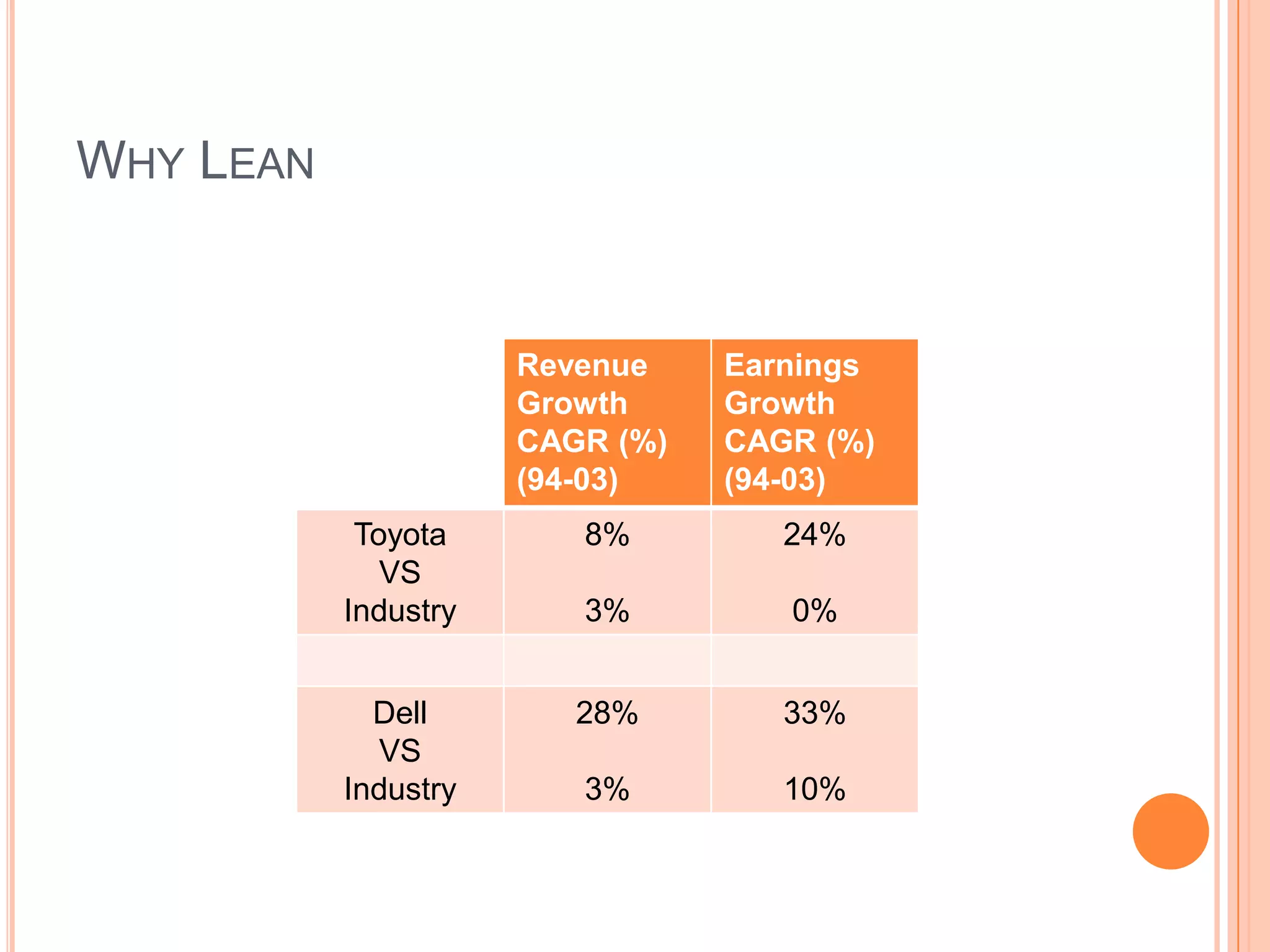
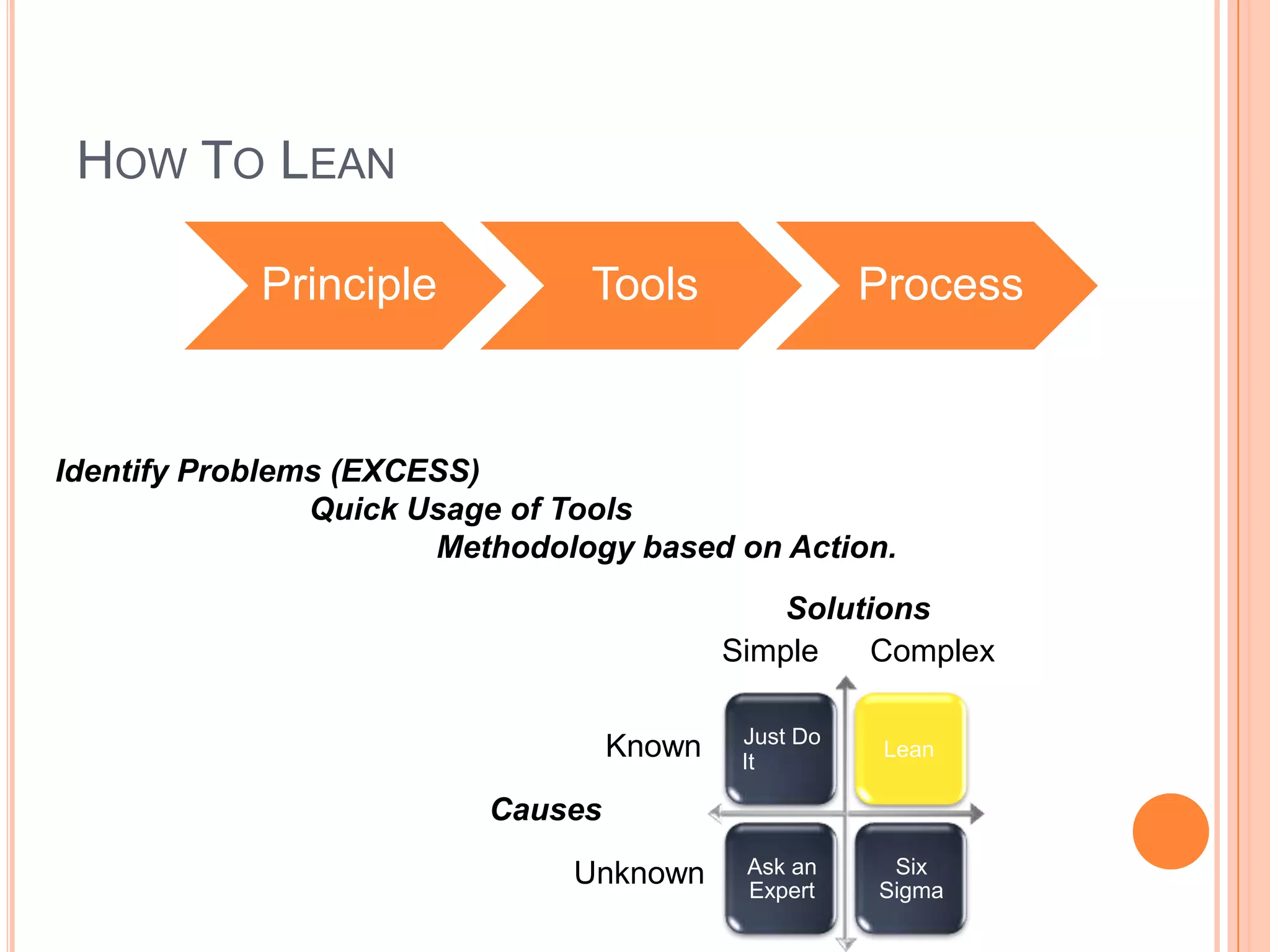
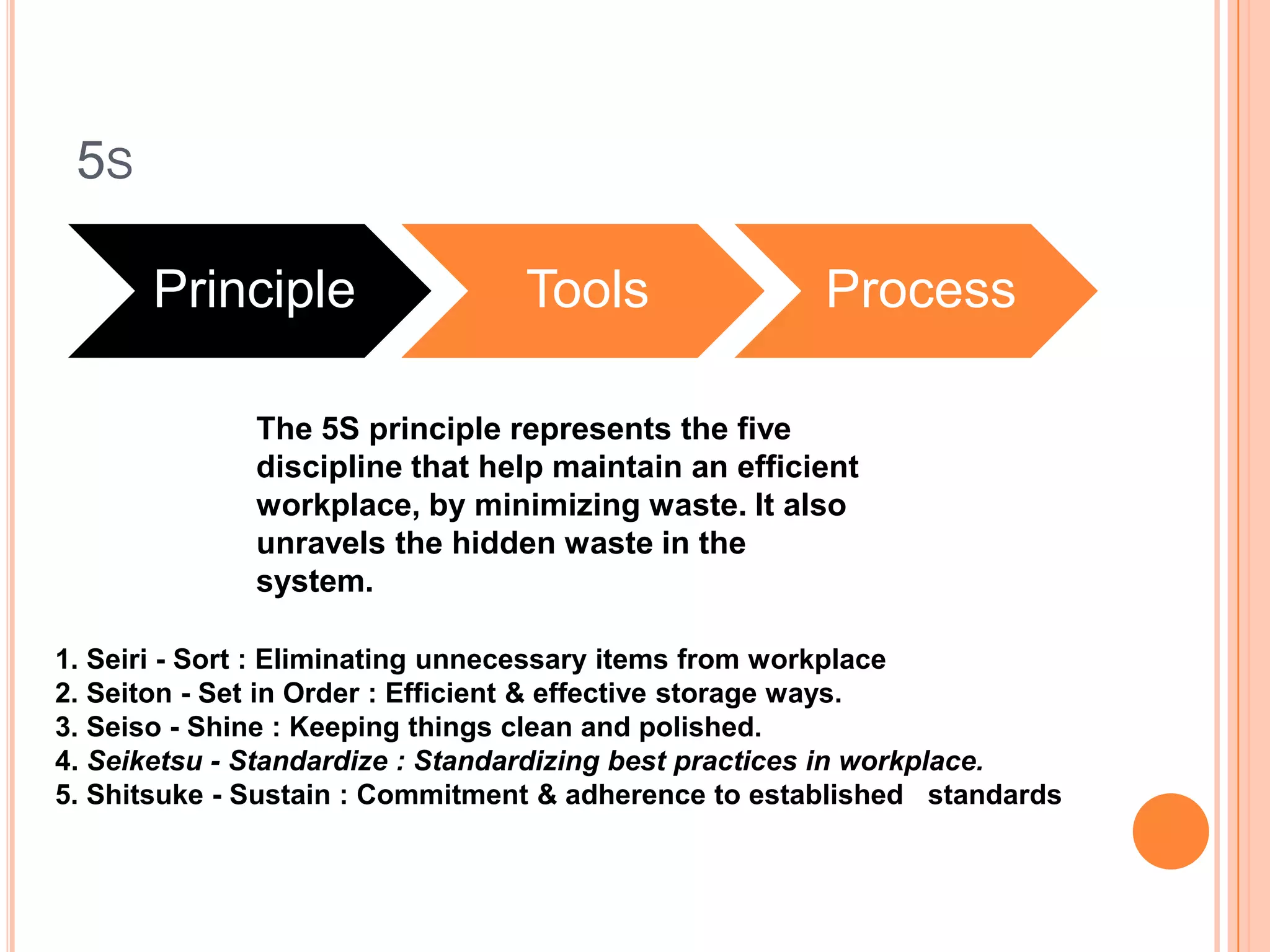
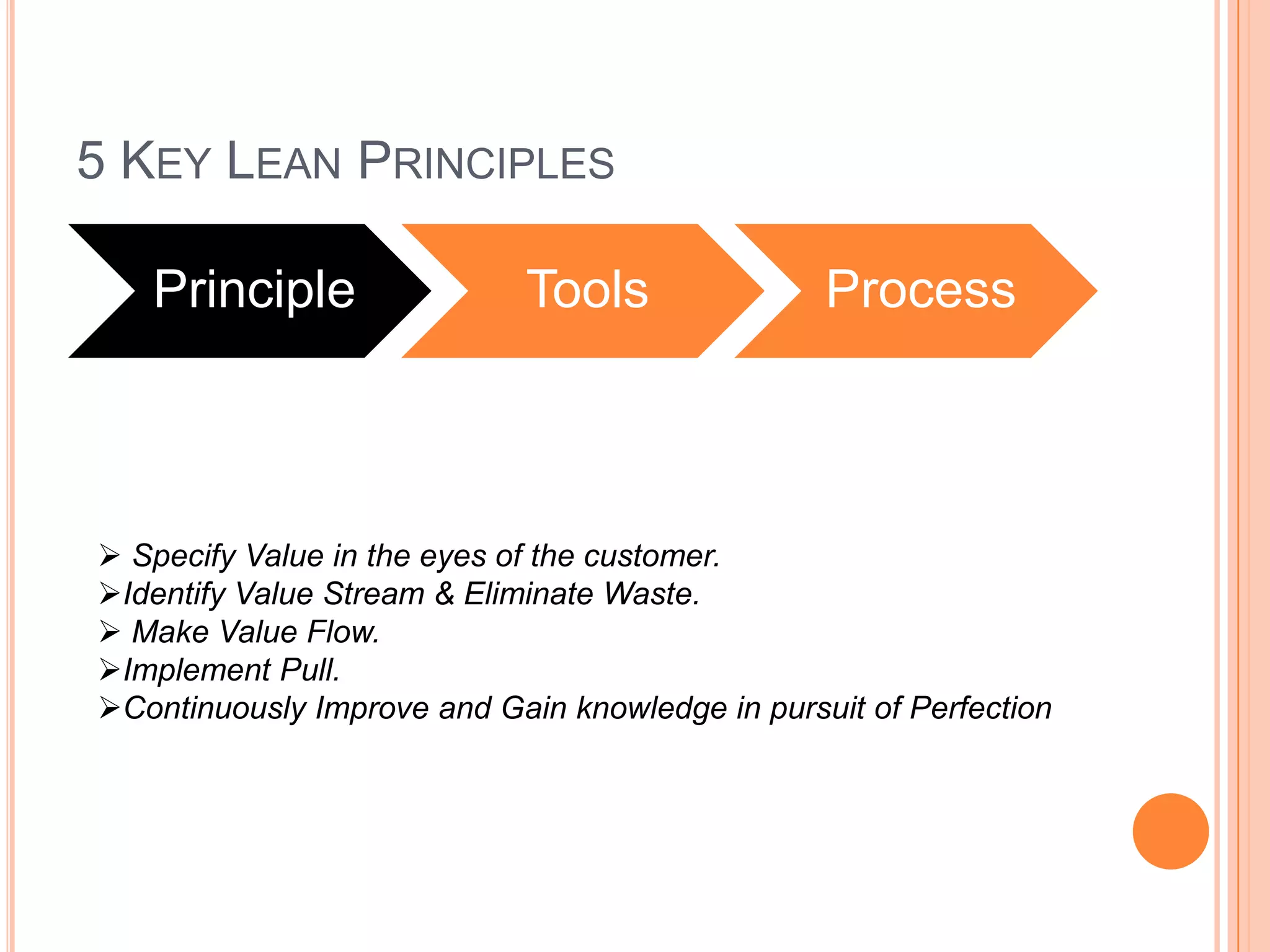
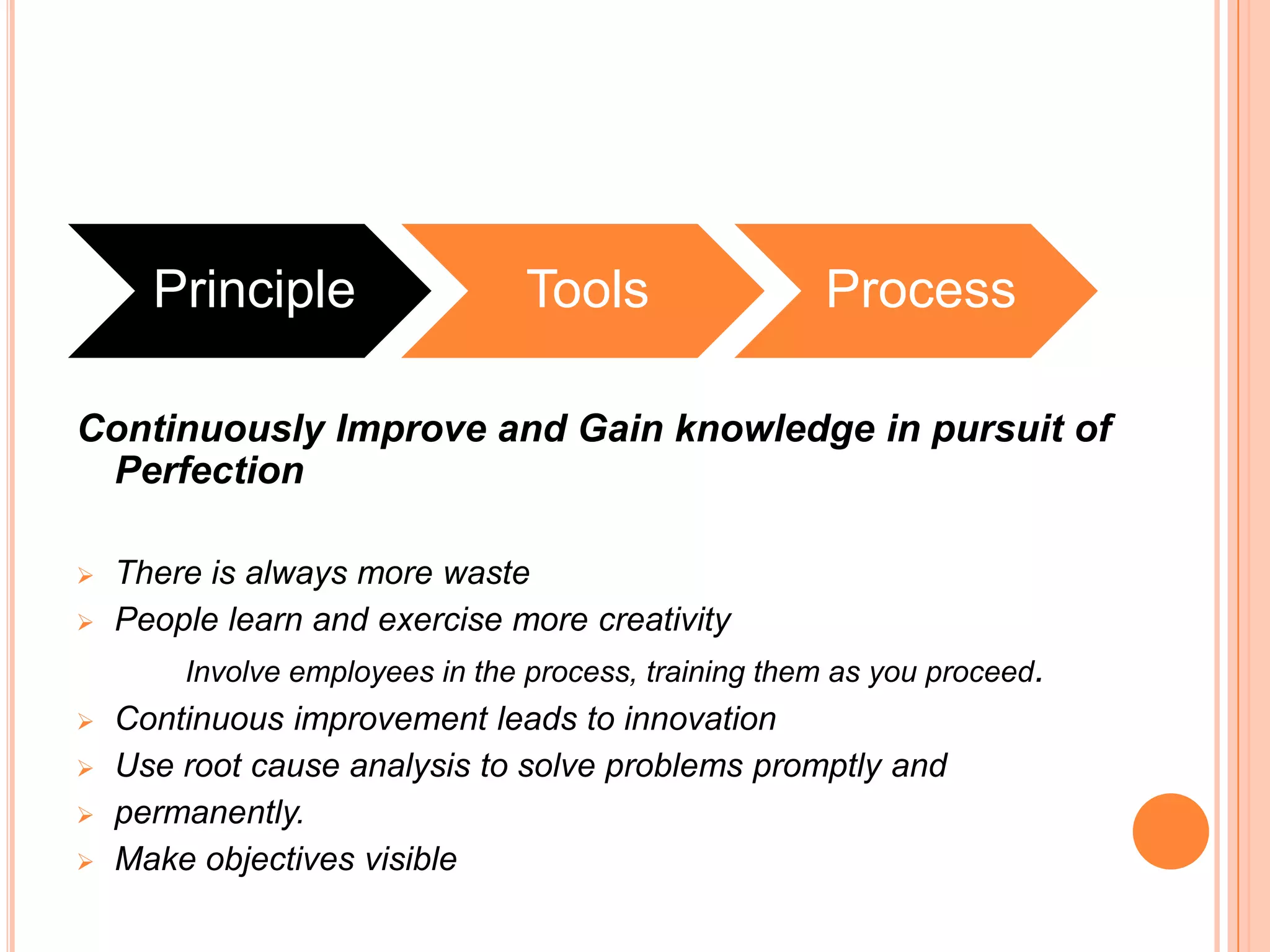
