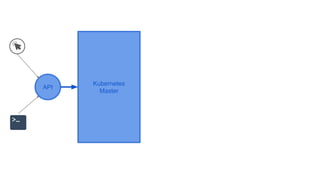
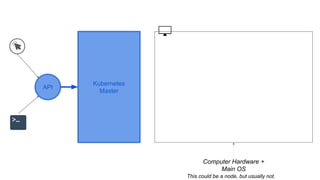
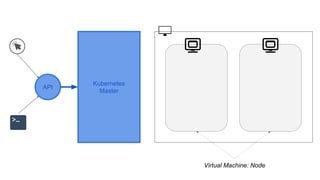
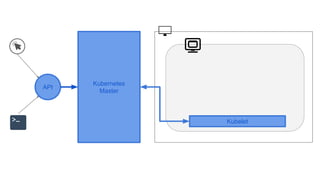
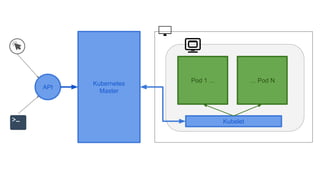
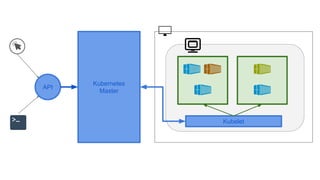
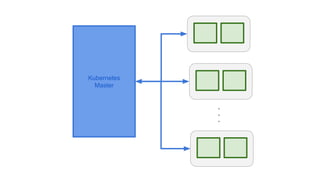
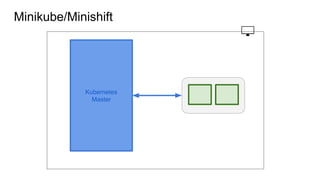
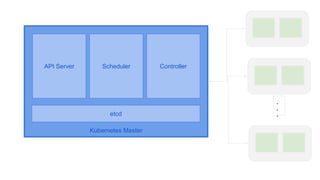
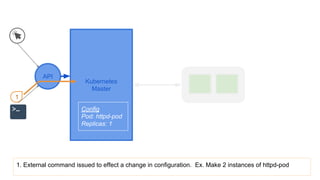
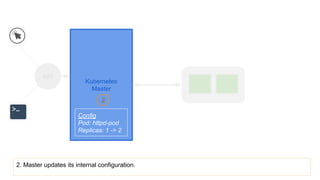
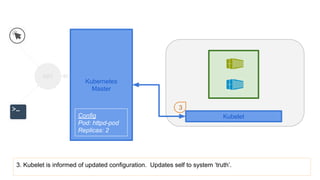
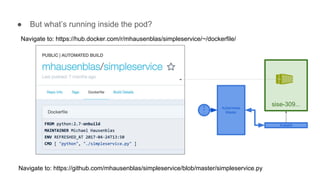
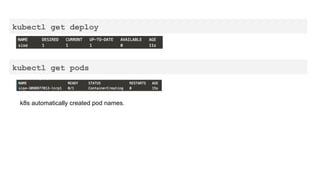
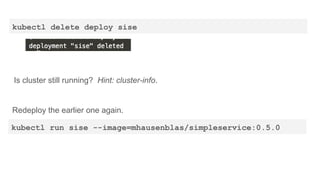
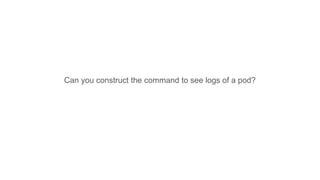
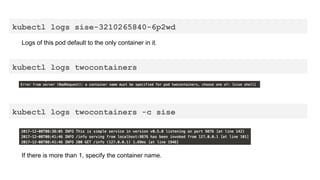
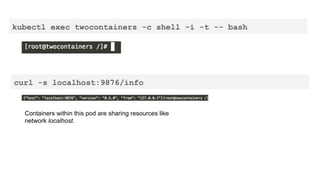
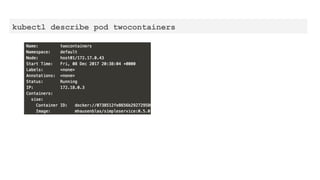
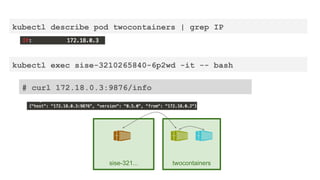
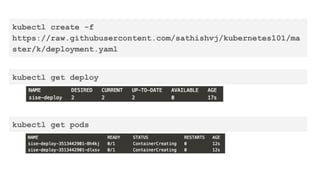
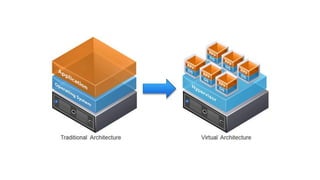
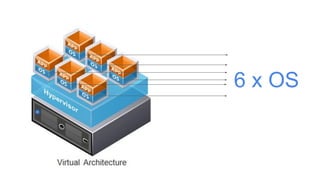
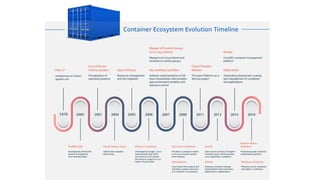
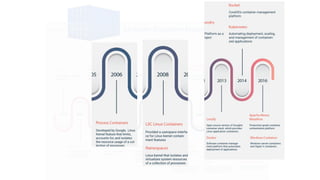
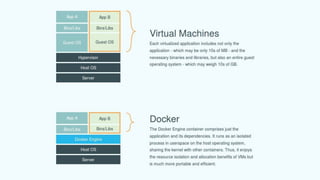
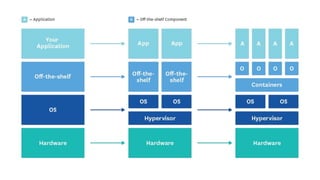
This document provides an overview of Docker and Kubernetes concepts and demonstrates how to create and run Docker containers and Kubernetes pods and deployments. It begins with an introduction to virtual machines and containers before demonstrating how to build a Docker image and container. It then introduces Kubernetes concepts like masters, nodes, pods and deployments. The document walks through running example containers and pods using commands like docker run, kubectl run, kubectl get and kubectl delete. It also shows how to create pods and deployments from configuration files and set resource limits.











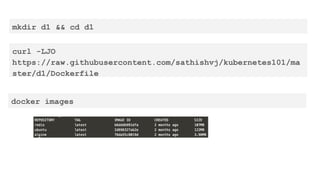
![FROM ubuntu:latest
MAINTAINER me@email.com v0.1
RUN apt-get update
&& apt-get install -y nginx
COPY nginx.conf /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
EXPOSE 80
CMD ["nginx", "-g", "daemon off;"]
filename: Dockerfile
Use the latest version of ubuntu as the base image.
You could add this note on who created/maintains the image.
Add this local file(s)/dir to the image. E.g. data, config files.
Run these commands in the image. E.g. software installs.
Allow port 80 to be accessed when the image is run.
Execute this command.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kubernetes101workshop-180311151007/85/Docker-and-Kubernetes-101-workshop-18-320.jpg)