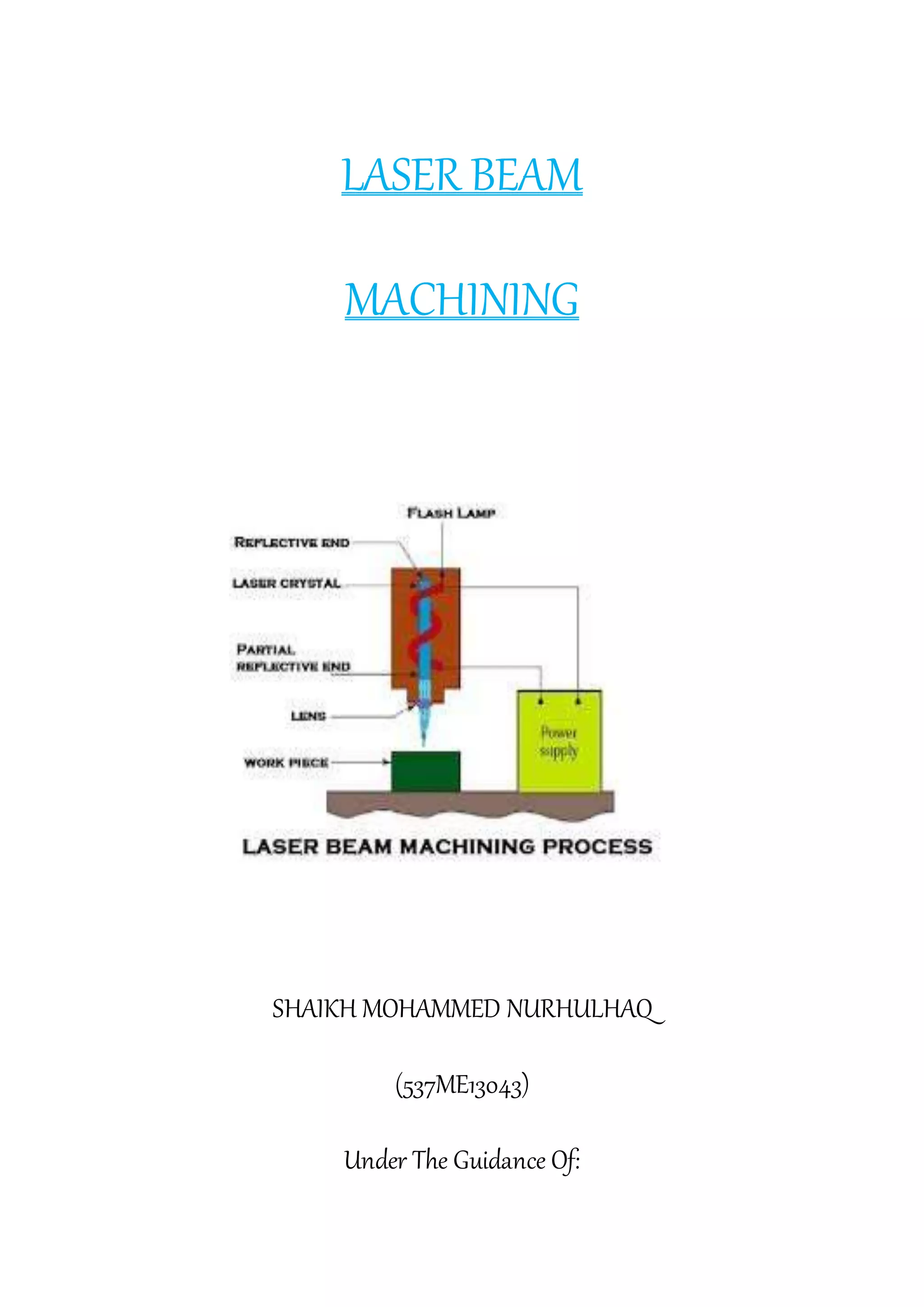
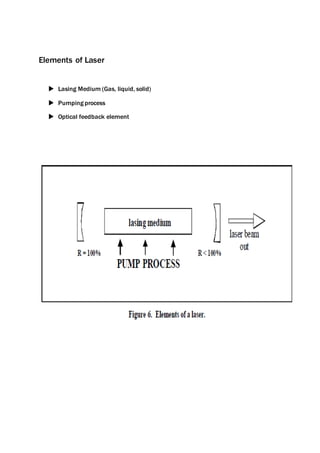
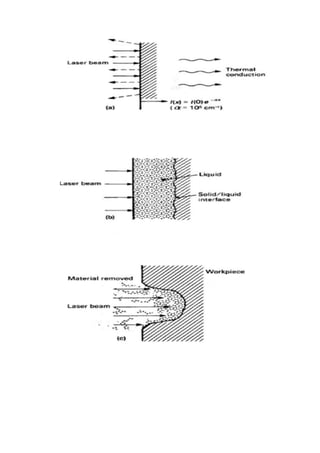
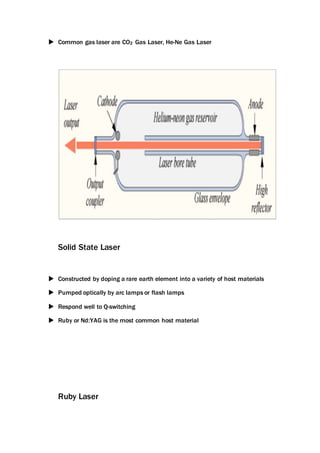
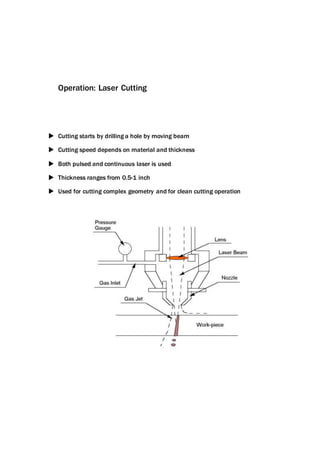
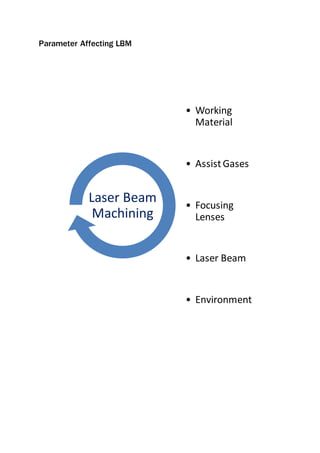
This document provides an overview of laser beam machining. It discusses what a laser is and the main components and types of lasers, including gas, solid state, and excimer lasers. Laser beam machining uses focused light energy from a laser to remove material through vaporization and ablation. Key applications of laser beam machining discussed include cutting, welding, cladding, and engraving/marking. Parameters that affect the laser beam machining process include the work material, focusing lenses, laser beam characteristics, and environment. Advantages are precision and flexibility, while disadvantages include high costs and needing specially trained operators.