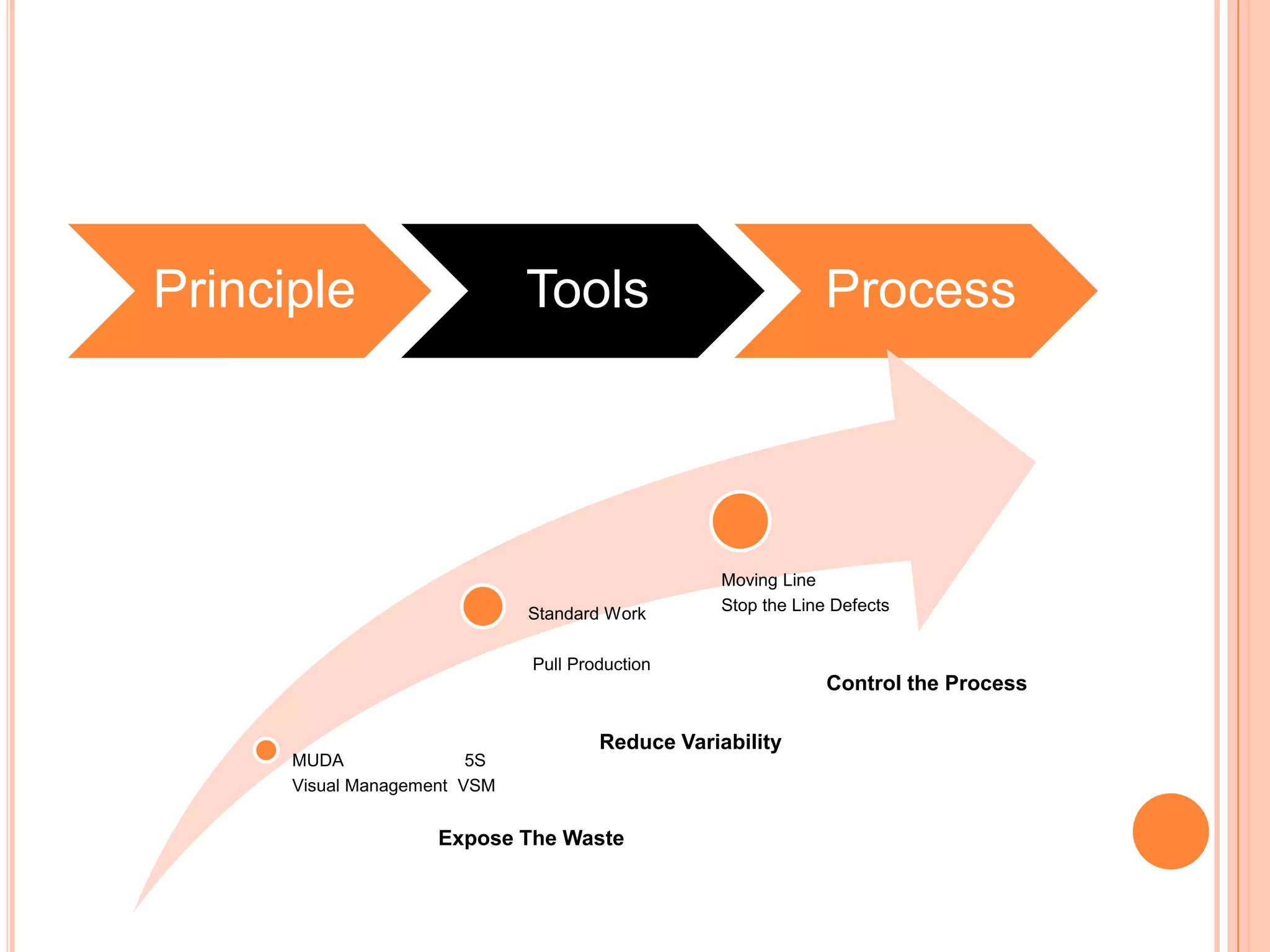
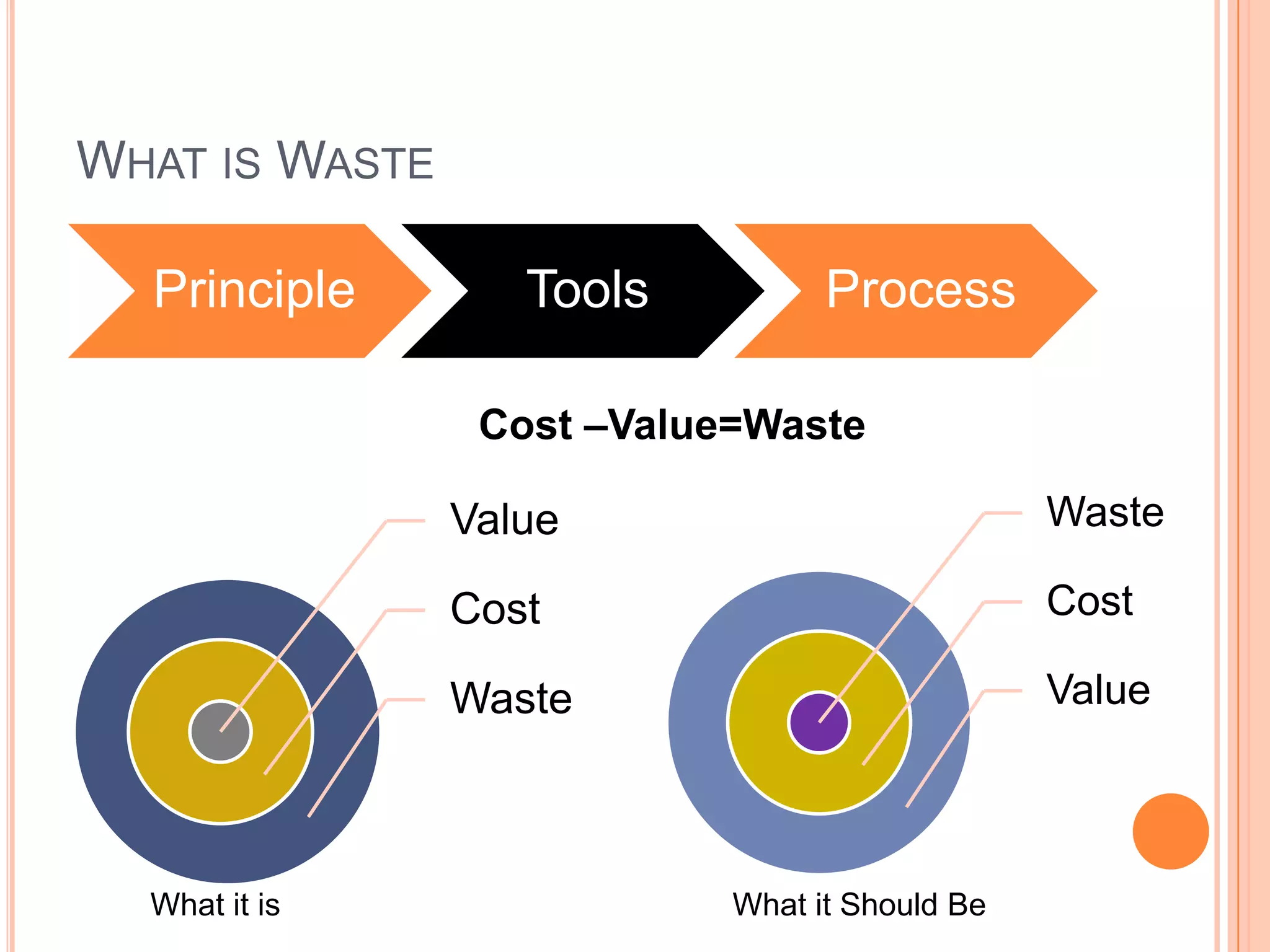
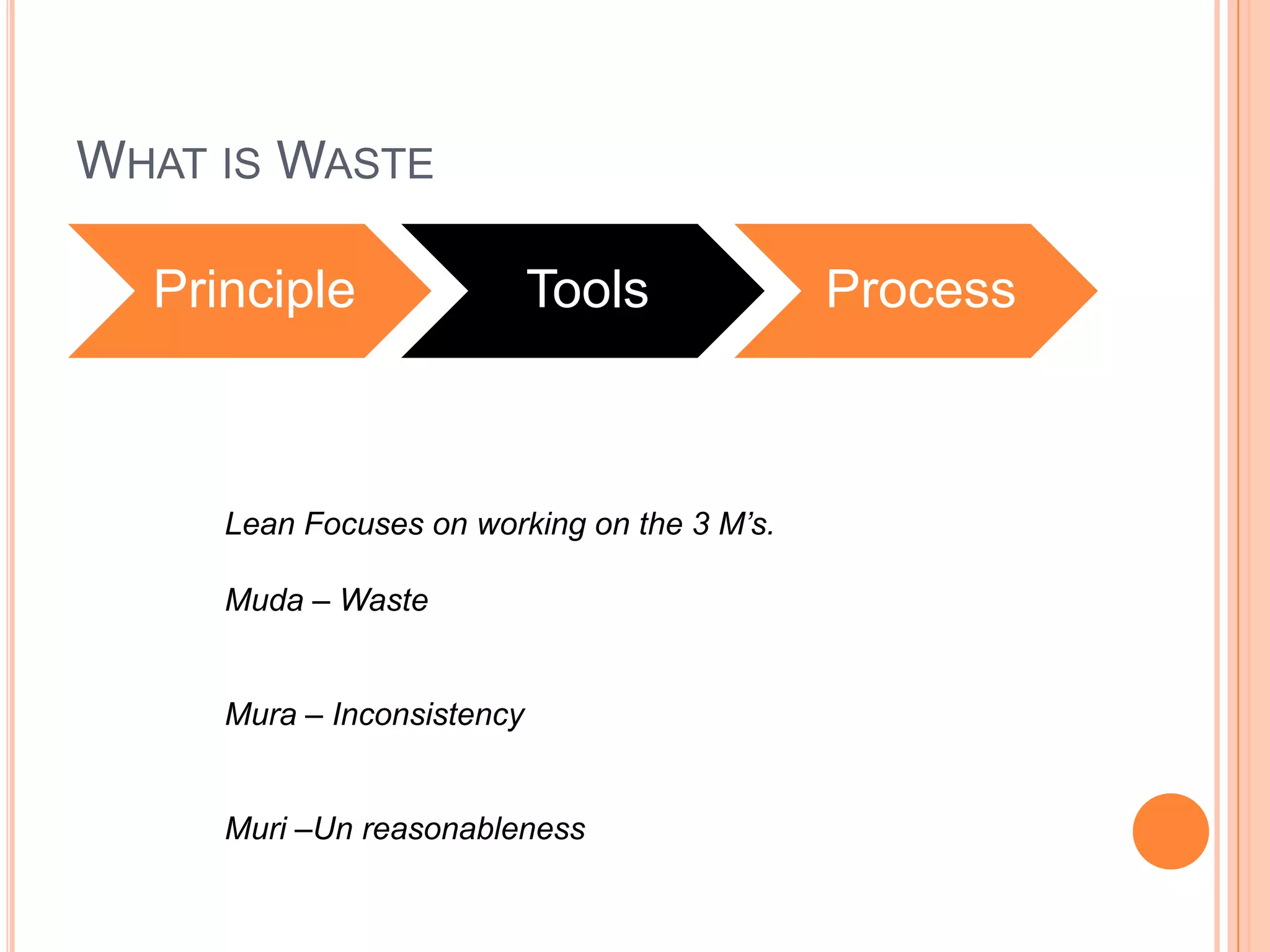
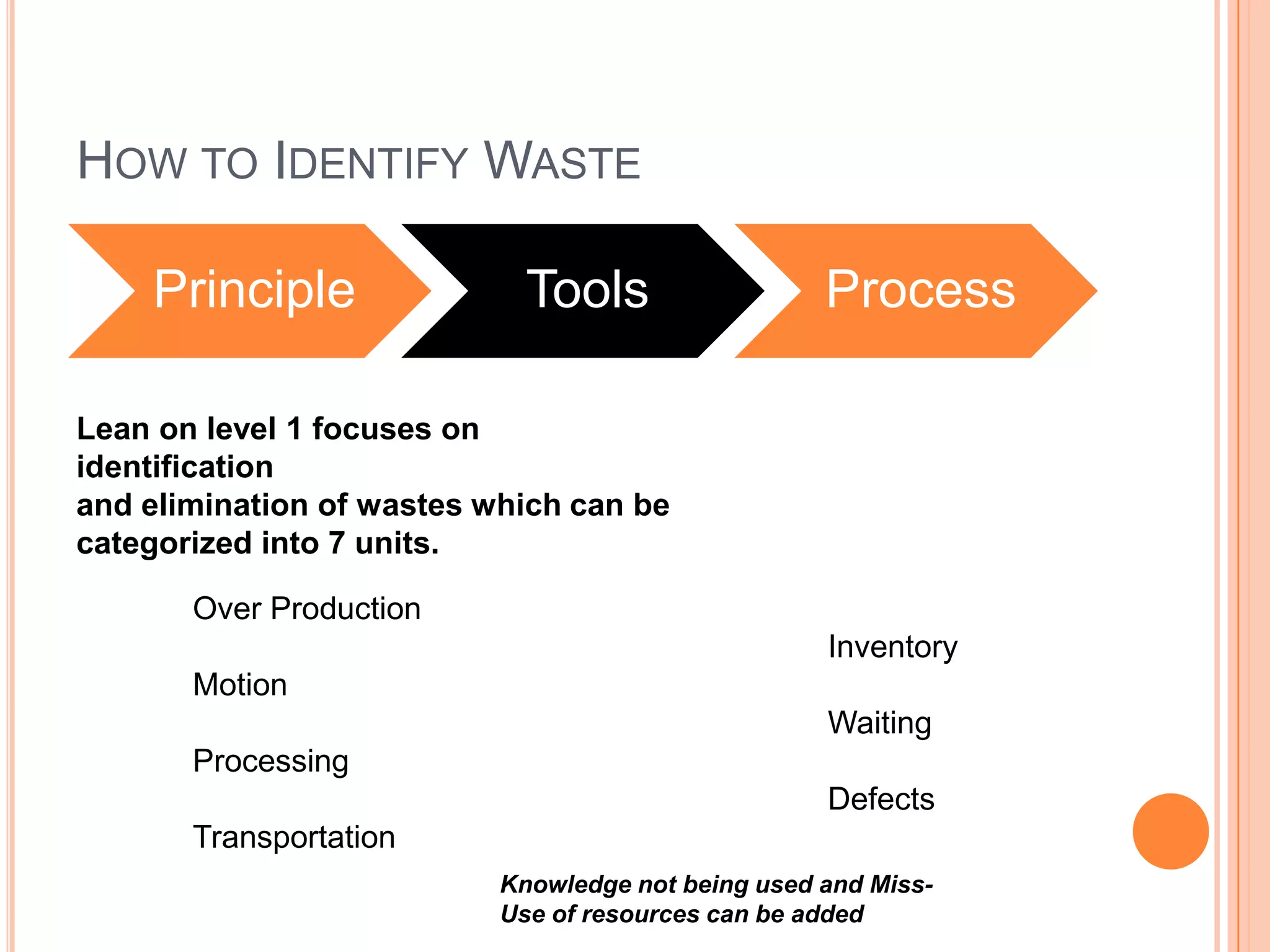
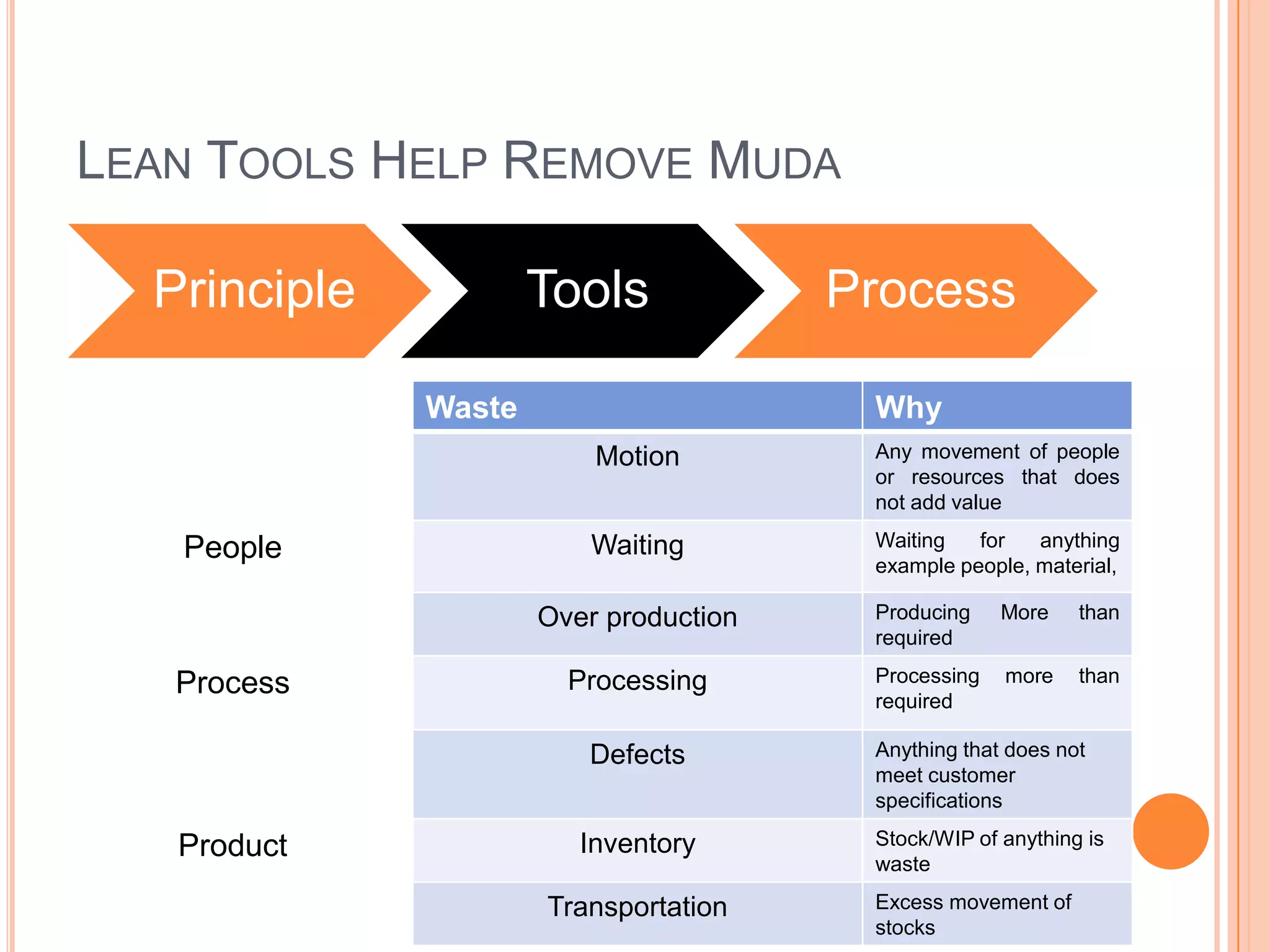
