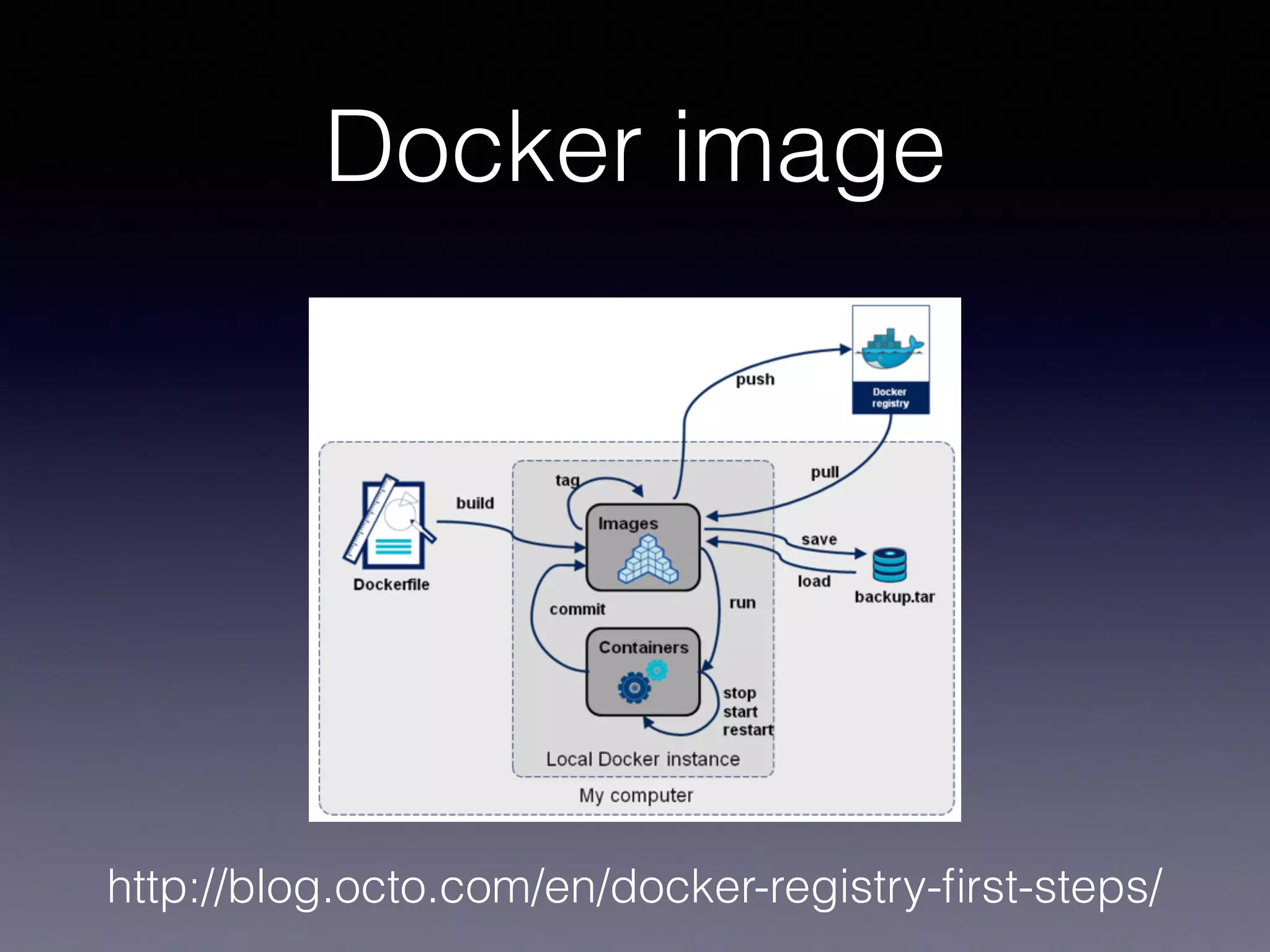
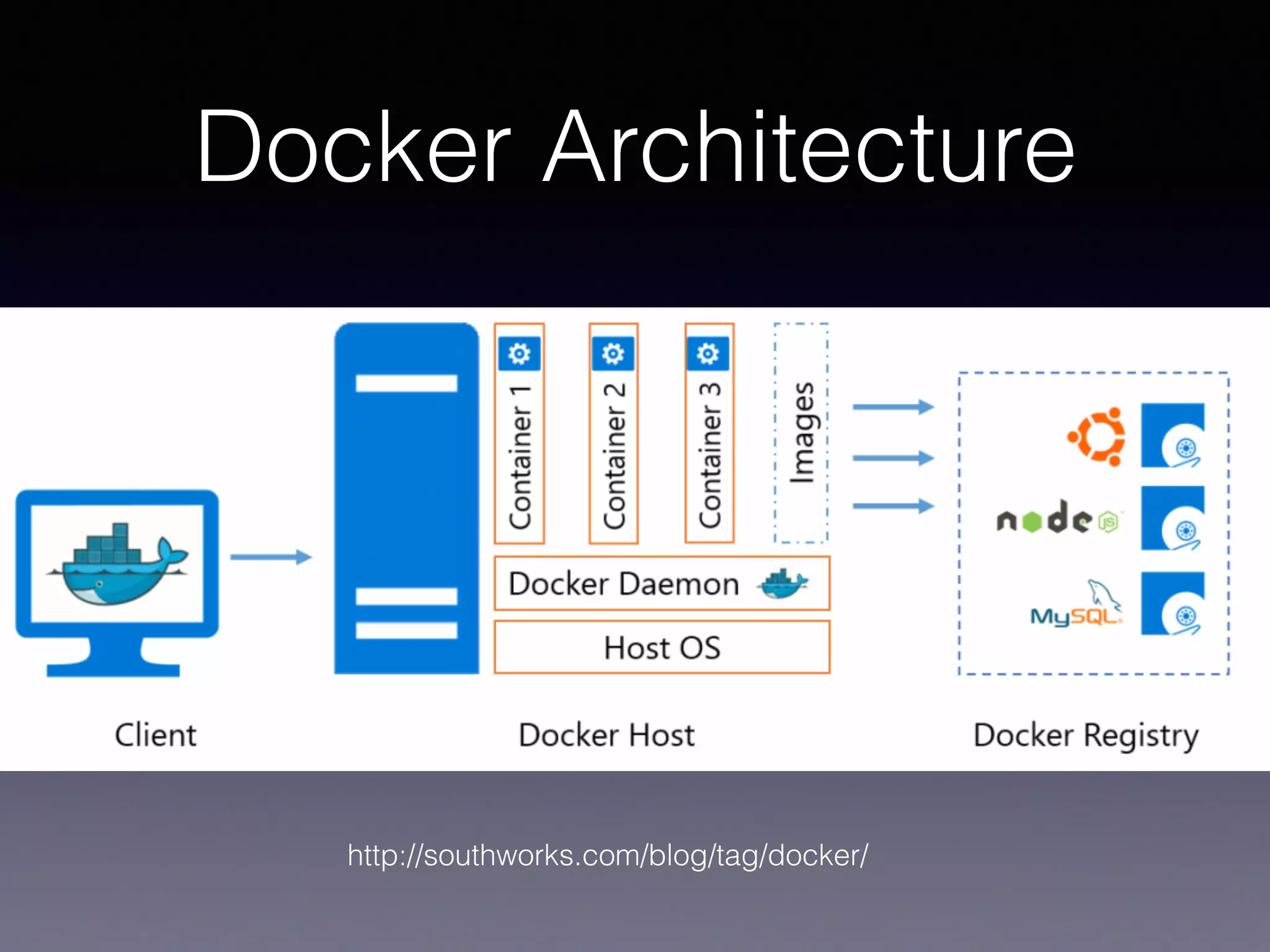
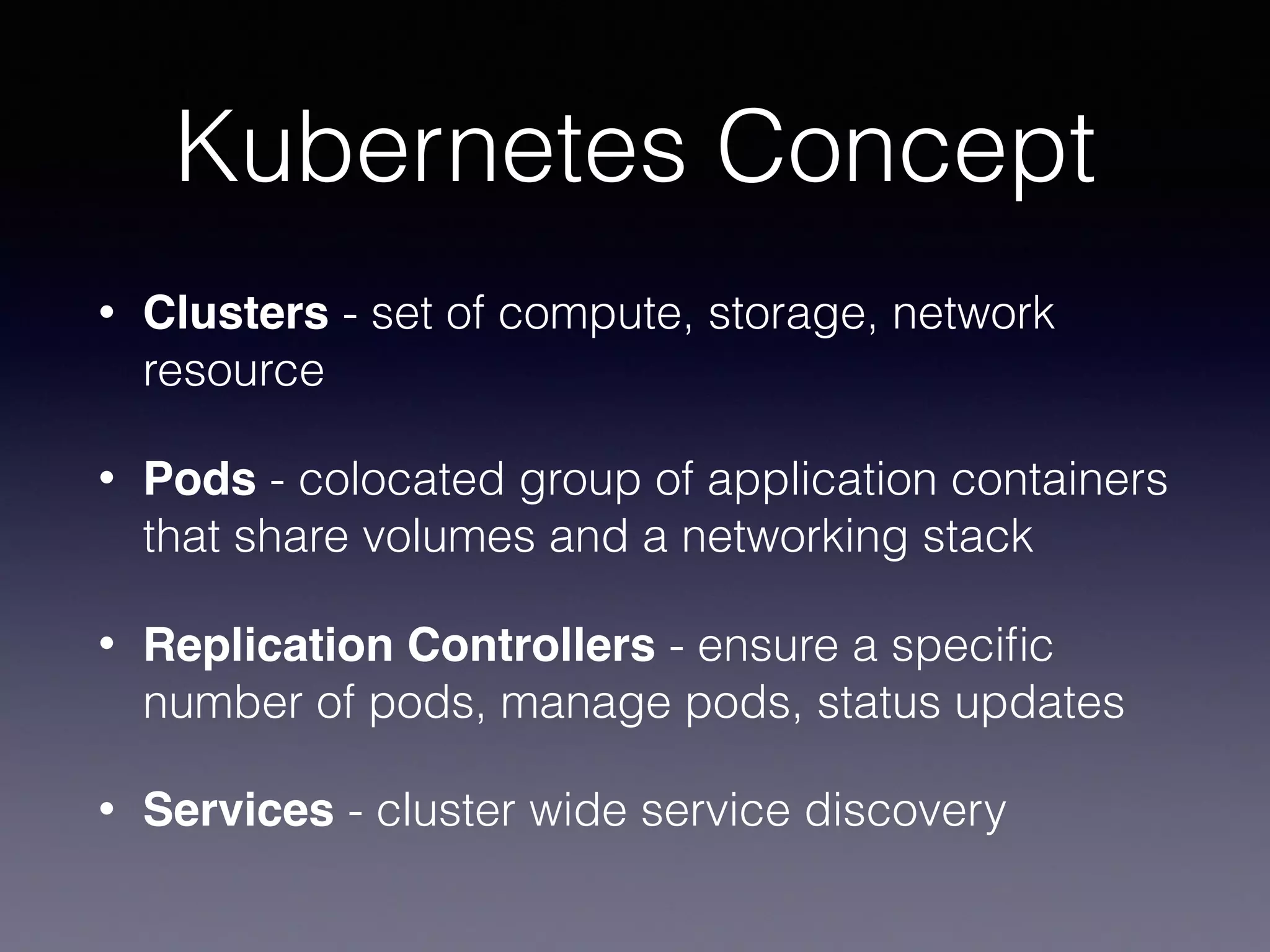
