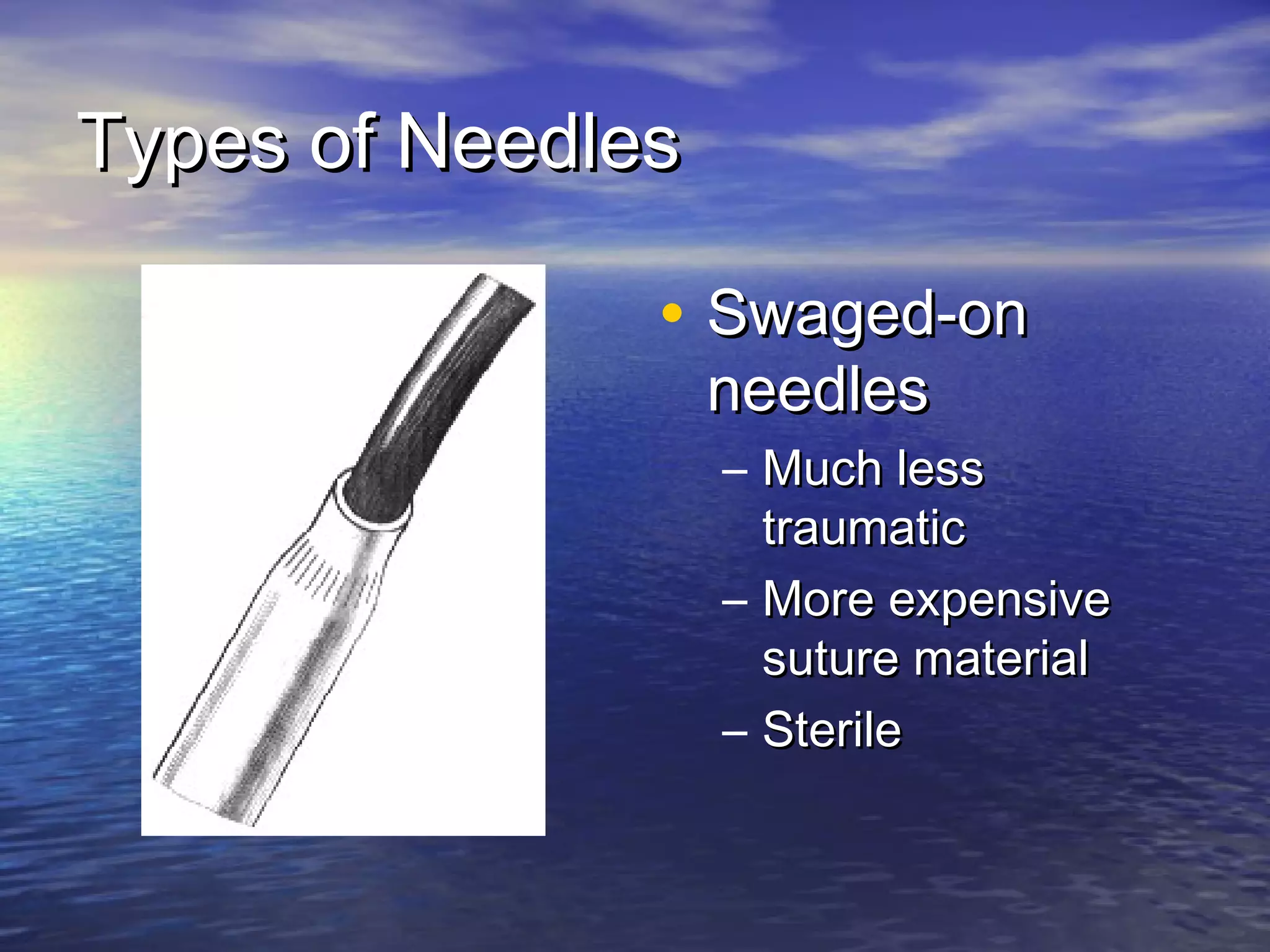
The document discusses various aspects of suture materials and techniques, focusing on ideal characteristics, types of needles, and differences between absorbable and non-absorbable sutures. It emphasizes the importance of selecting appropriate sutures based on their handling, tissue reaction, and knot security for various surgical applications. Additionally, it outlines specific properties of different suture materials and their uses in surgery, including advantages and limitations.