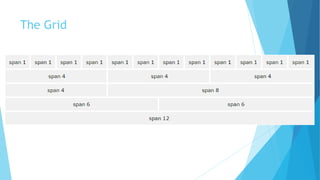
Bootstrap is a free front-end framework for building responsive, mobile-first websites. It includes HTML and CSS templates for common elements like typography, forms, buttons, navigation, tables, images and more. Bootstrap also utilizes a responsive 12-column grid system and is compatible with all modern browsers. Websites built with Bootstrap are automatically responsive on devices ranging from small phones to large desktops.