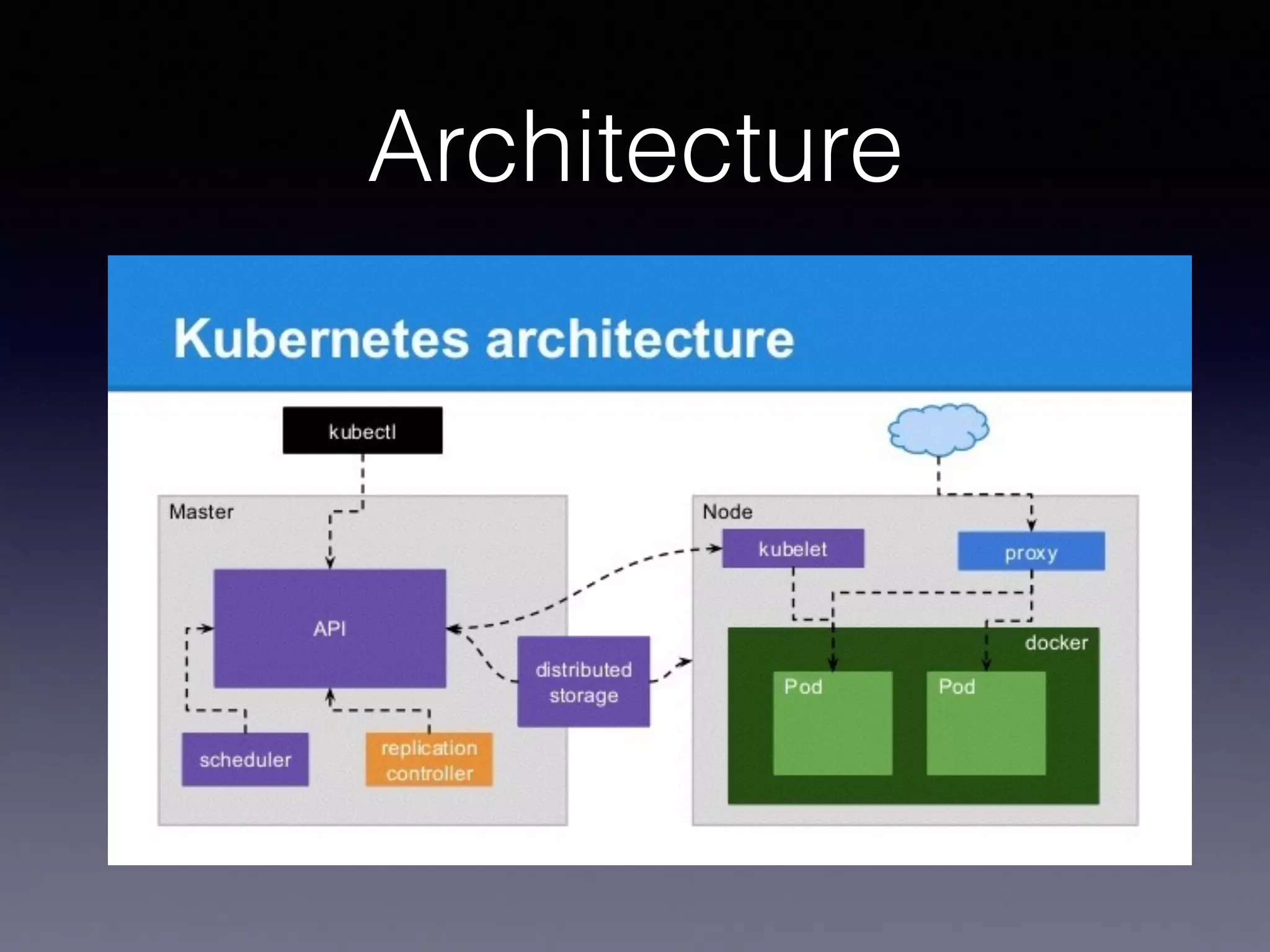
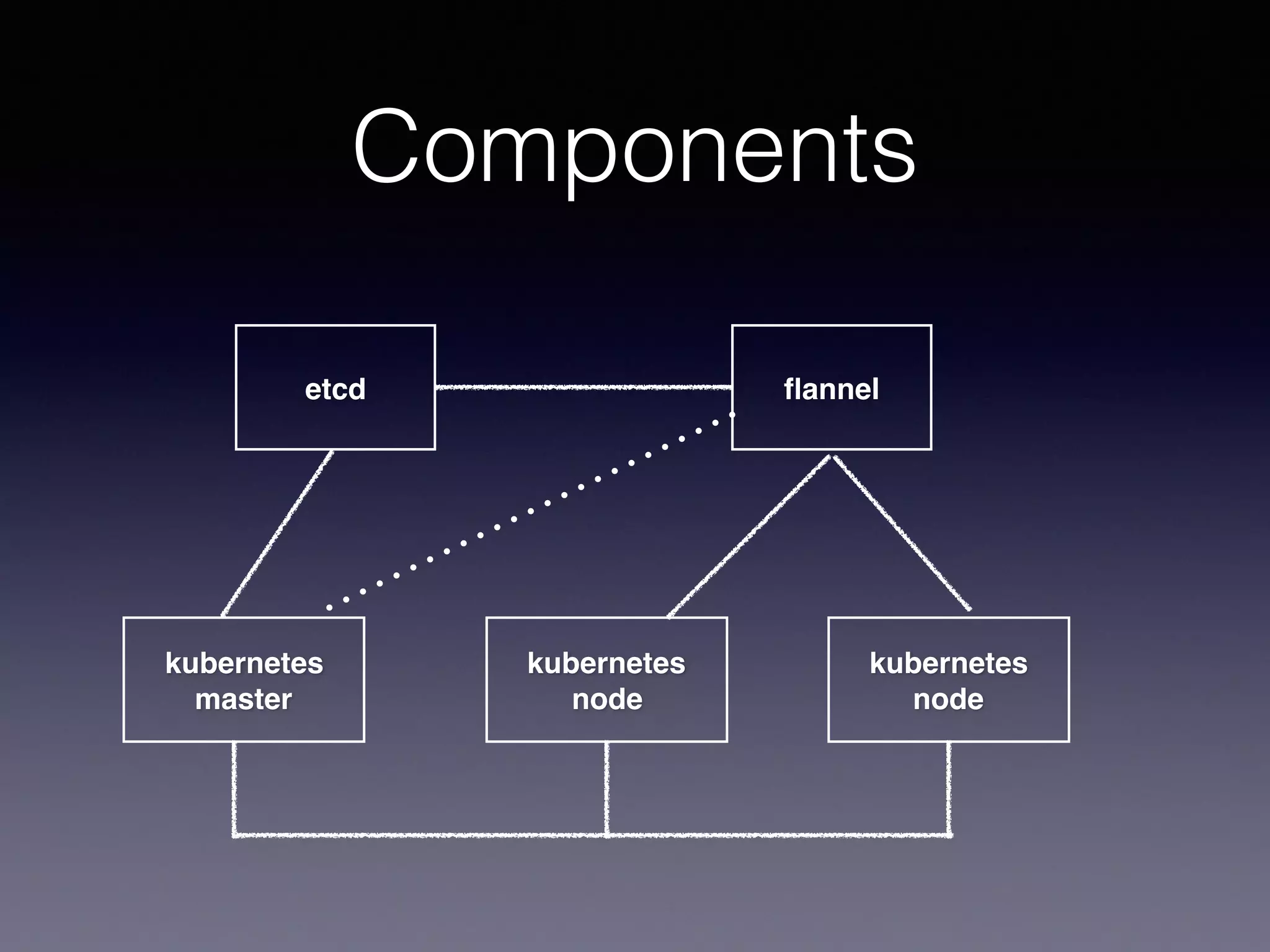
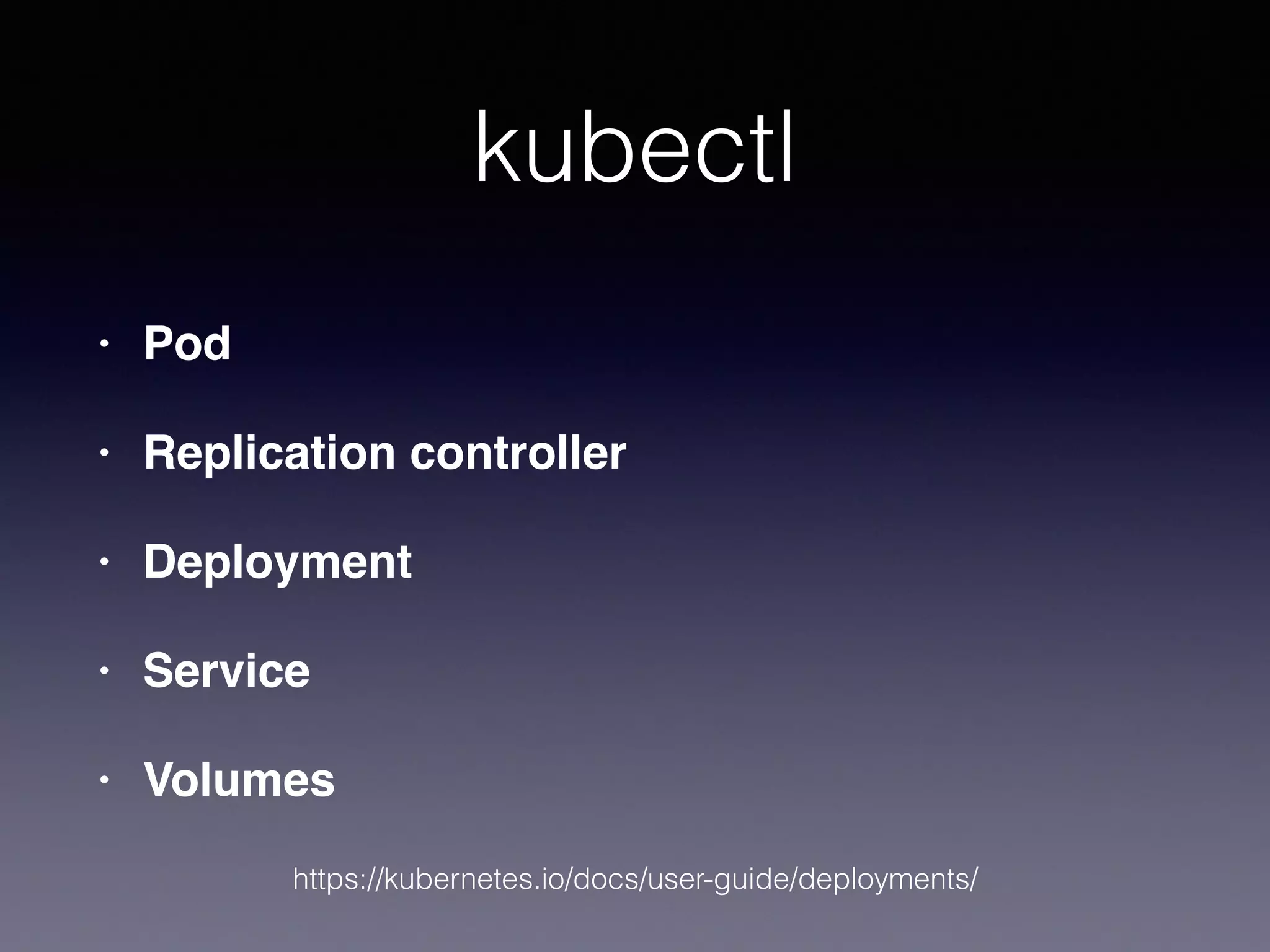