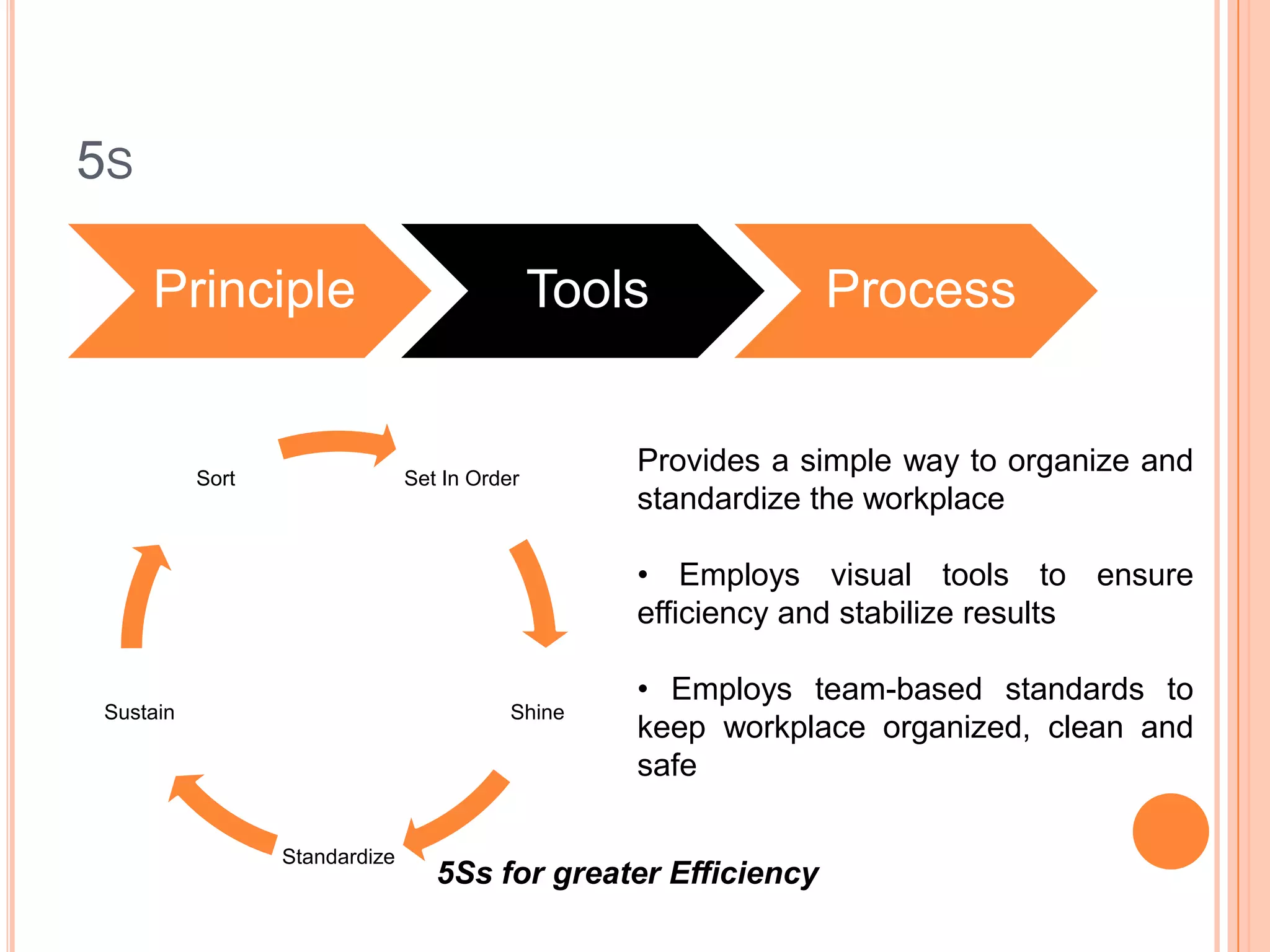
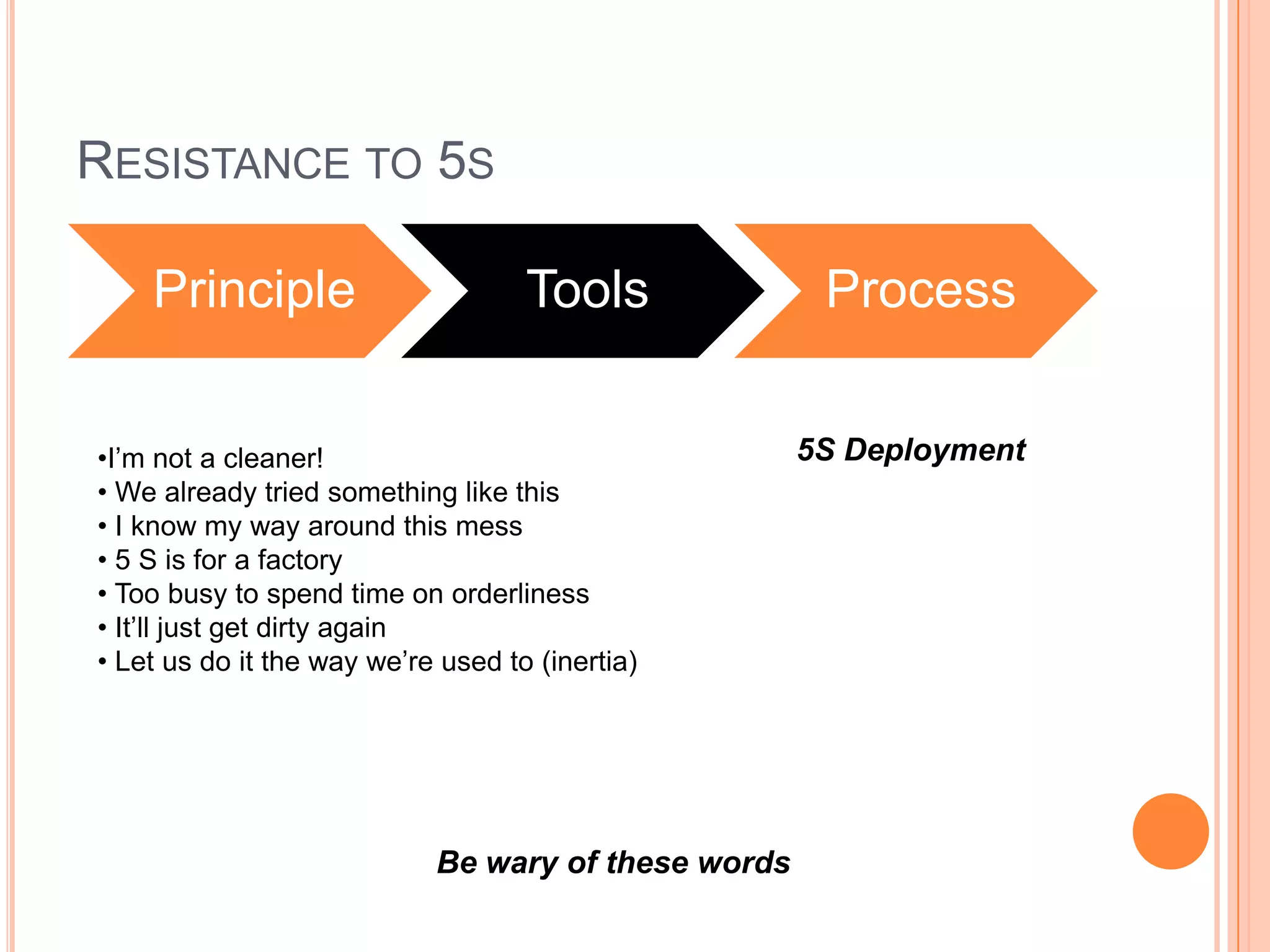
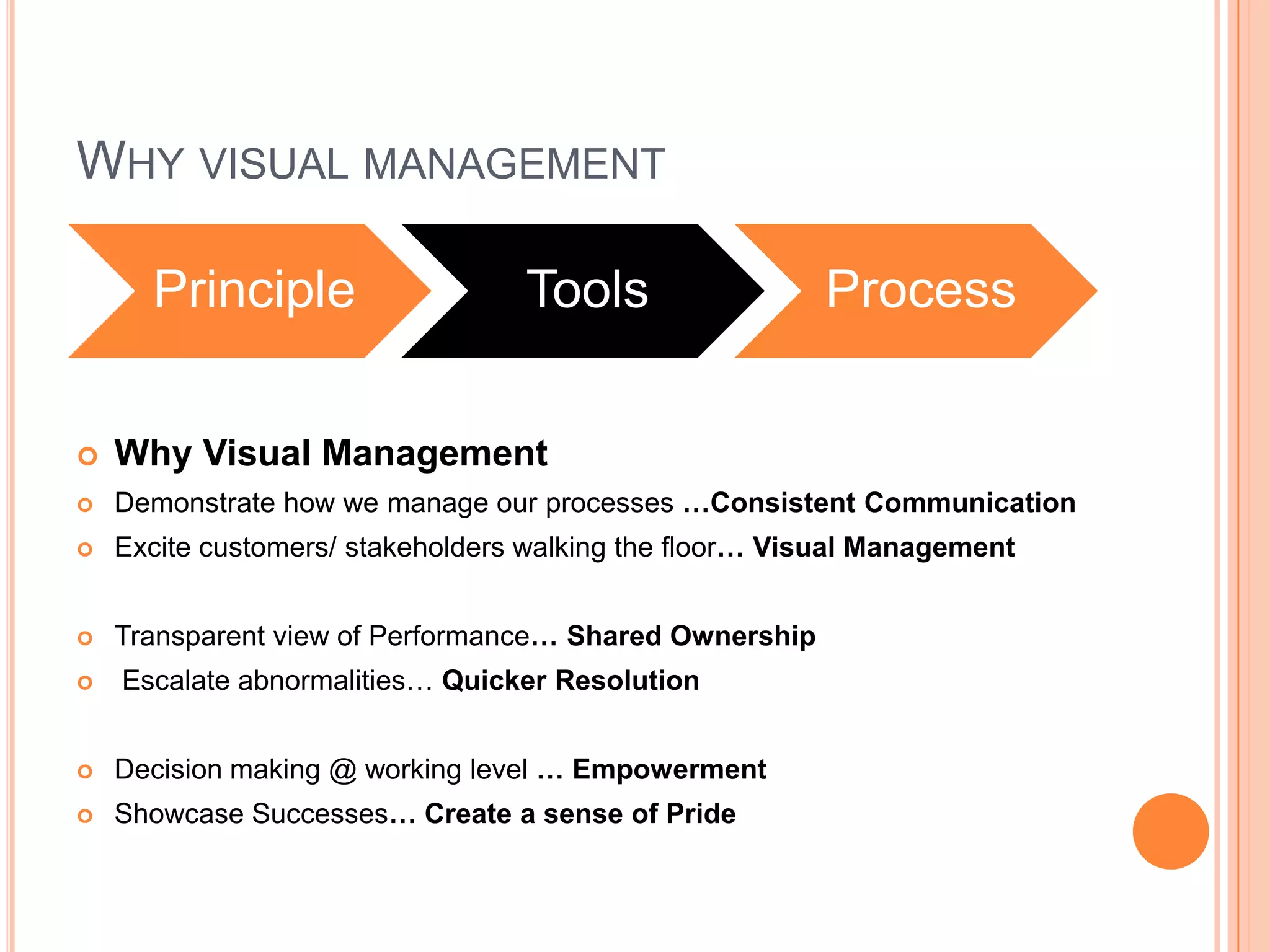
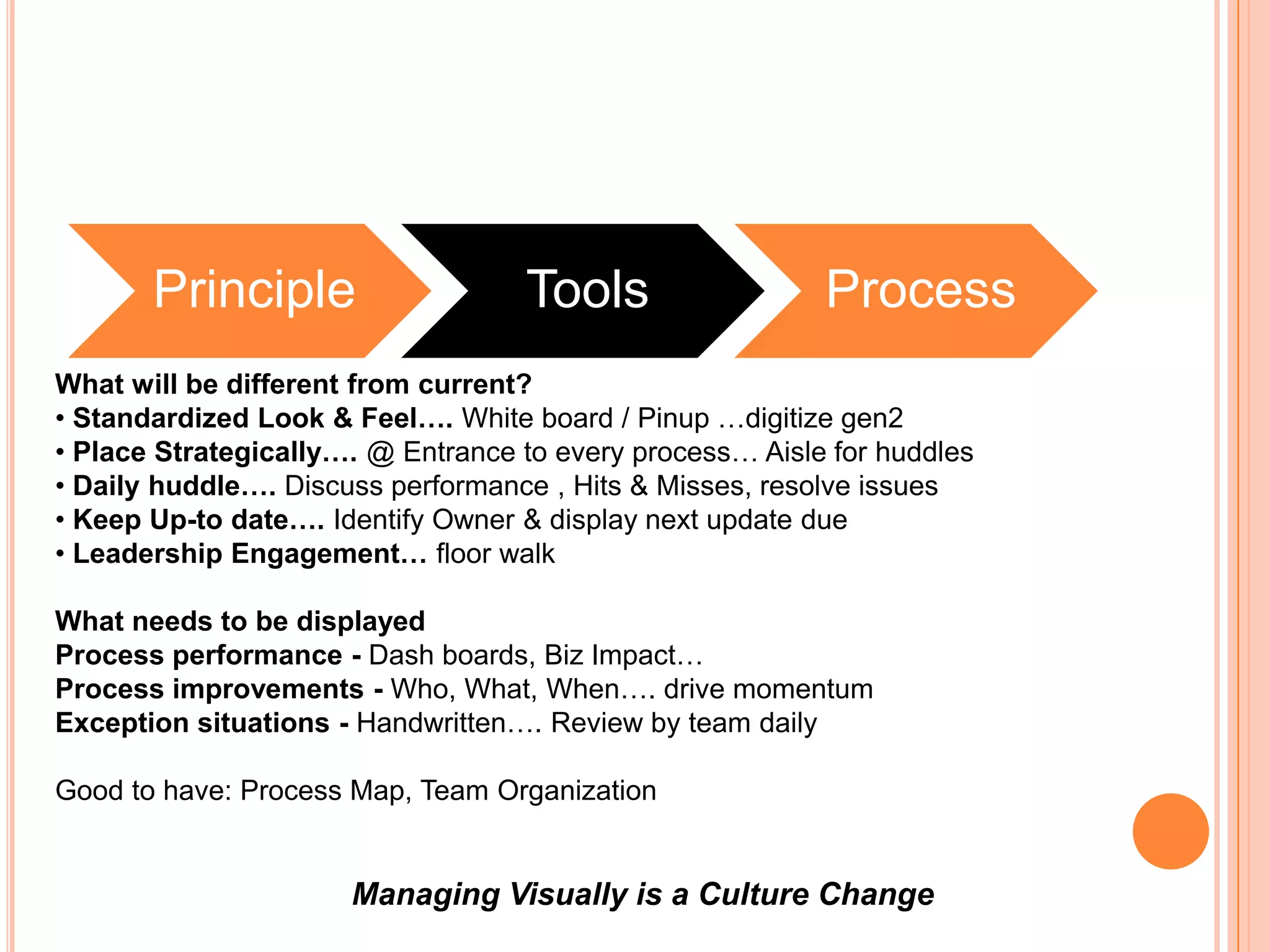
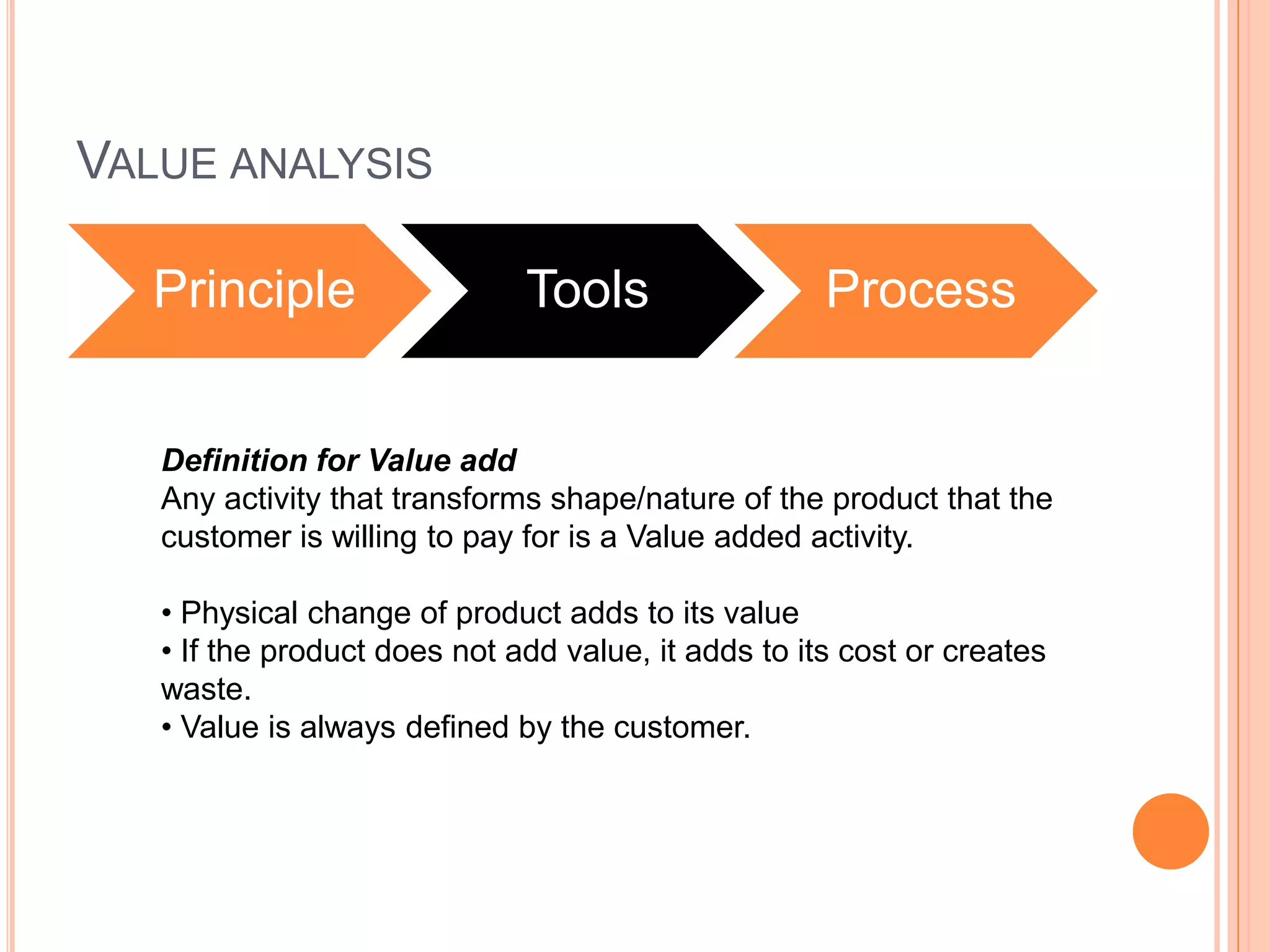
