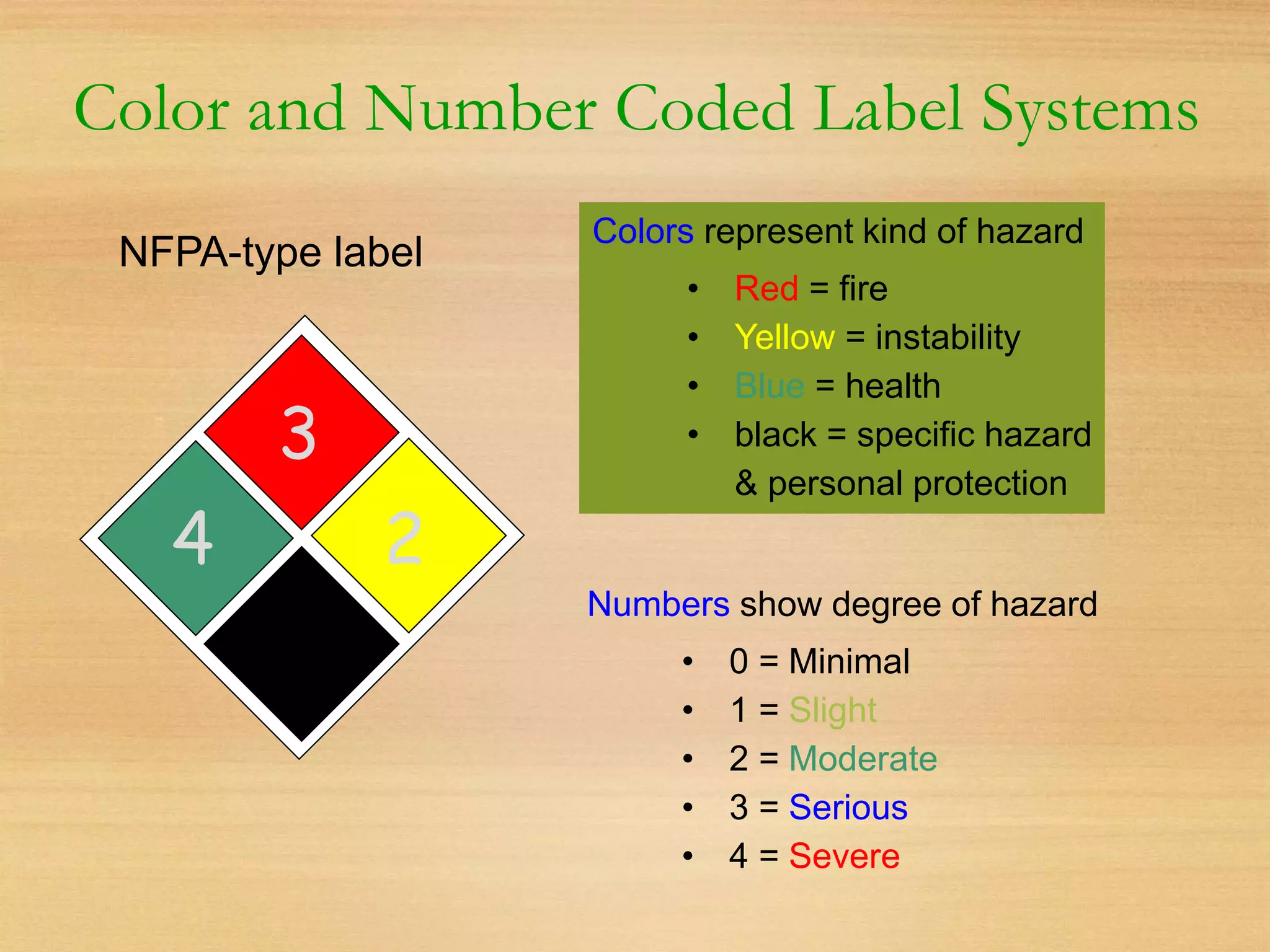
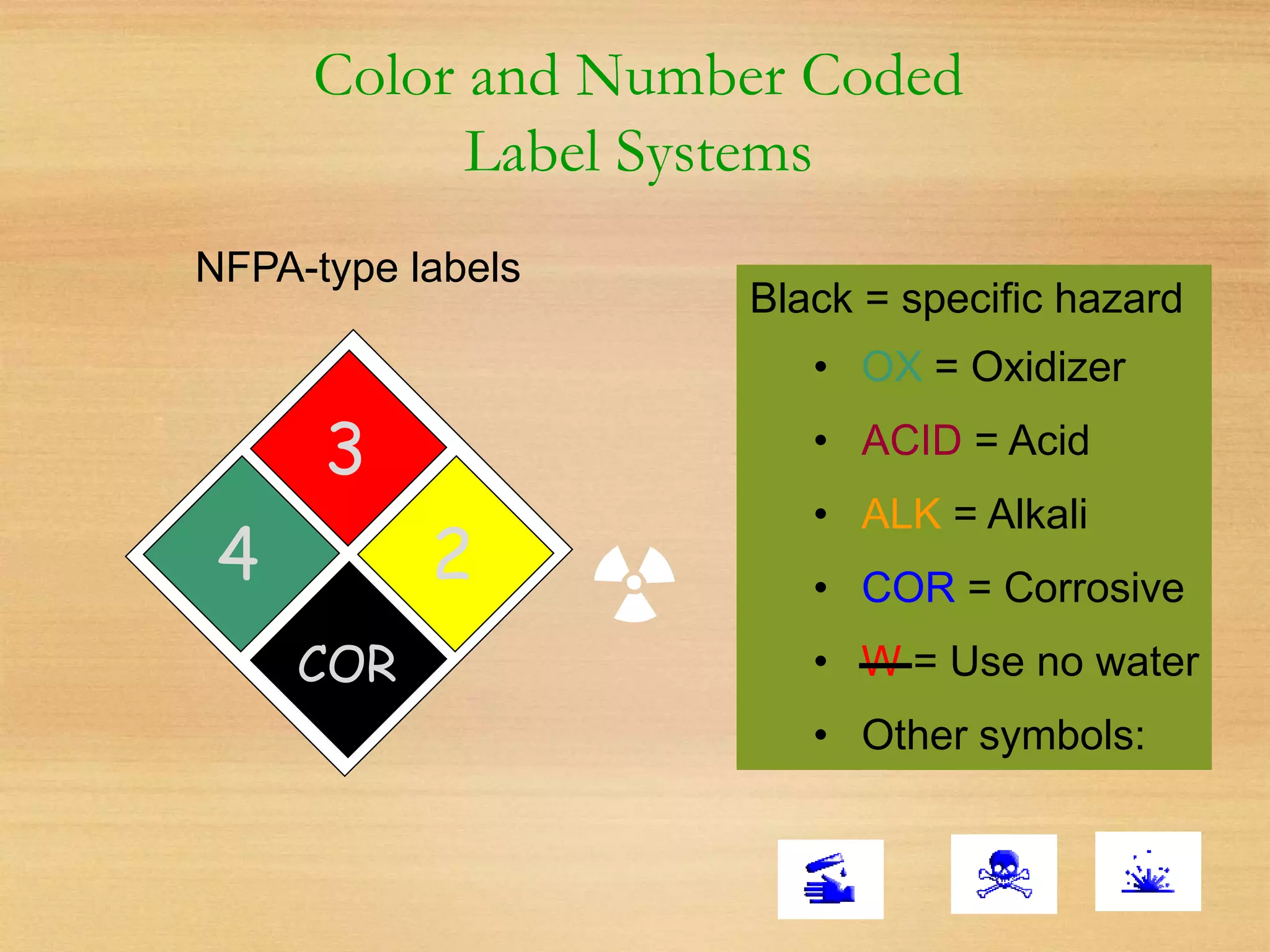
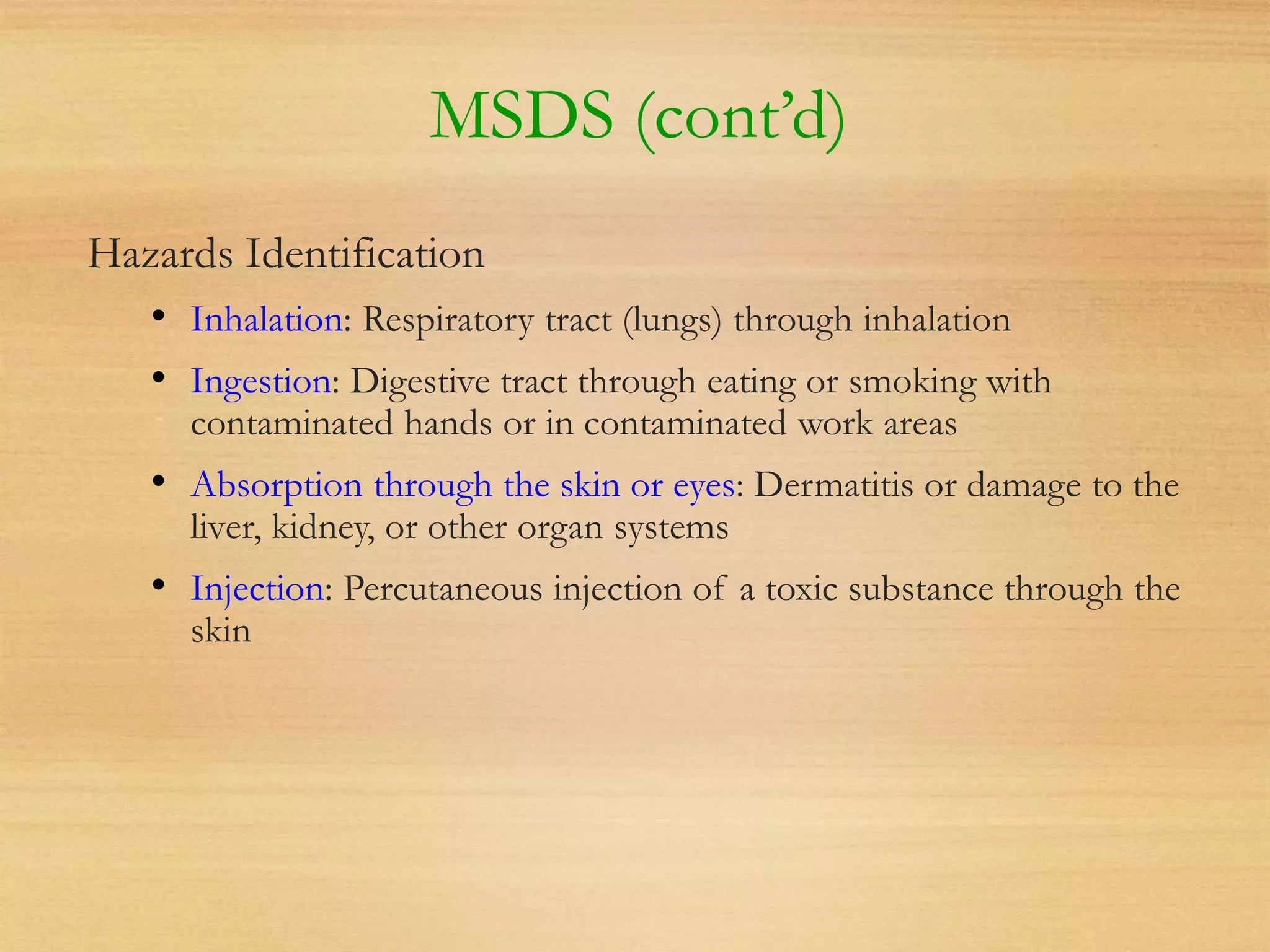
This document outlines essential laboratory safety training, emphasizing the importance of reading chemical labels and material safety data sheets (MSDS) for safe handling of chemicals. It details health hazards, precautionary measures, and proper storage and disposal procedures, along with emergency protocols and protective equipment required in labs. The document also highlights the significance of having a chemical hygiene plan to ensure safe work practices when dealing with hazardous substances.