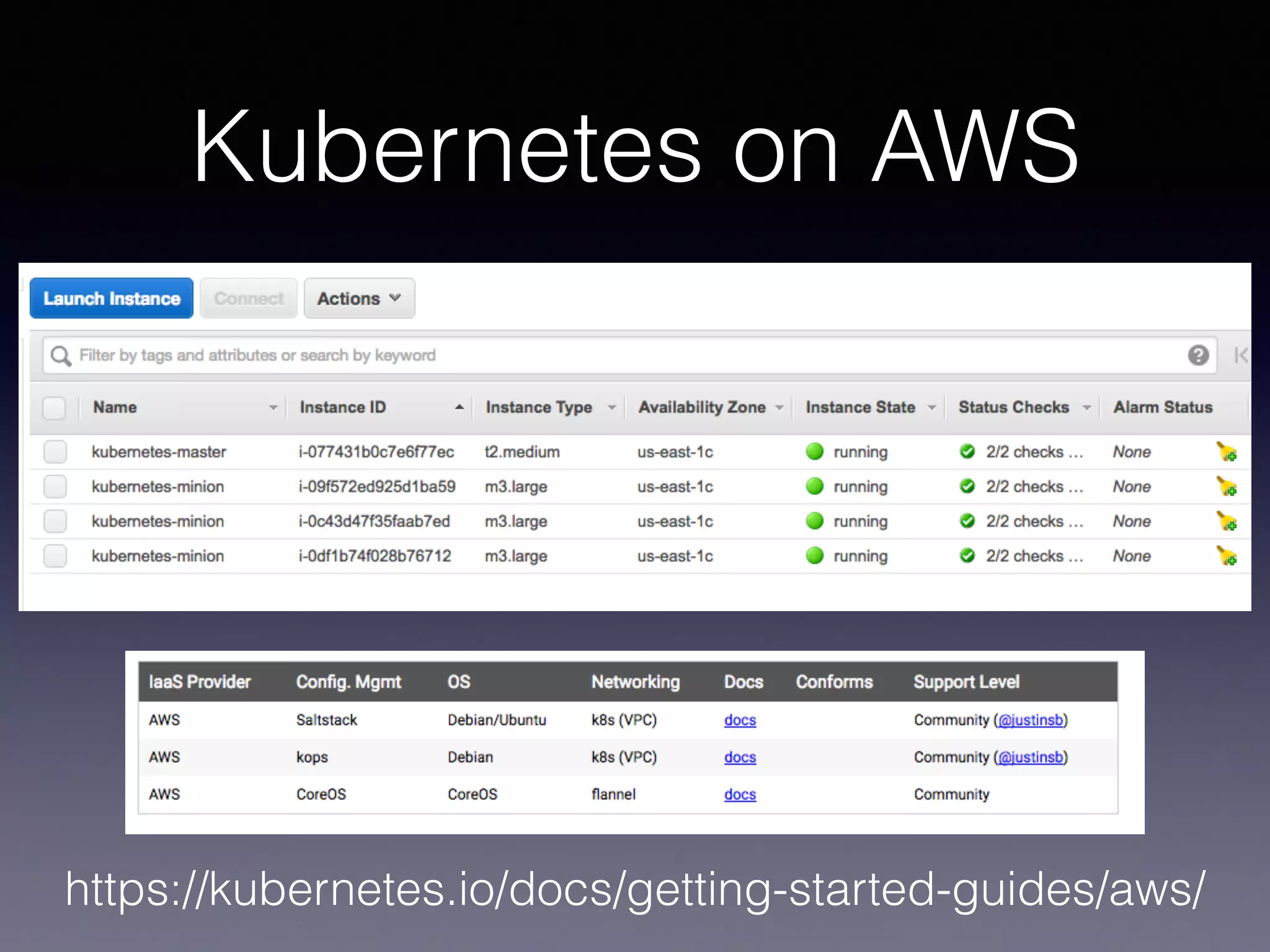
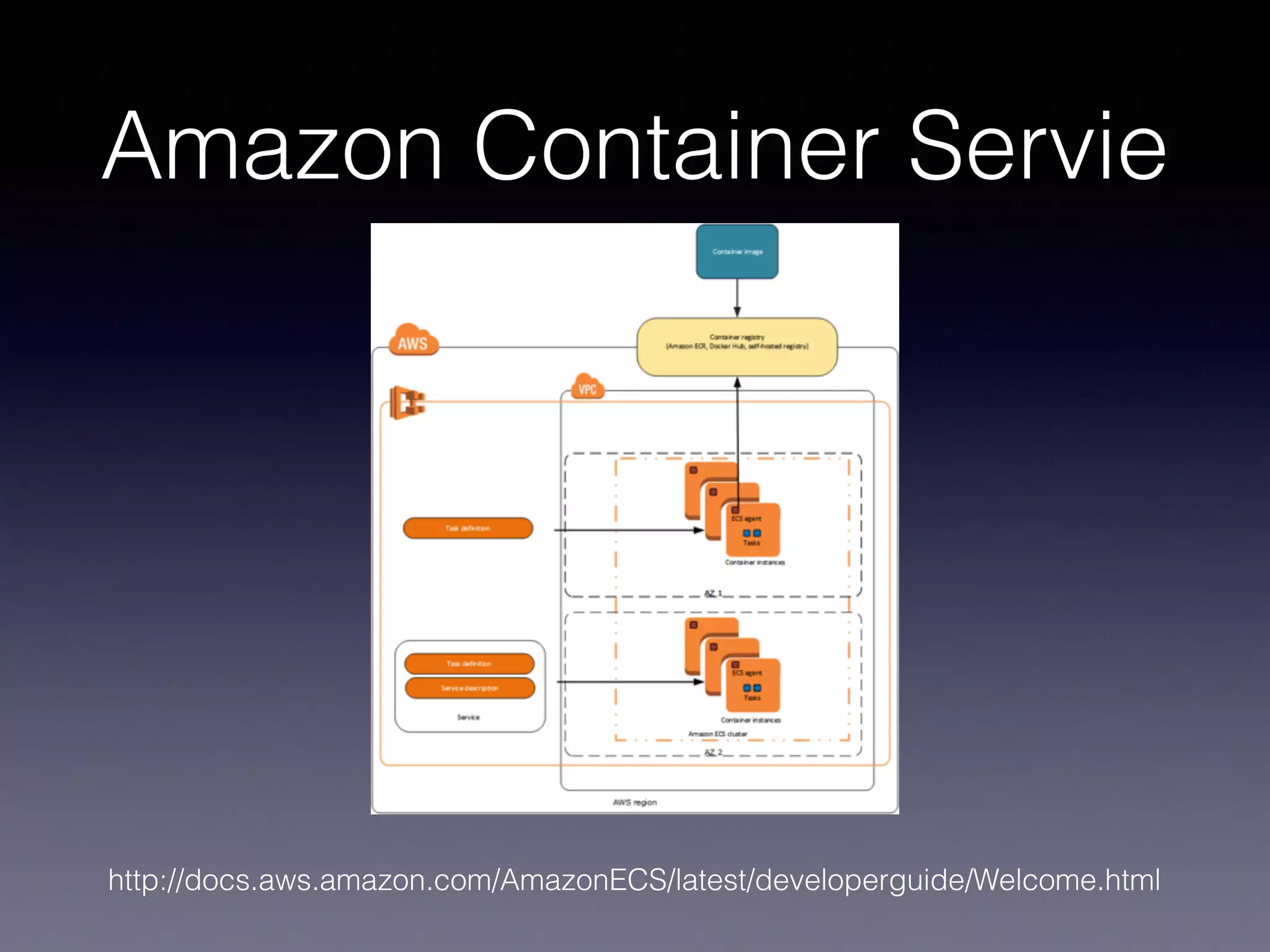
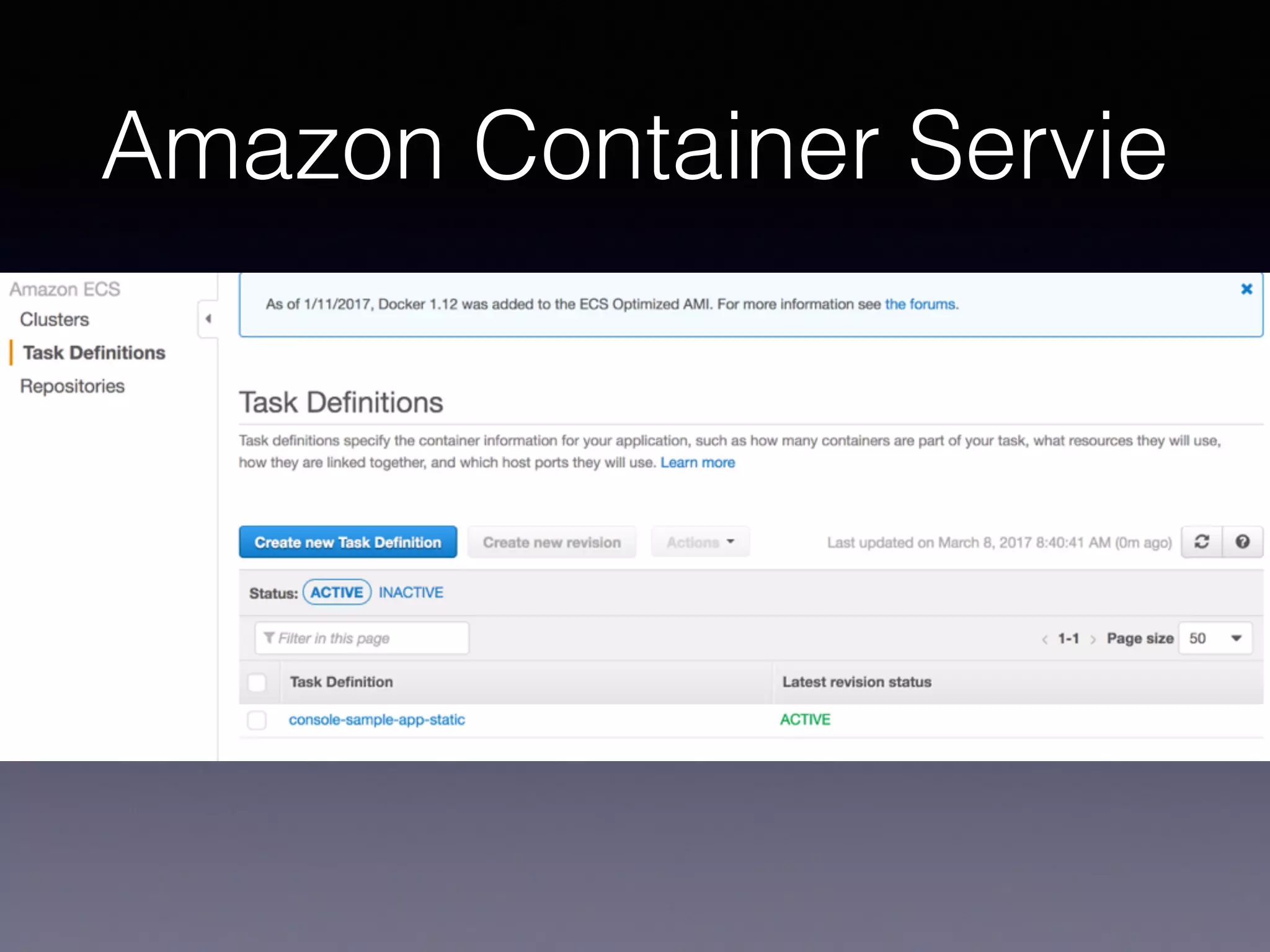
