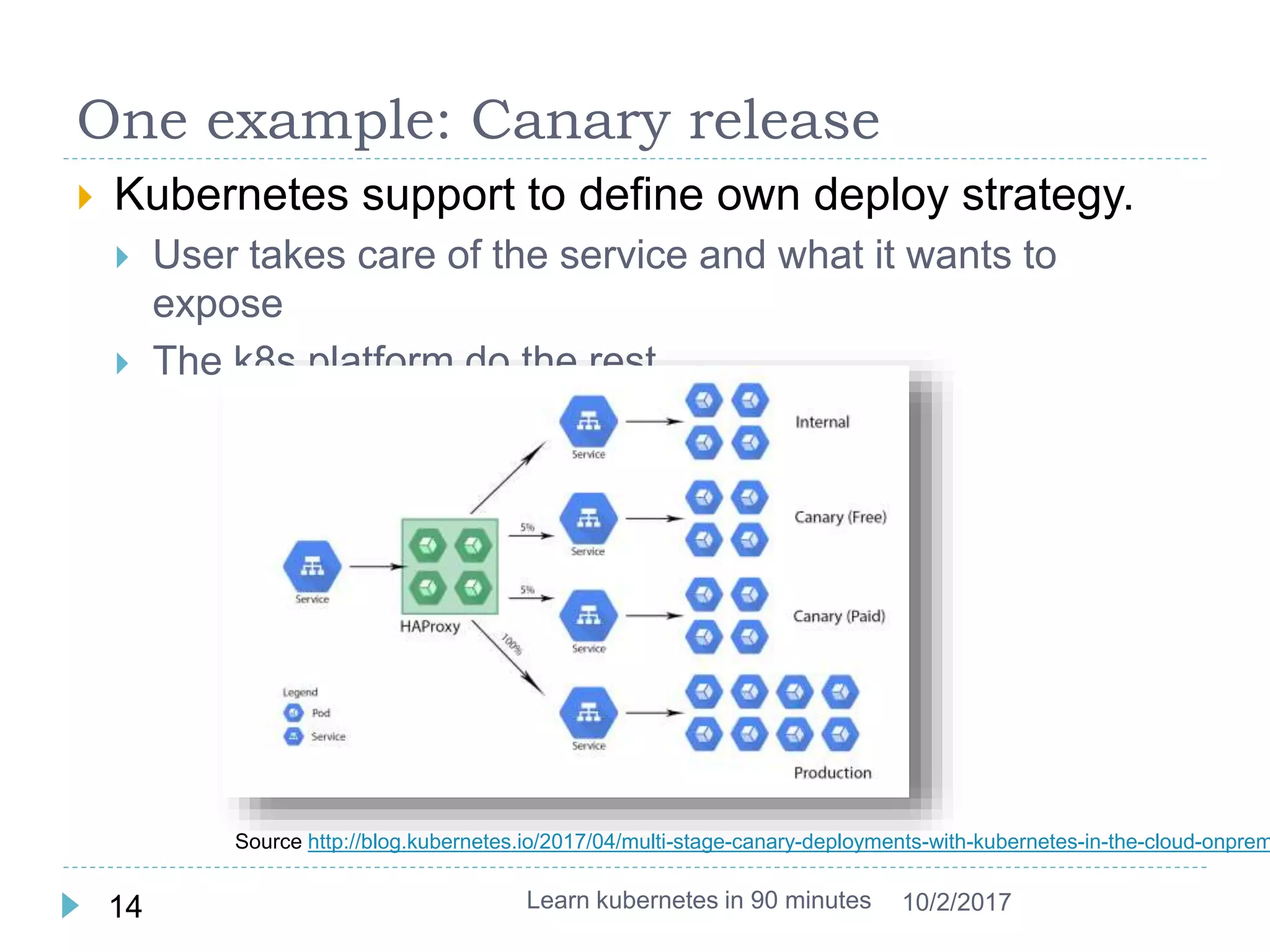
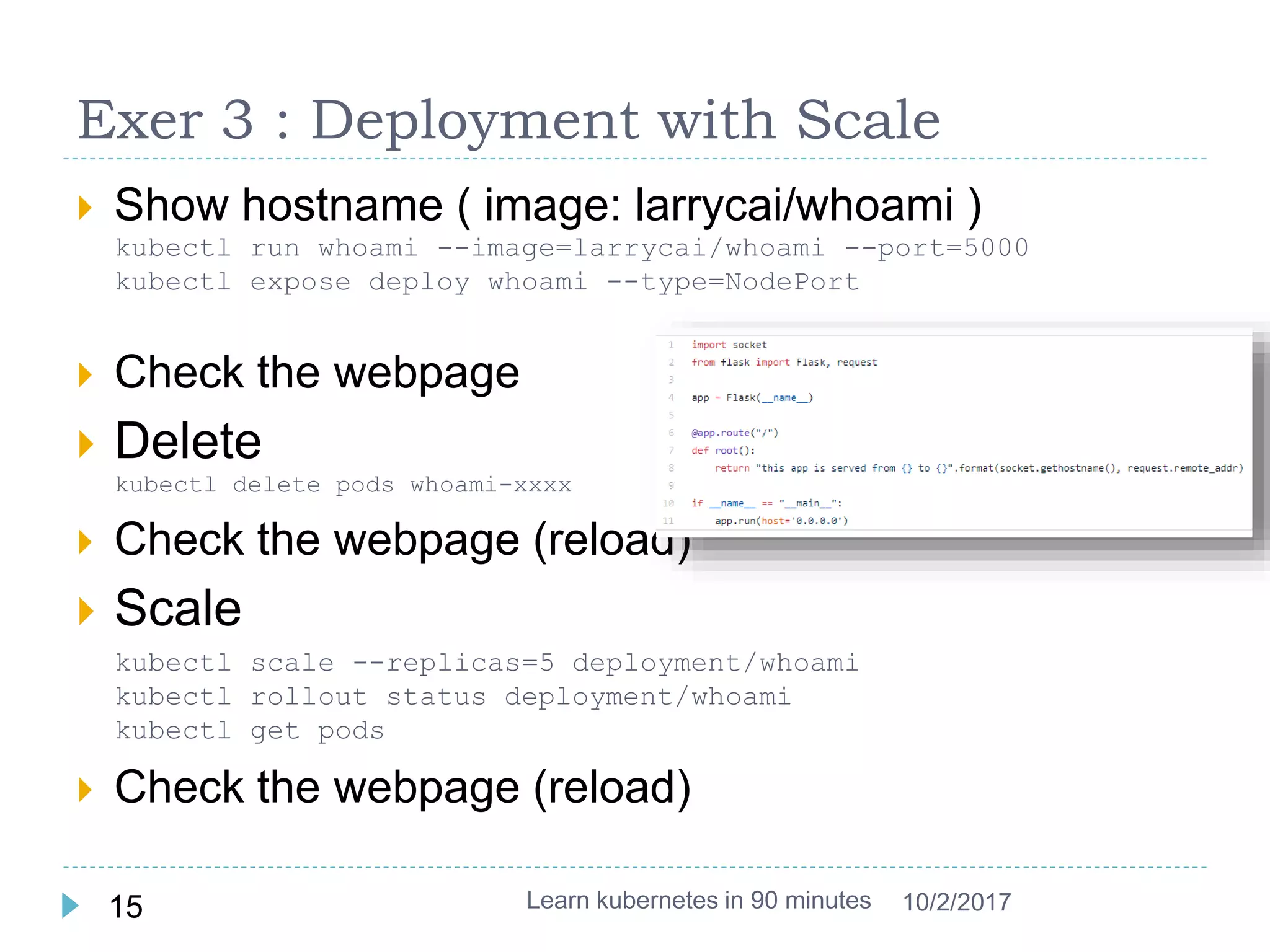
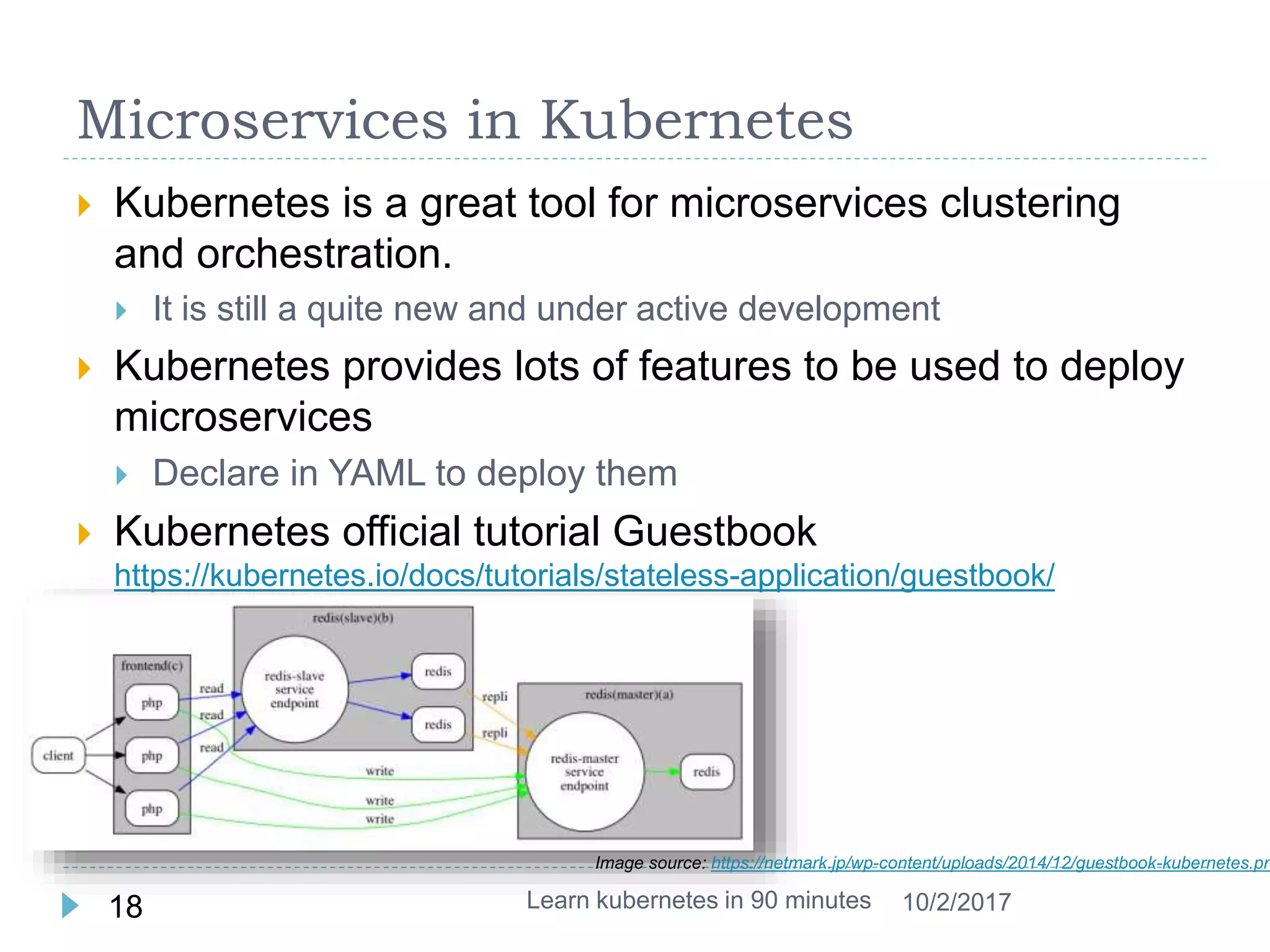
