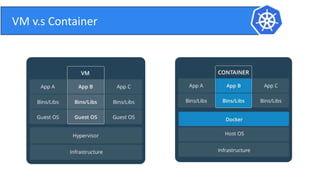
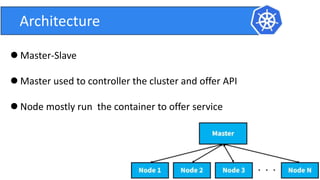
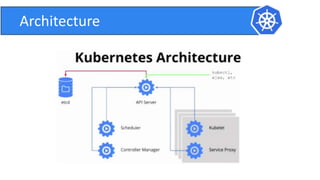
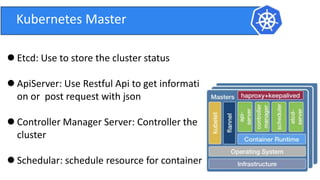
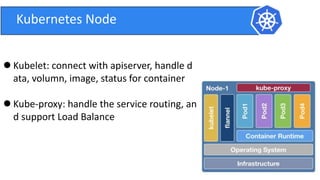
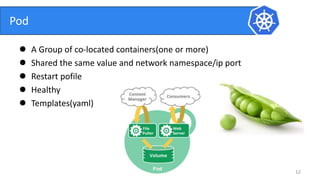
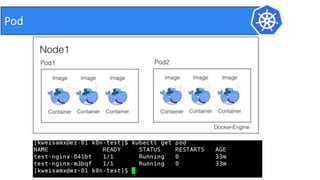
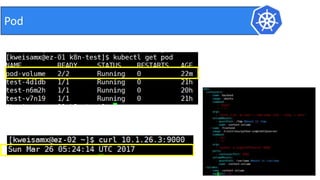
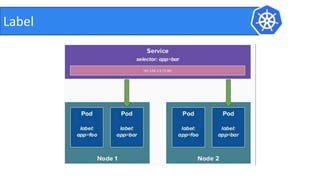
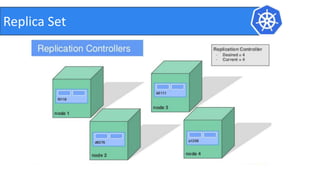
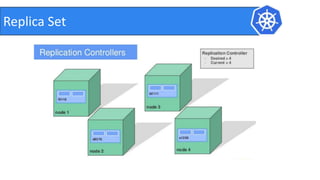
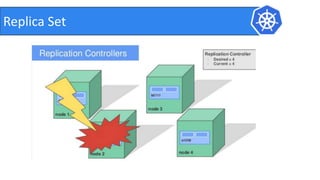
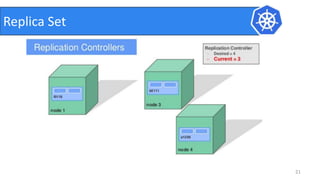
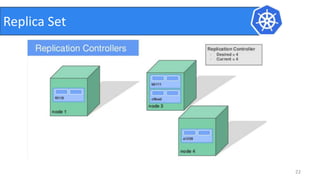
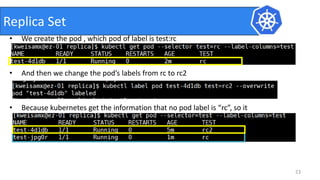
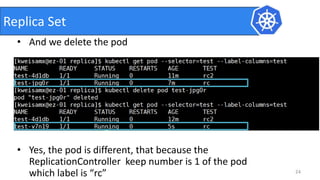
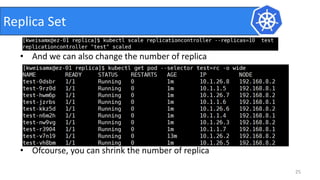
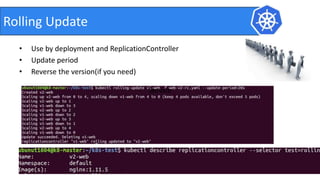
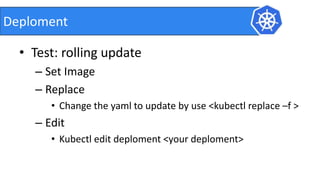
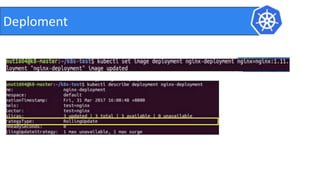
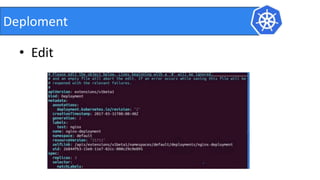
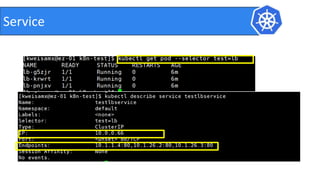
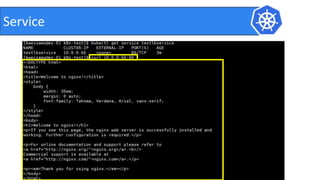
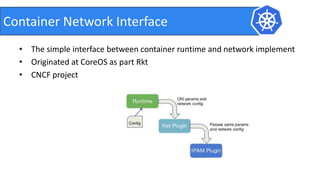
This document provides an introduction to Kubernetes and Container Network Interface (CNI). It begins with an introduction to the presenter and their background. It then discusses the differences between VMs and containers before explaining why Kubernetes is needed for container orchestration. The rest of the document details the architecture of Kubernetes, including the master node, worker nodes, pods, labels, replica sets, deployments, services, and how to build a Kubernetes cluster. It concludes with a brief introduction to CNI and a call for questions.