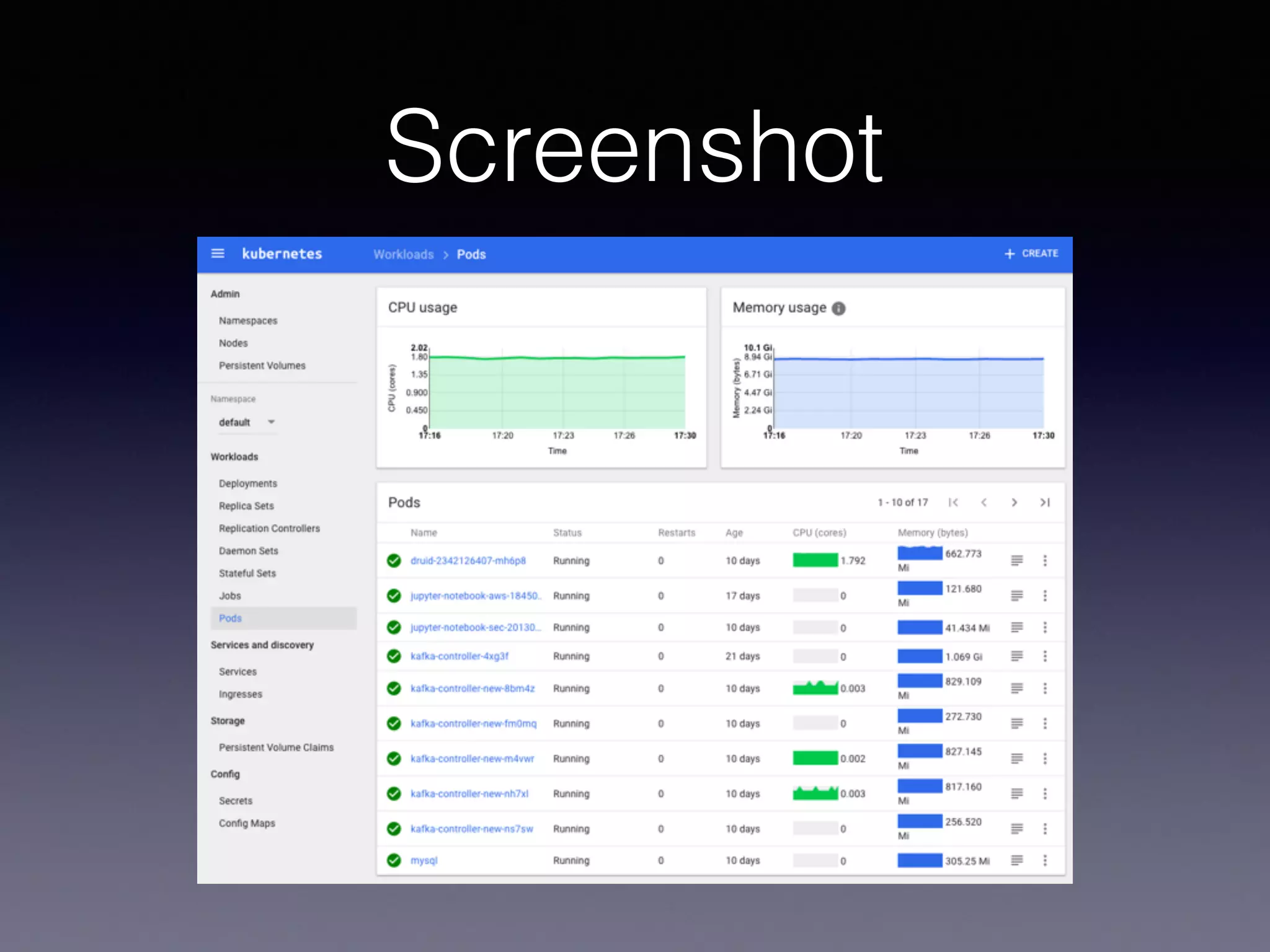
Kubernetes on AWS allows users to deploy and manage Kubernetes clusters on the AWS cloud infrastructure. It provides tools to create clusters across multiple AWS availability zones for high availability. Users can define Kubernetes objects like pods, services, deployments etc using kubectl and utilize AWS services like EBS volumes for persistent storage. The presentation demonstrated setting up a Kubernetes cluster on AWS using kube-up.sh along with examples of using EBS volumes in pods through persistent volume claims. It also showed monitoring and managing applications running on the Kubernetes cluster deployed on AWS.