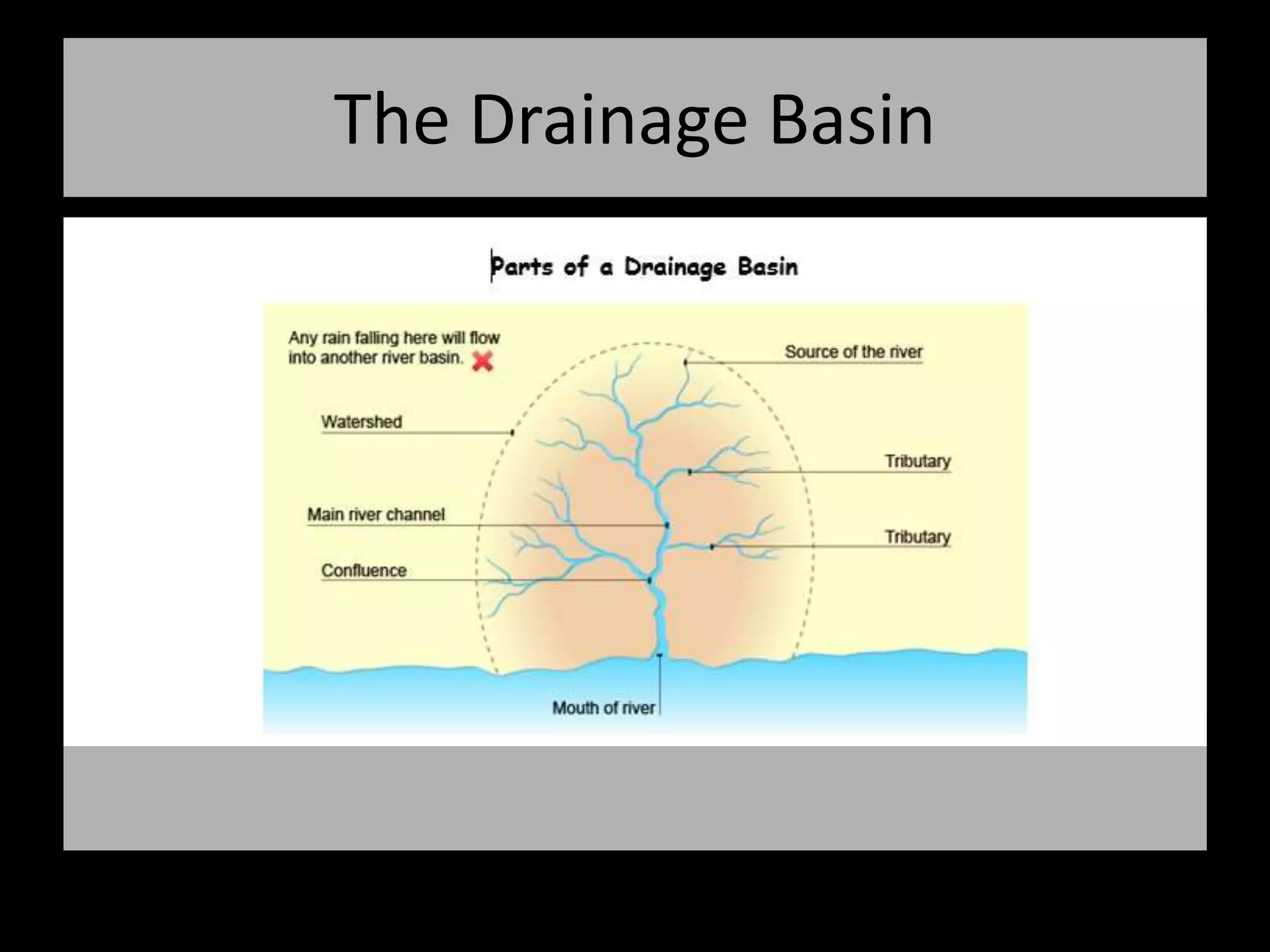
