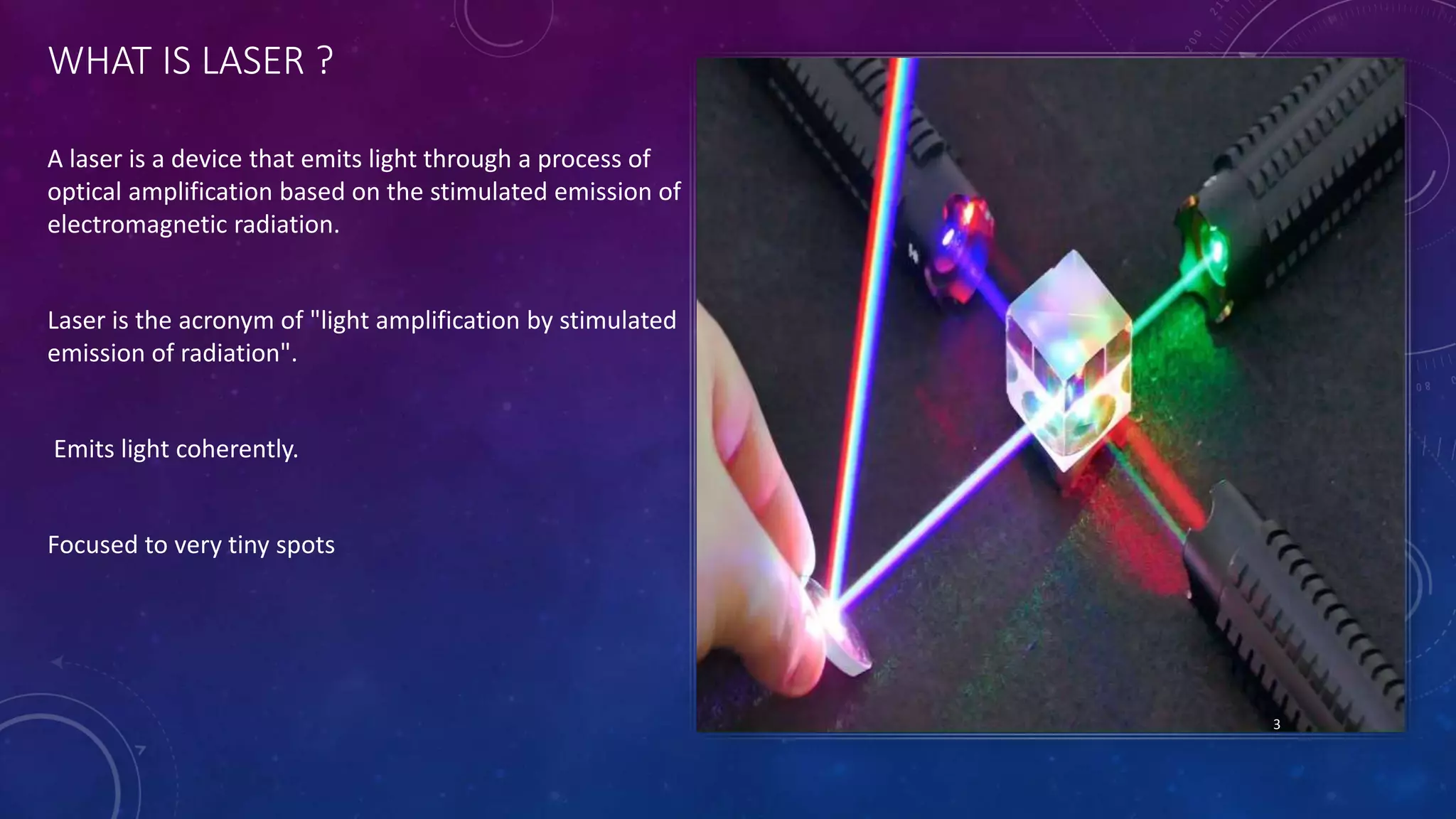
Laser Beam Machining (LBM) is a non-traditional manufacturing process utilizing a laser for material removal via thermal energy, suitable for brittle and low conductivity materials. Various types of lasers, including gas, solid-state, and excimer lasers, are employed for diverse applications such as welding, cutting, and micro-machining. While offering advantages like minimal tool wear and precision, challenges include limited applicability for thick materials, potential cost concerns, and a requirement for skilled operators.