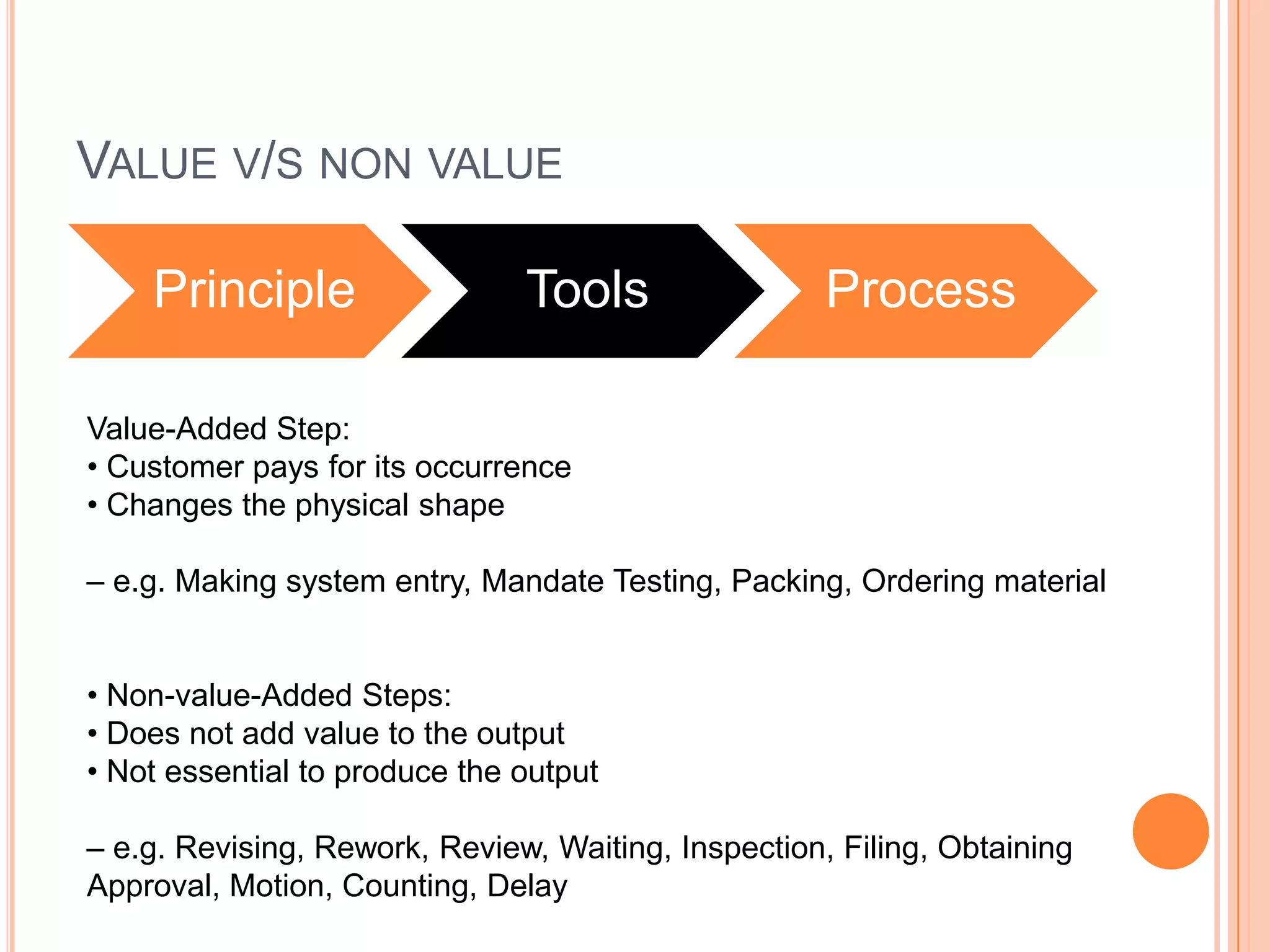
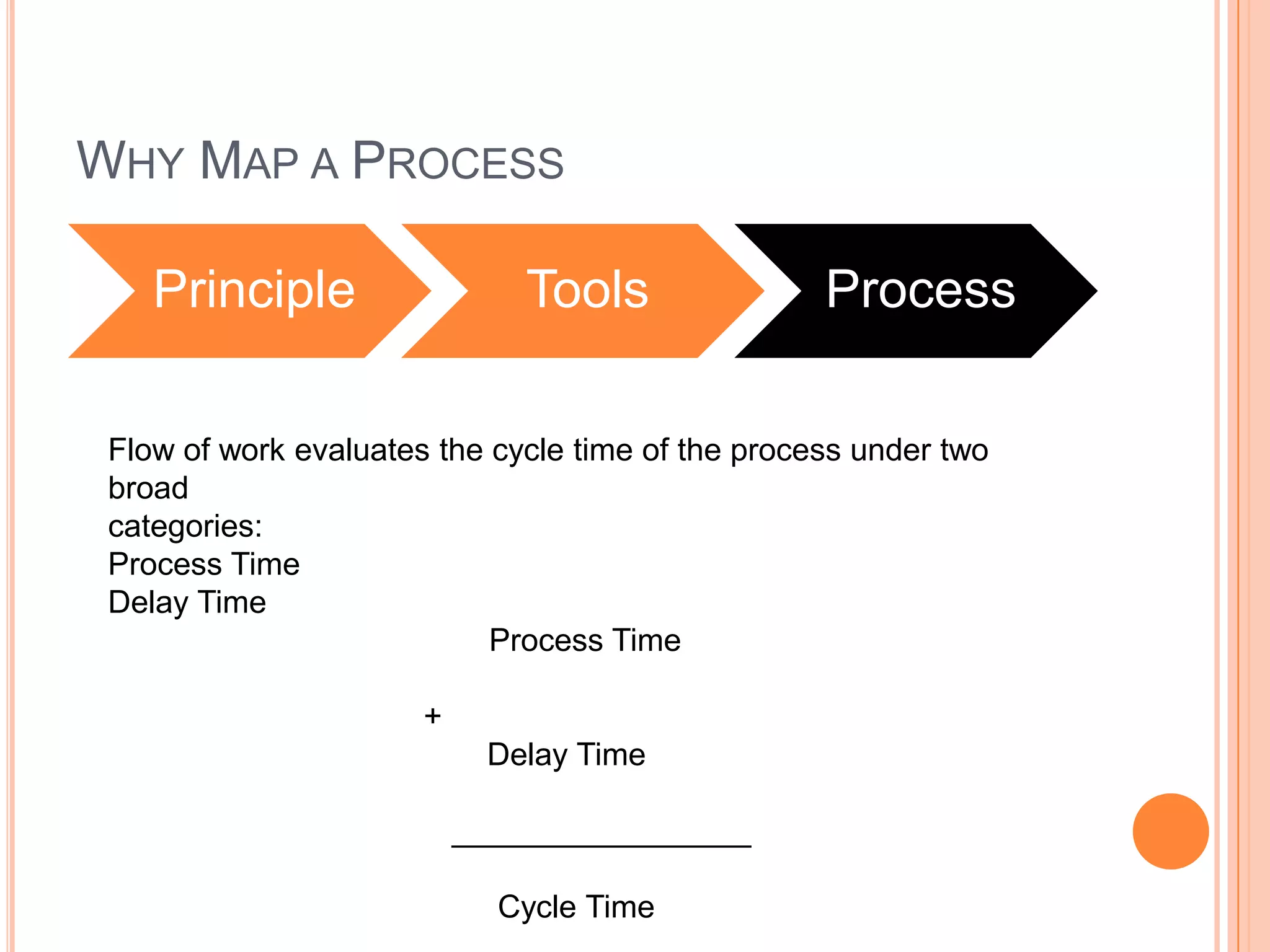
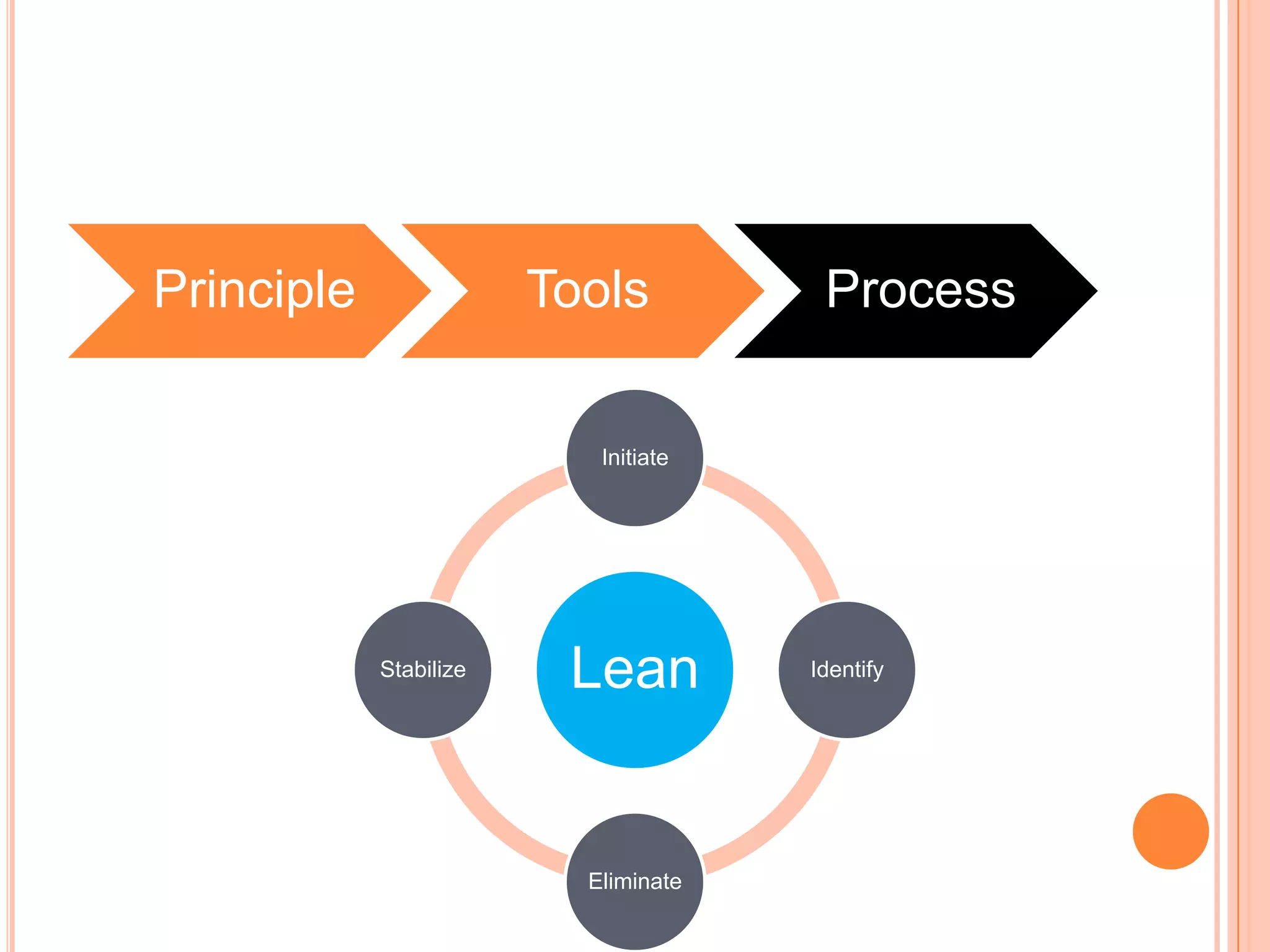
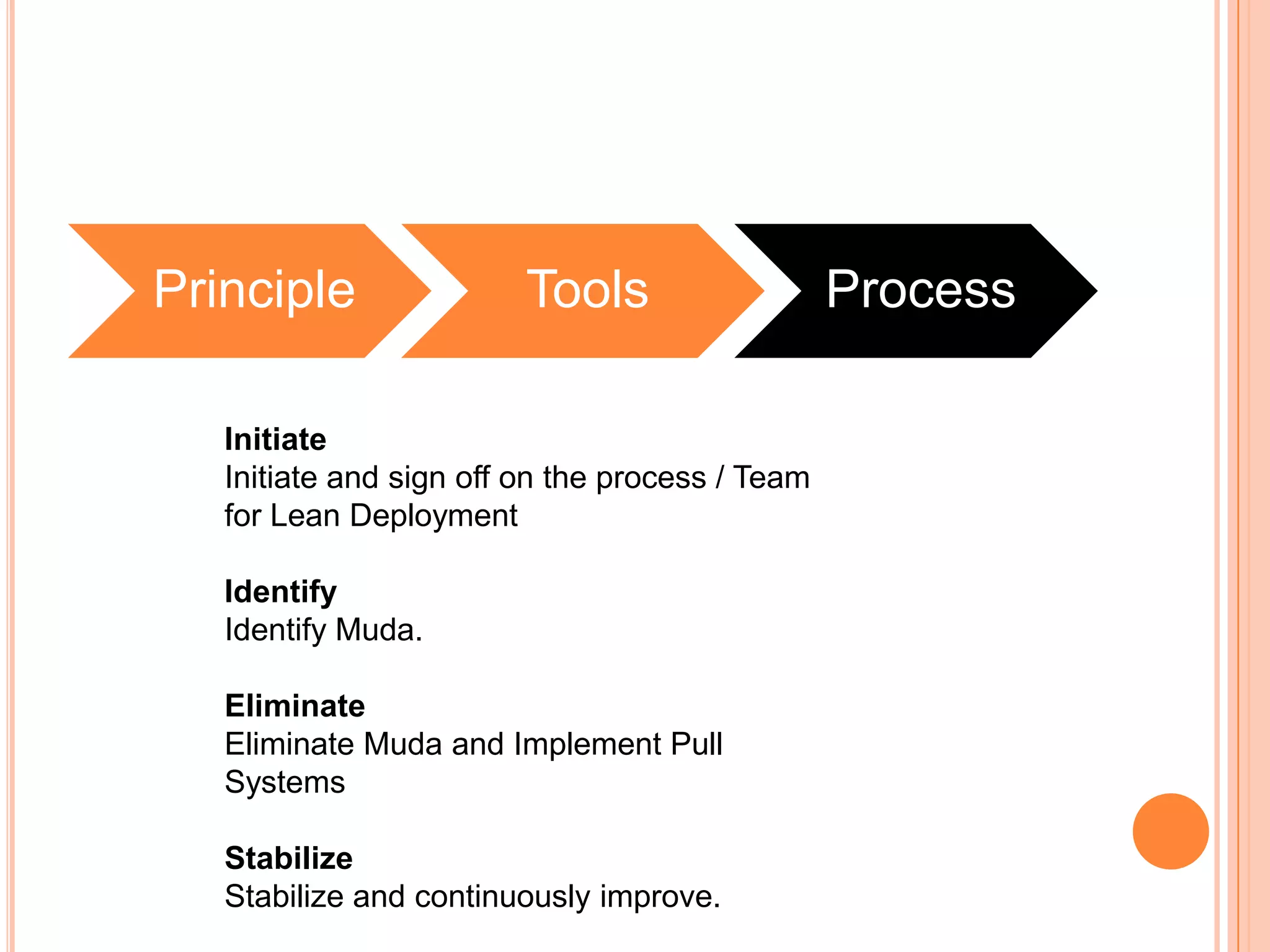