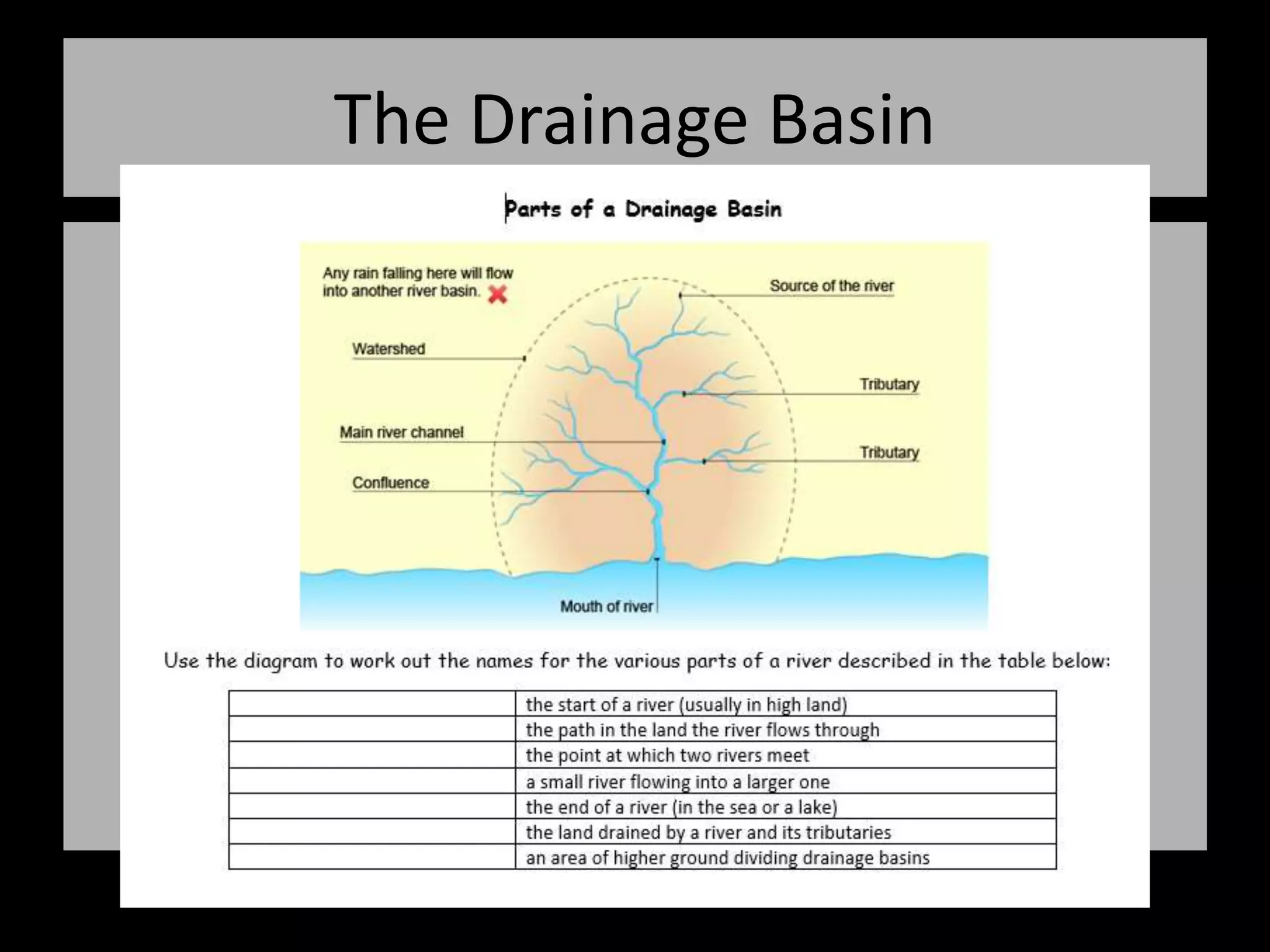