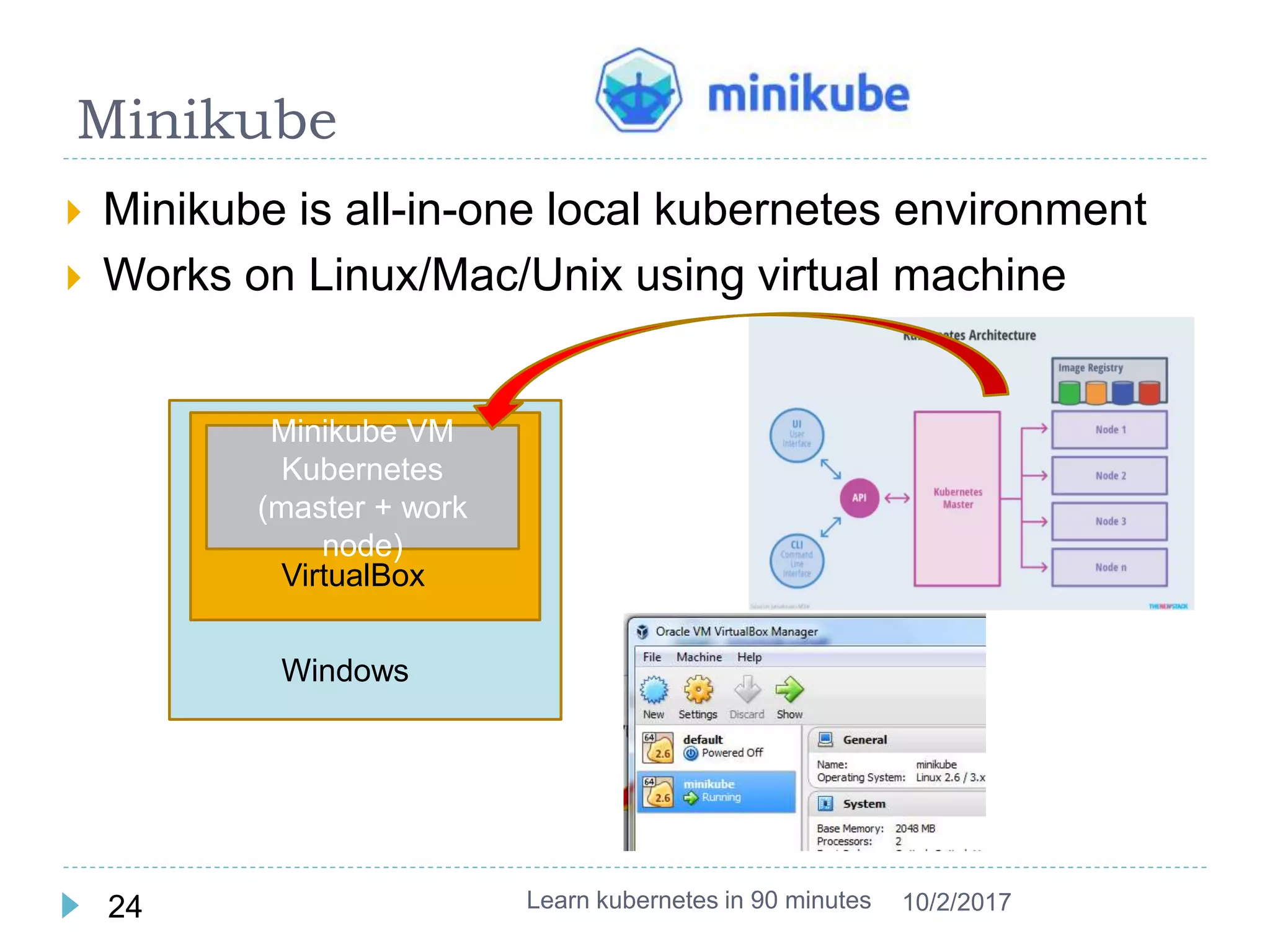
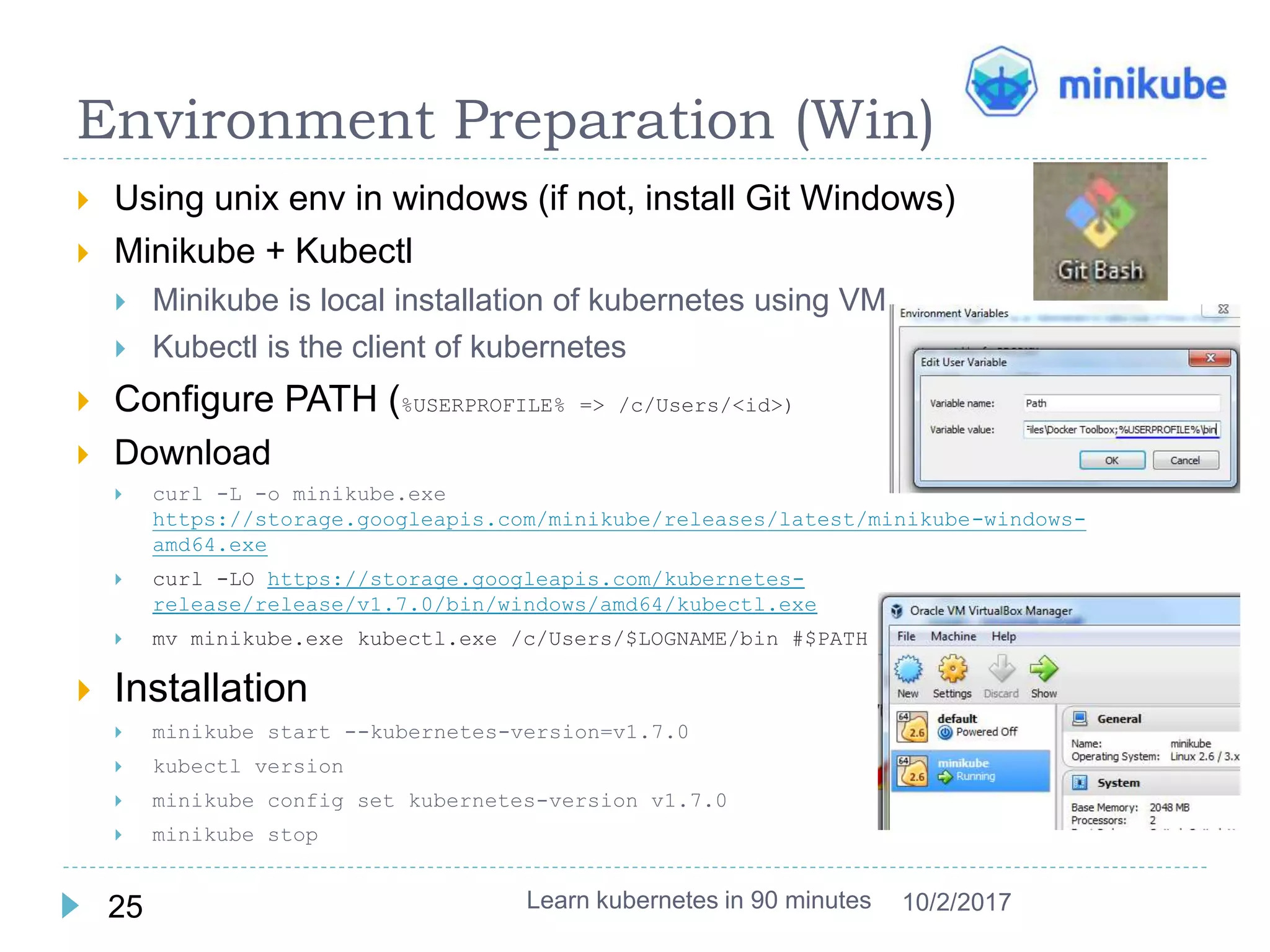
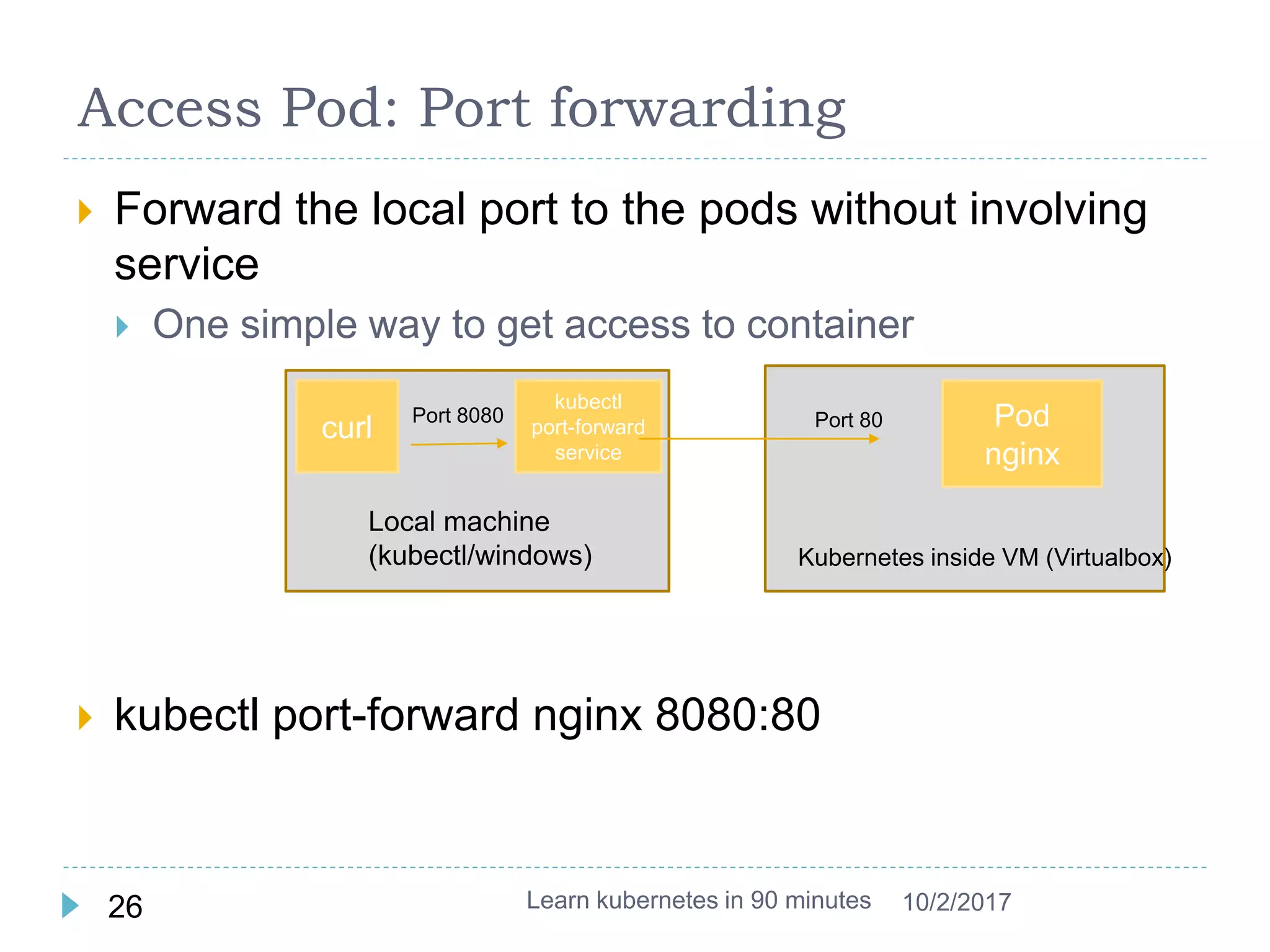
