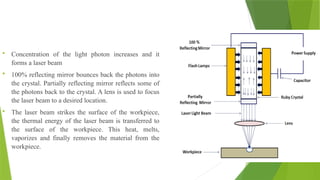
Laser Beam Machining (LBM) utilizes high-power laser beams to produce thermal energy that heats, melts, and vaporizes materials from a workpiece. It is advantageous for machining complex parts with high precision in various industries such as automotive and aerospace, although it comes with high initial costs and requires skilled operators. LBM operates on the principle of stimulated emission, using gas or solid-state lasers, and offers capabilities like cutting small holes but has limitations on material thickness and removal rates.