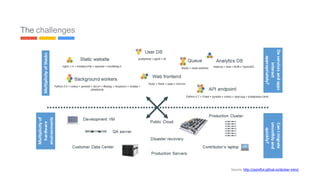
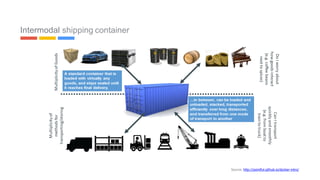
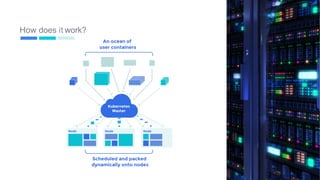
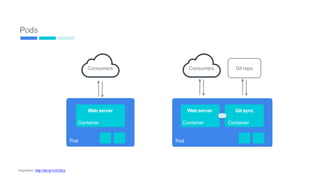
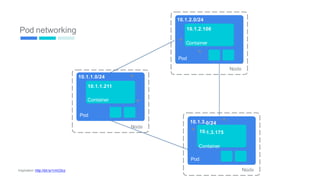
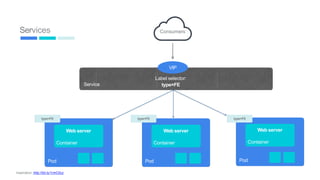
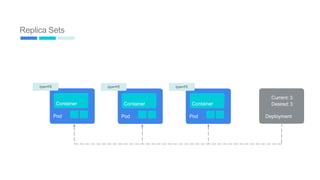
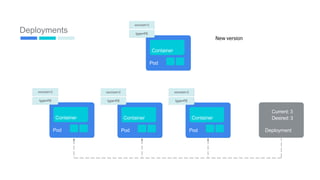
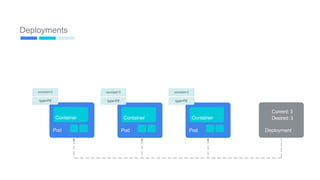
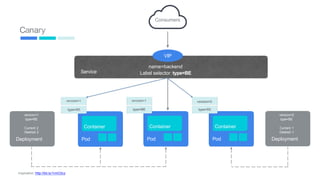
This document provides an introduction to Kubernetes, including definitions of key concepts like pods, services, labels, replica sets, deployments, and horizontal pod autoscaling. It explains how Kubernetes abstracts and virtualizes resources to run and manage containers across a cluster. Examples and diagrams illustrate concepts like pod networking and canary deployments. The document recommends resources for learning more about Kubernetes and getting started, including Google Cloud Platform and a demo of Kubernetes capabilities.













![resilience
or resiliency
[ri-zil-yuh ns, -zil-ee-uh ns]
noun
2.
1. the power or ability to return to the original form, position, etc., after being bent,
compressed, or stretched: elasticity.
ability to recover readily from illness, depression, adversity, or the like; buoyancy
Source: http://www.dictionary.com/browse/resilience
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/understandingkubernetes-170317090737/85/Understanding-Kubernetes-14-320.jpg)