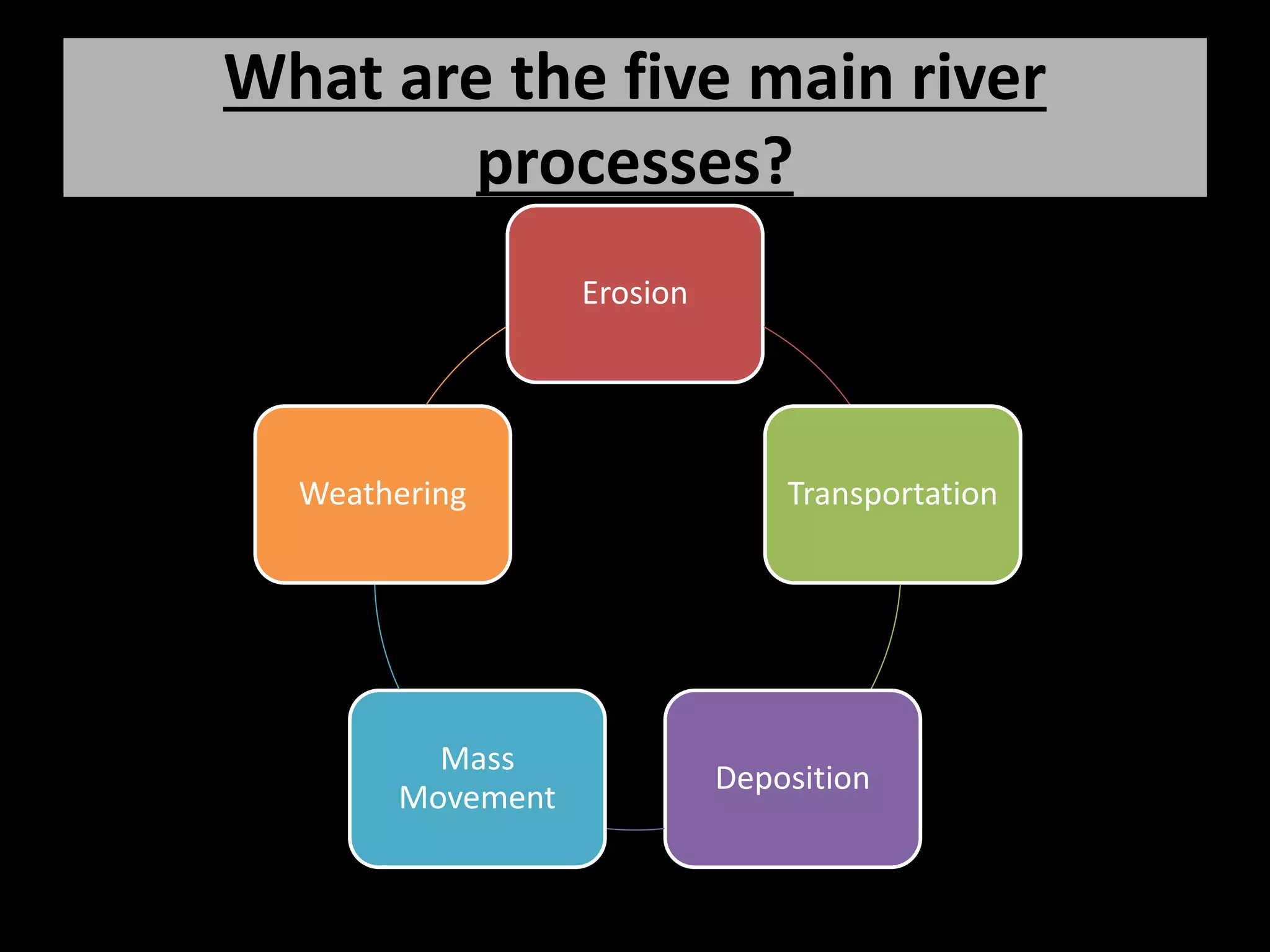
