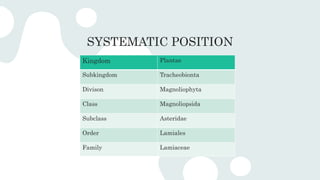
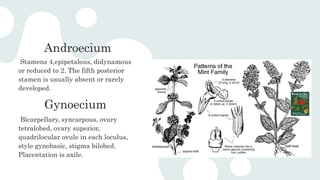
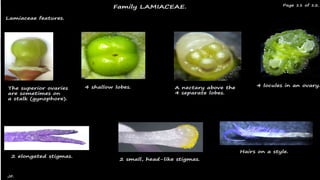
The document provides an overview of the Lamiaceae family, also known as the mint family, detailing its systematic position, distribution, and morphological characteristics such as habit, leaves, inflorescence, and reproductive structures. It emphasizes the economic importance of various species, including their use as sources of aromatic oils, ornamental plants, and culinary herbs. Key species mentioned include Lavandula vera for lavender oil, Mentha piperita for peppermint oil, and various others with medicinal and culinary applications.