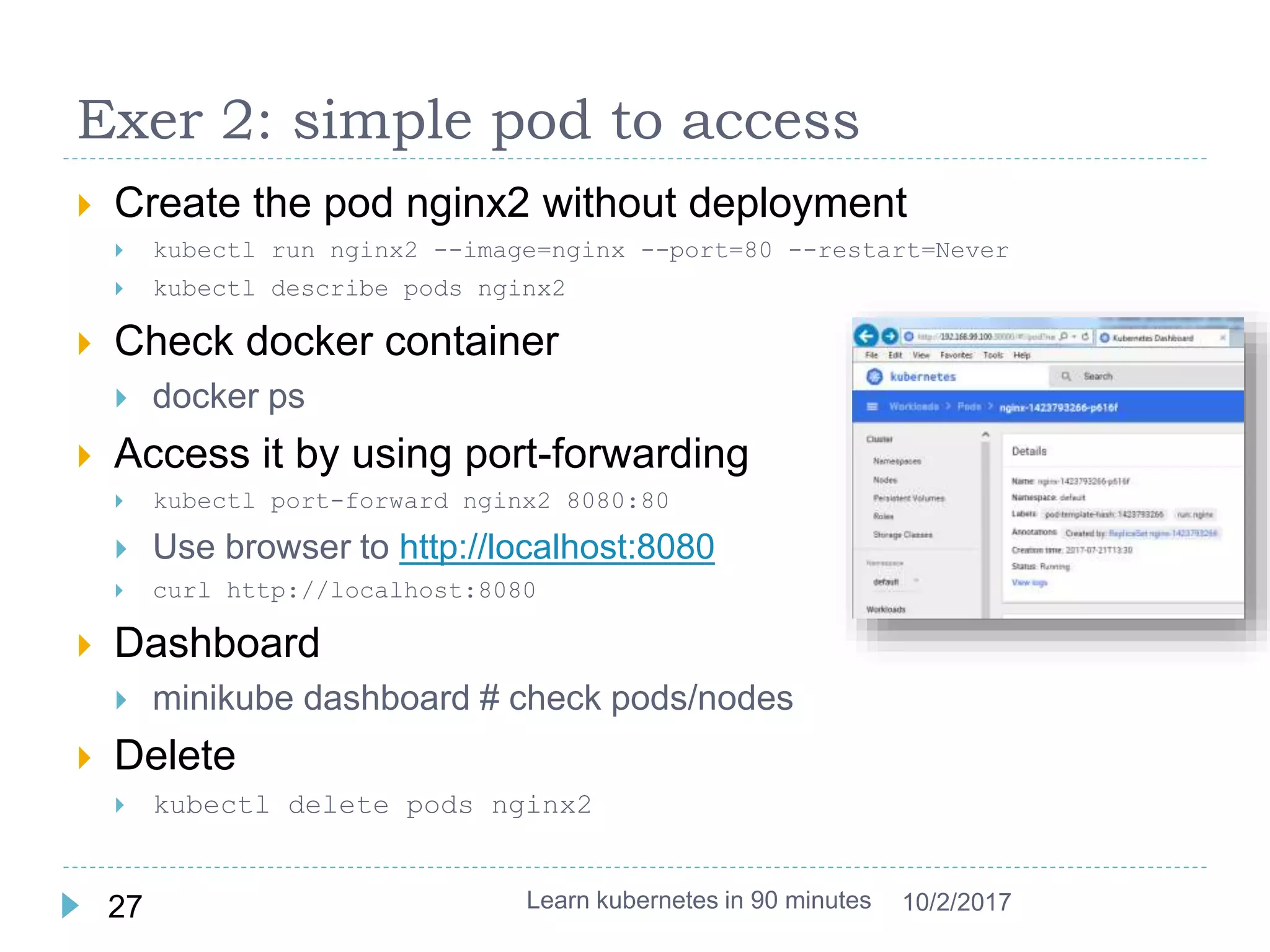
This document provides an agenda and instructions for learning Kubernetes in 90 minutes. The agenda includes exercises on running a first web service in Kubernetes, revisiting pods, deployments and services, deploying with YAML files, and installing a microservices application called Guestbook. Key Kubernetes concepts covered include pods, deployments, services, YAML descriptors, and using deployments to scale applications. The document also provides background on containers, Docker, and the Kubernetes architecture.