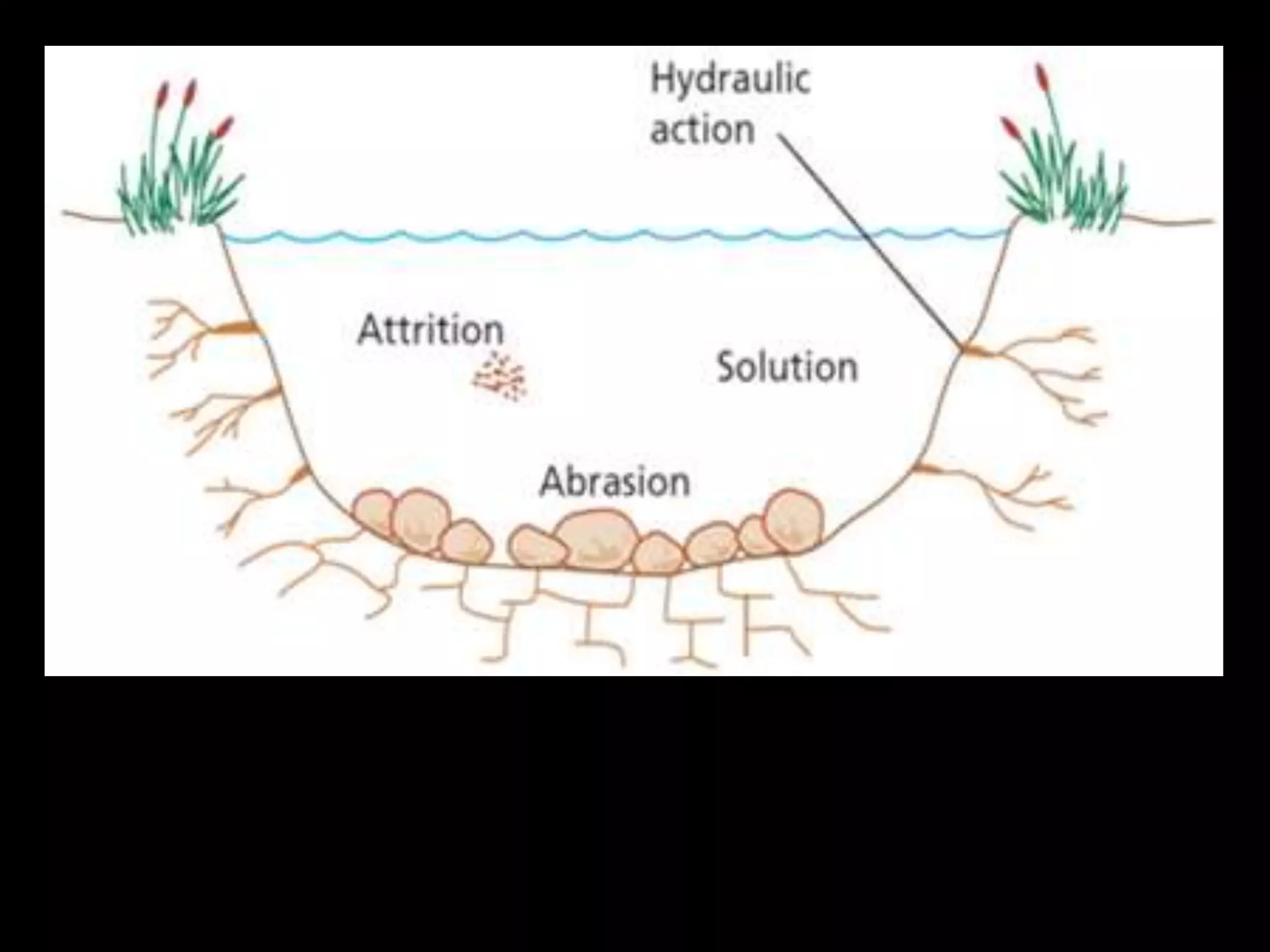