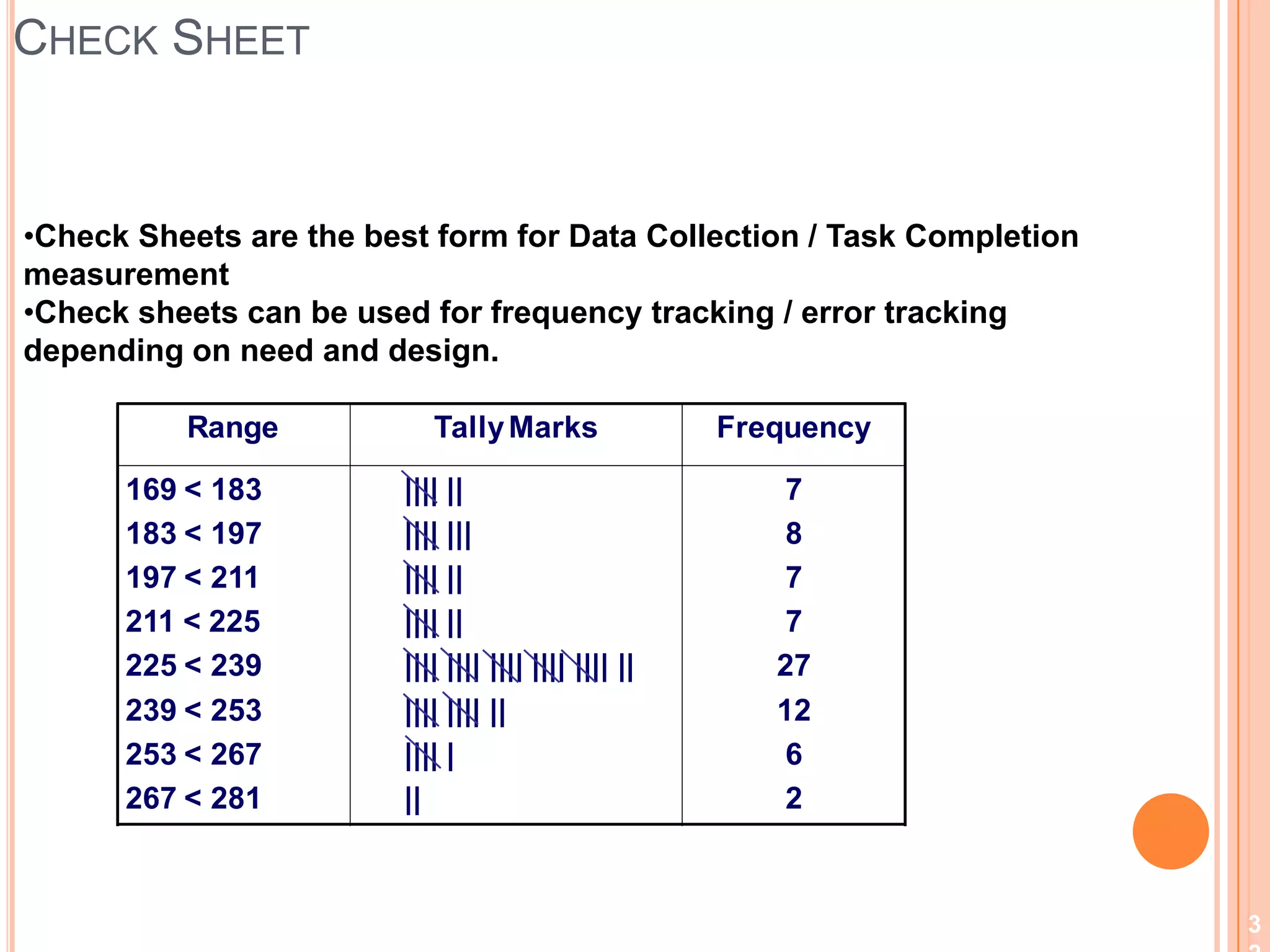
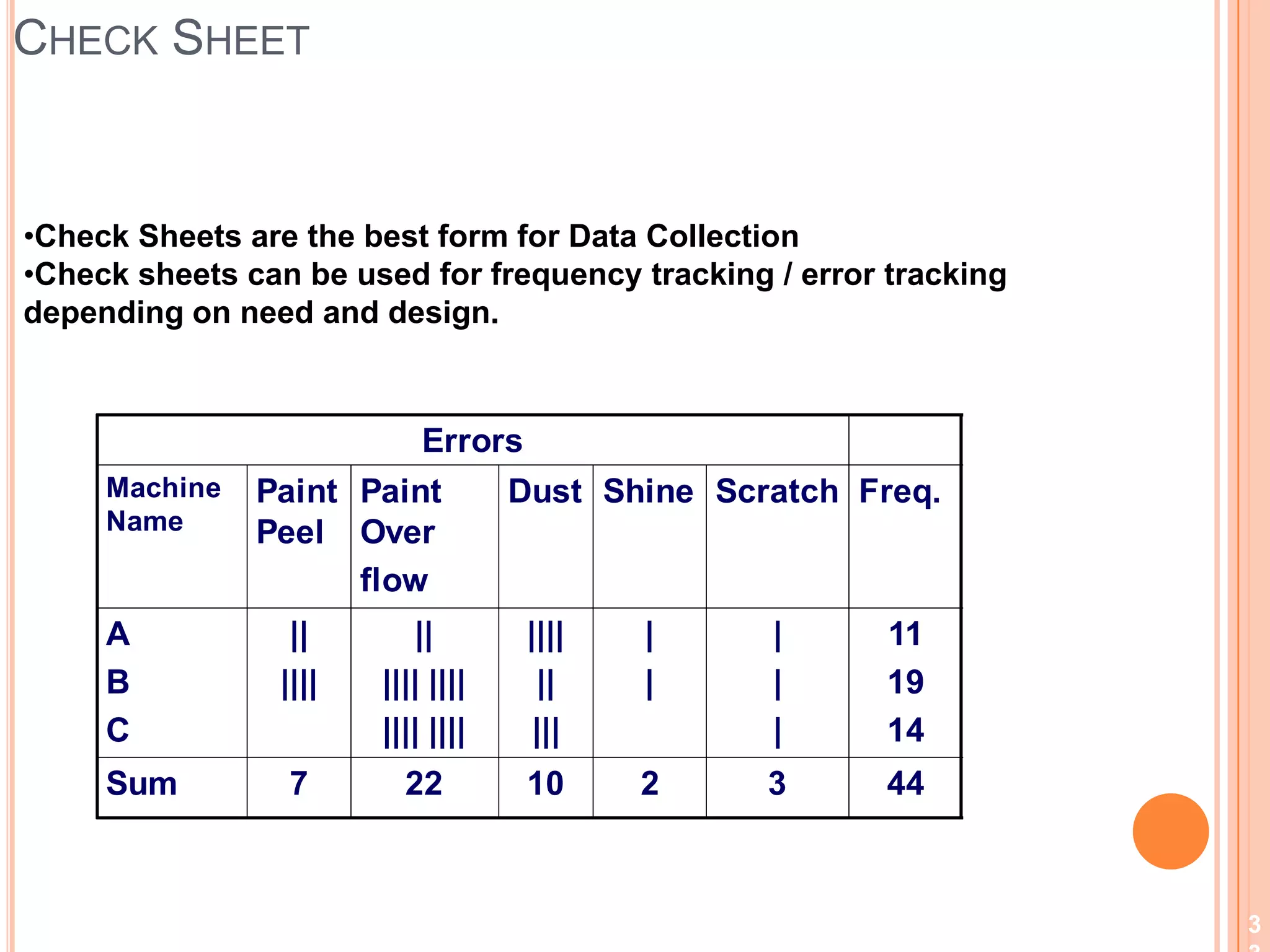
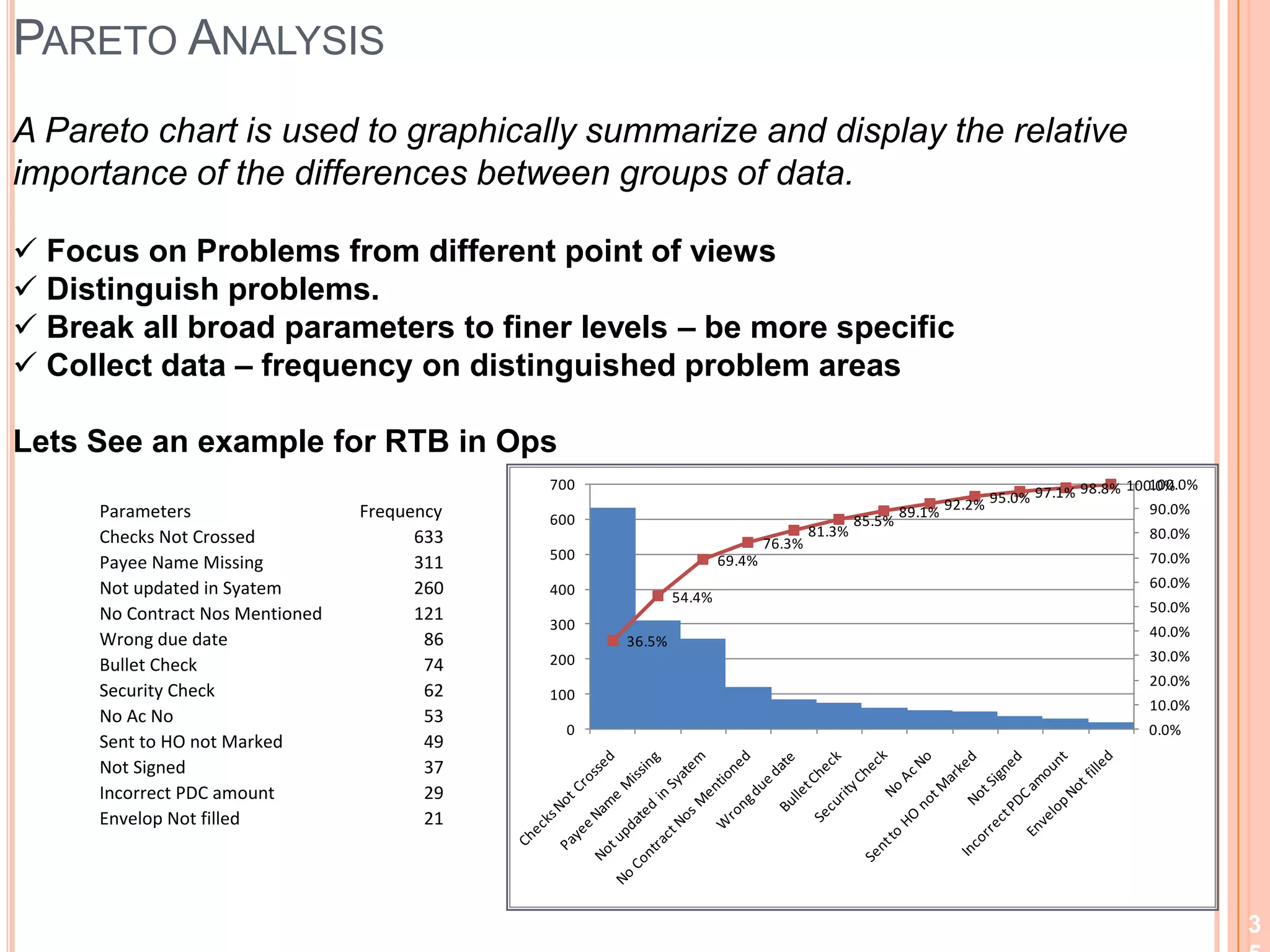
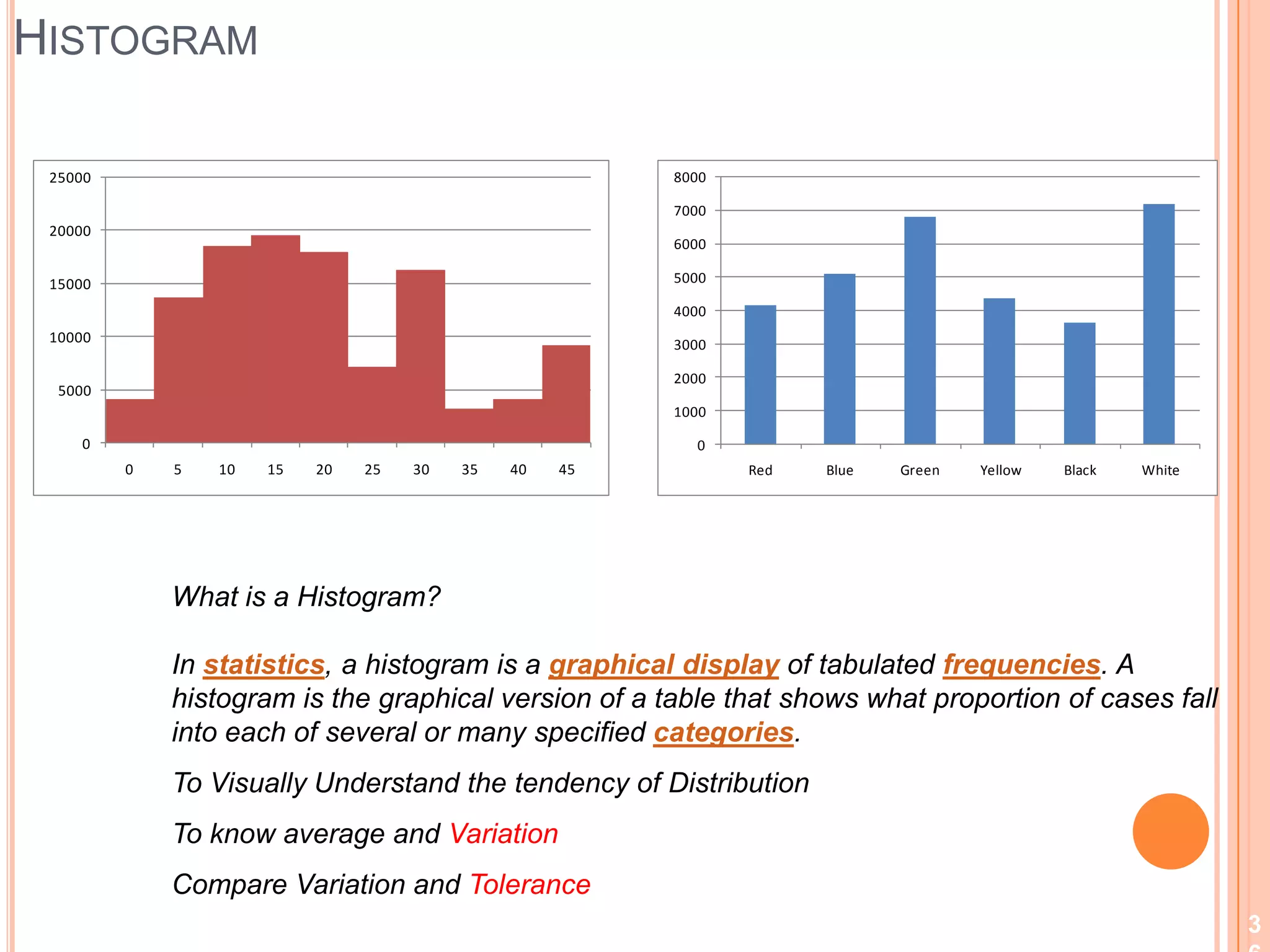
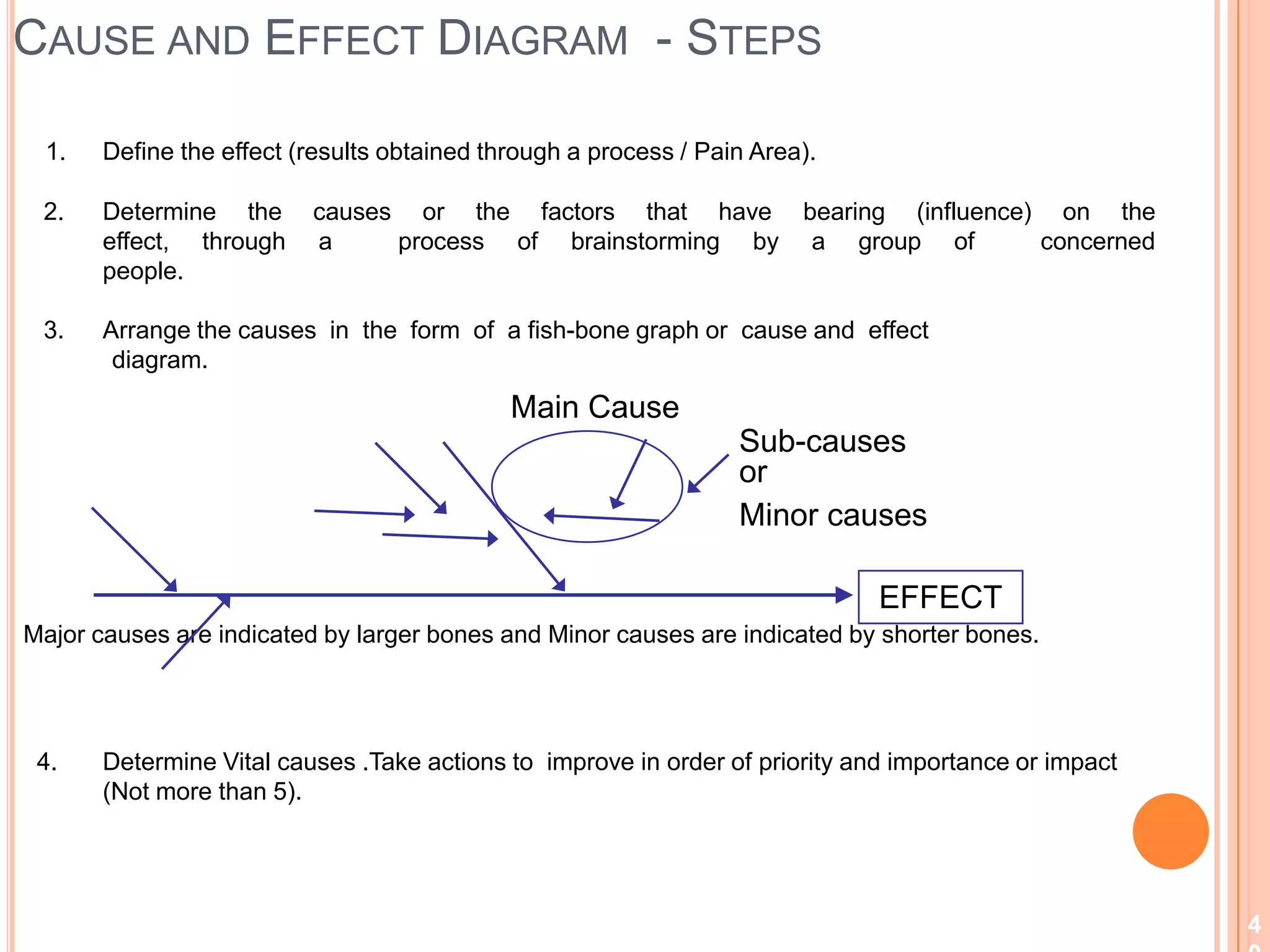
