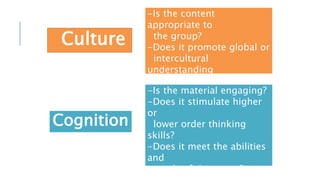
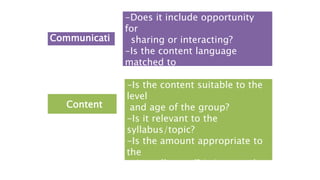
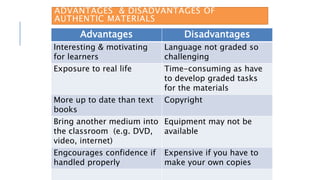
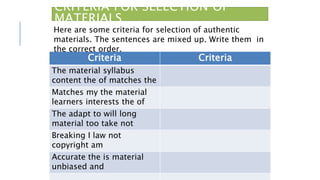
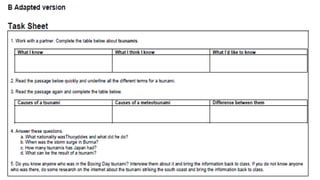
This document discusses selecting and adapting materials for language teaching. It begins by distinguishing between published materials like course books and authentic materials. Several criteria for selecting course books are outlined, including suitability for learners' level, skills focus, price, availability, and cultural sensitivity. Ways to evaluate course books are also presented. The document then discusses different types of adapting materials, such as adding, deleting, modifying, simplifying, and reordering. Considerations for selecting authentic materials and criteria for choosing materials in general are provided.