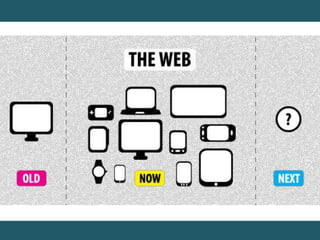
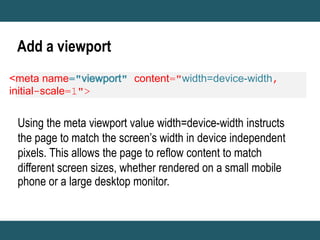
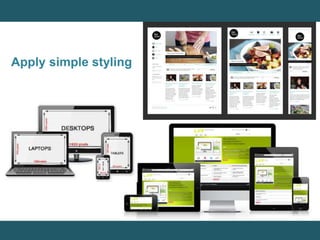
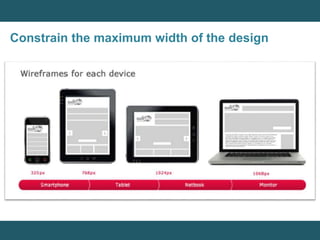
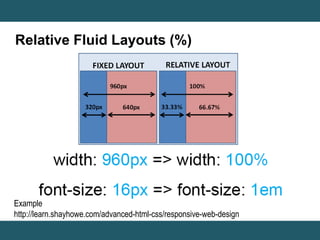
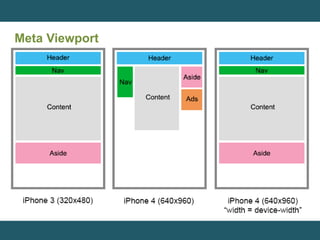
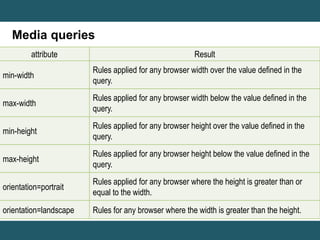
This document discusses responsive web design and provides steps to create responsive websites. It begins by defining responsive web design and listing the initial steps: adding a viewport, applying basic styling, and setting the first breakpoint. It then covers techniques like constraining width, adjusting padding and text size, adapting elements, and using media queries. The document provides examples and references for creating responsive layouts and adjusting designs based on screen size.