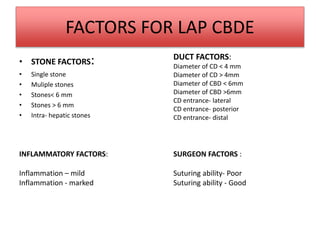
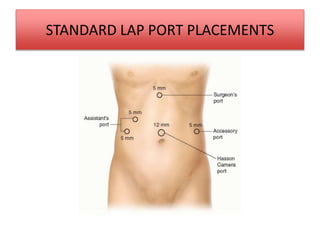
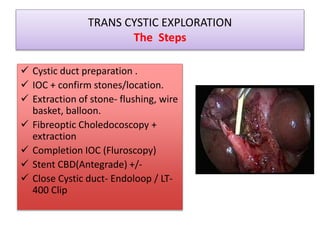
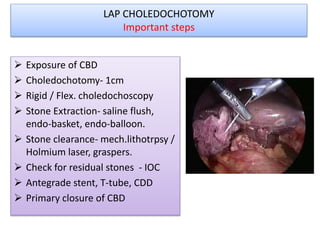
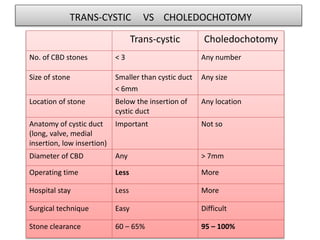
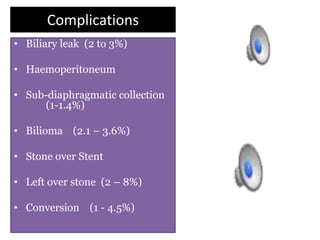
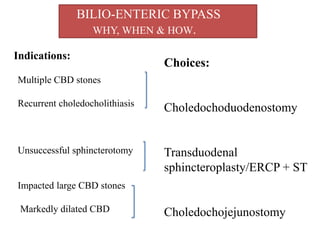
This document discusses laparoscopic common bile duct exploration (LCBDE) for the treatment of CBD stones. It outlines the advantages of the laparoscopic approach, including reduced costs, hospitalization and recovery time compared to open surgery. It describes the two main laparoscopic techniques for CBD stone removal - trans-cystic duct approach and laparoscopic choledochotomy. Key factors that determine technique selection include stone size and location, cystic/CBD duct anatomy and size, and surgeon skill. Standard port placements and step-by-step descriptions of each technique are provided. Complications are discussed. The document concludes with a brief overview of bilioenteric bypass indications and options.