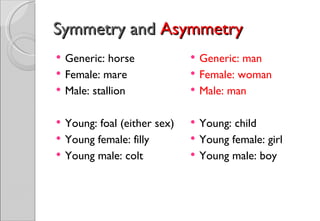
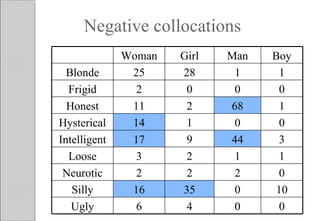
This document discusses how language can reinforce gender biases and inequality between men and women. It provides examples of how language is often asymmetric when referring to males and females, such as generic words defaulting to the male form. Additionally, it notes that some words have neutral or positive connotations when used for men but negative meanings when used for women. The document concludes that language plays a role in shaping attitudes and the status of men and women in society by often treating males as the norm and using forms that diminish women's positions.