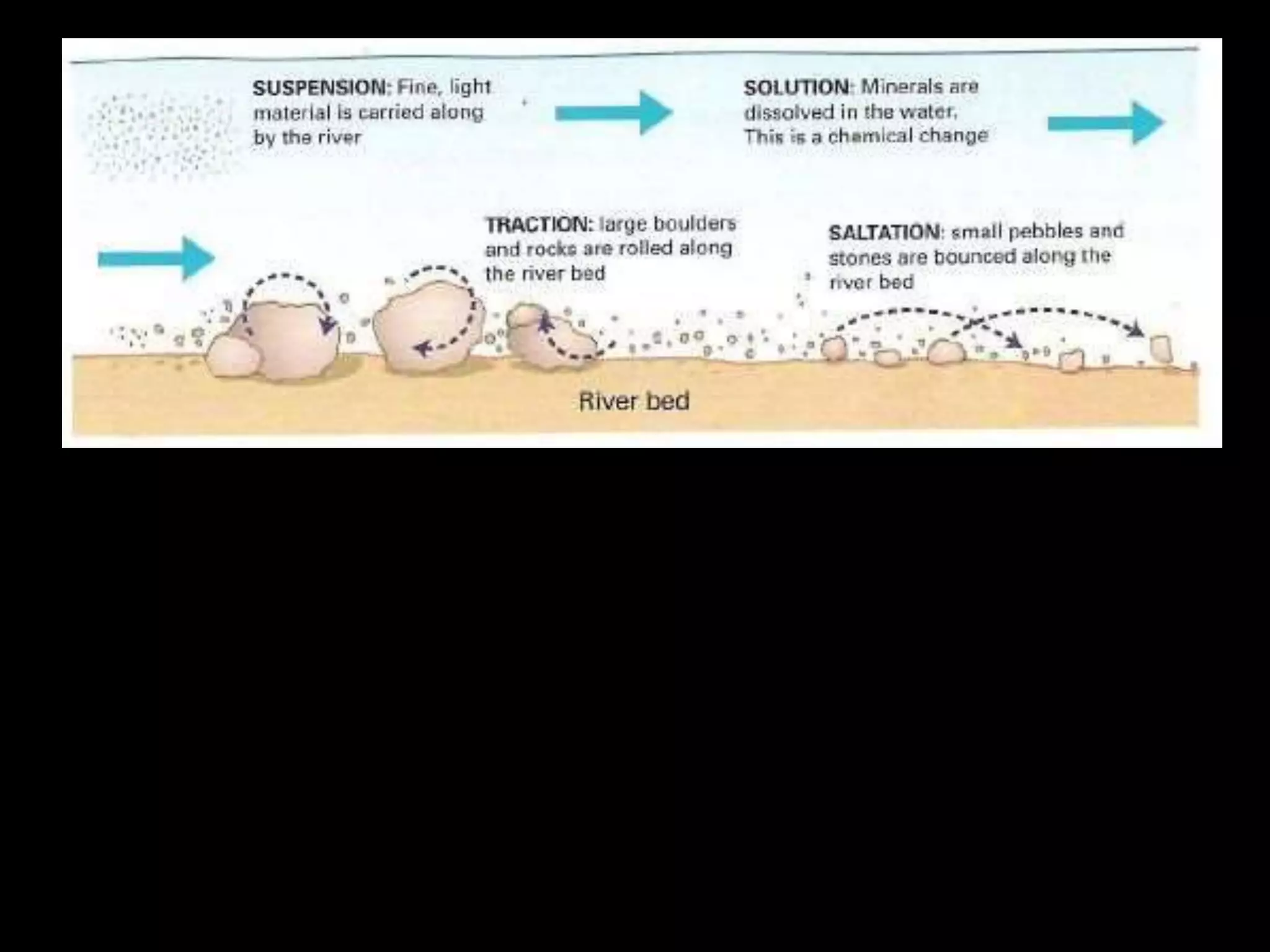