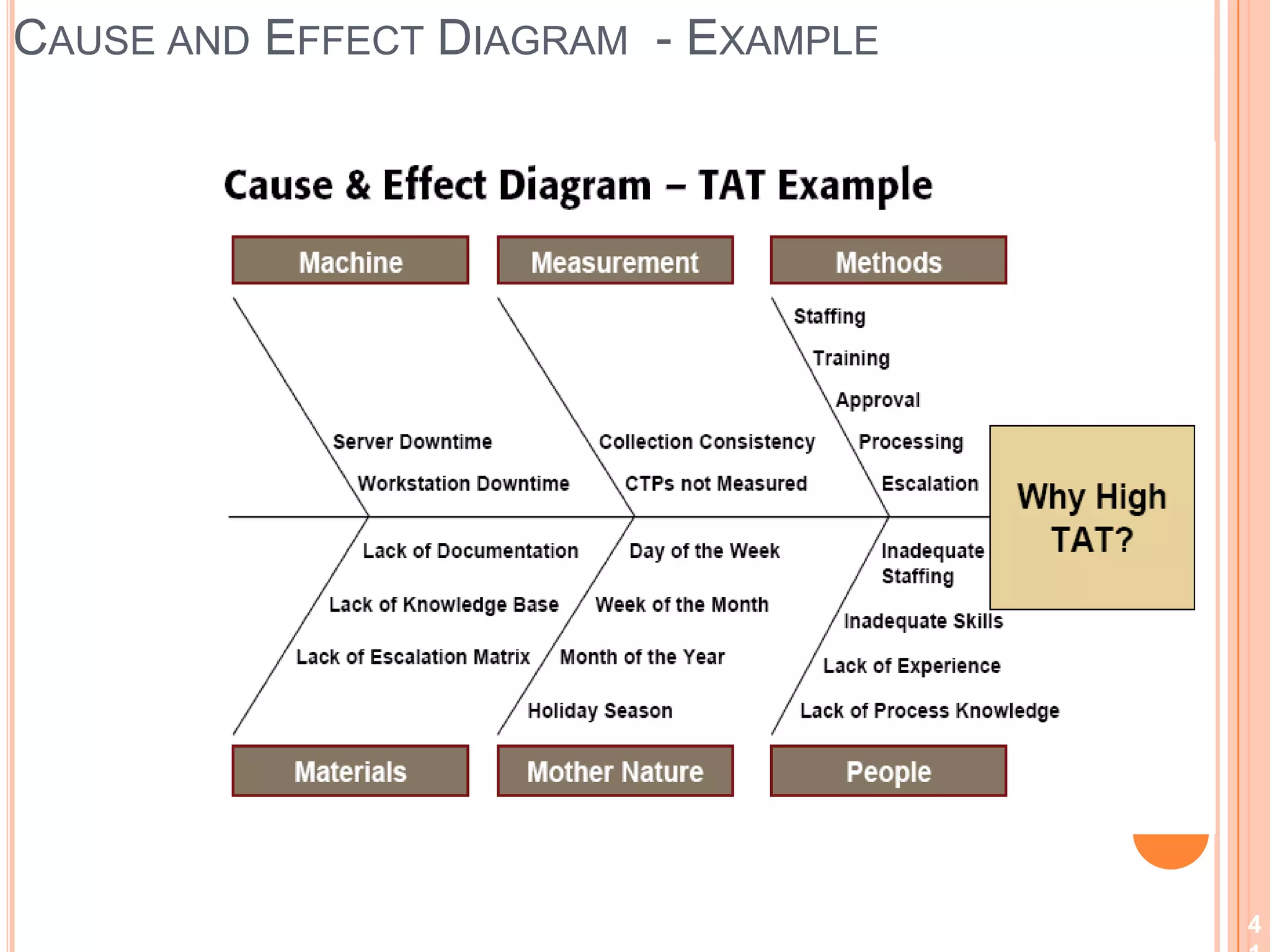
The document provides an overview of lean principles and quality control tools. It discusses lean as a philosophy focused on eliminating waste through continuous improvement. The key lean principles are specified as: specify value, identify the value stream and eliminate waste, make value flow, implement pull, and continuously improve. Quality control tools covered include check sheets, Pareto analysis, histograms, cause-and-effect diagrams, and brainstorming. 5S methodology and its five disciplines are also explained as a tool to maintain an efficient workplace.