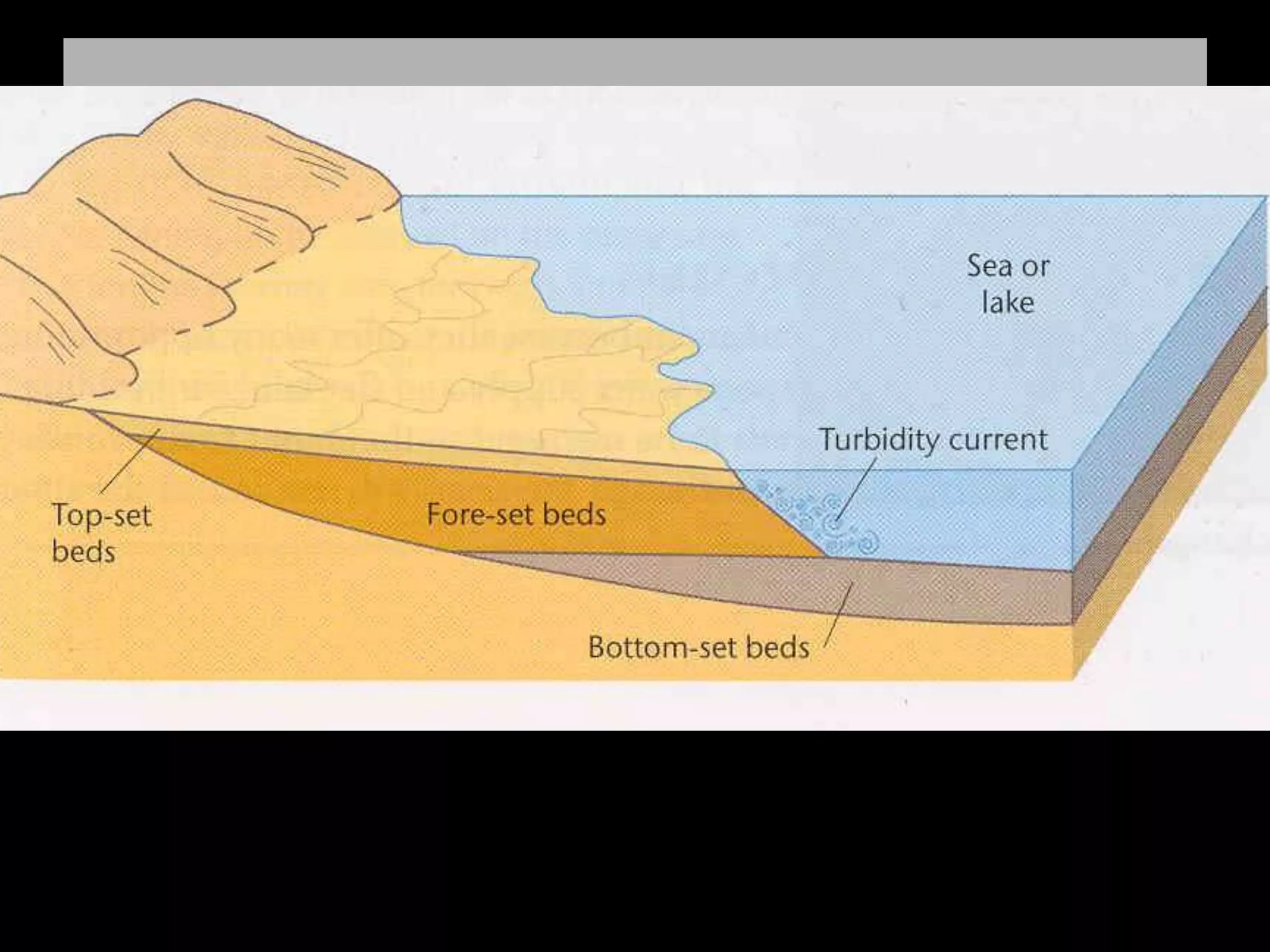
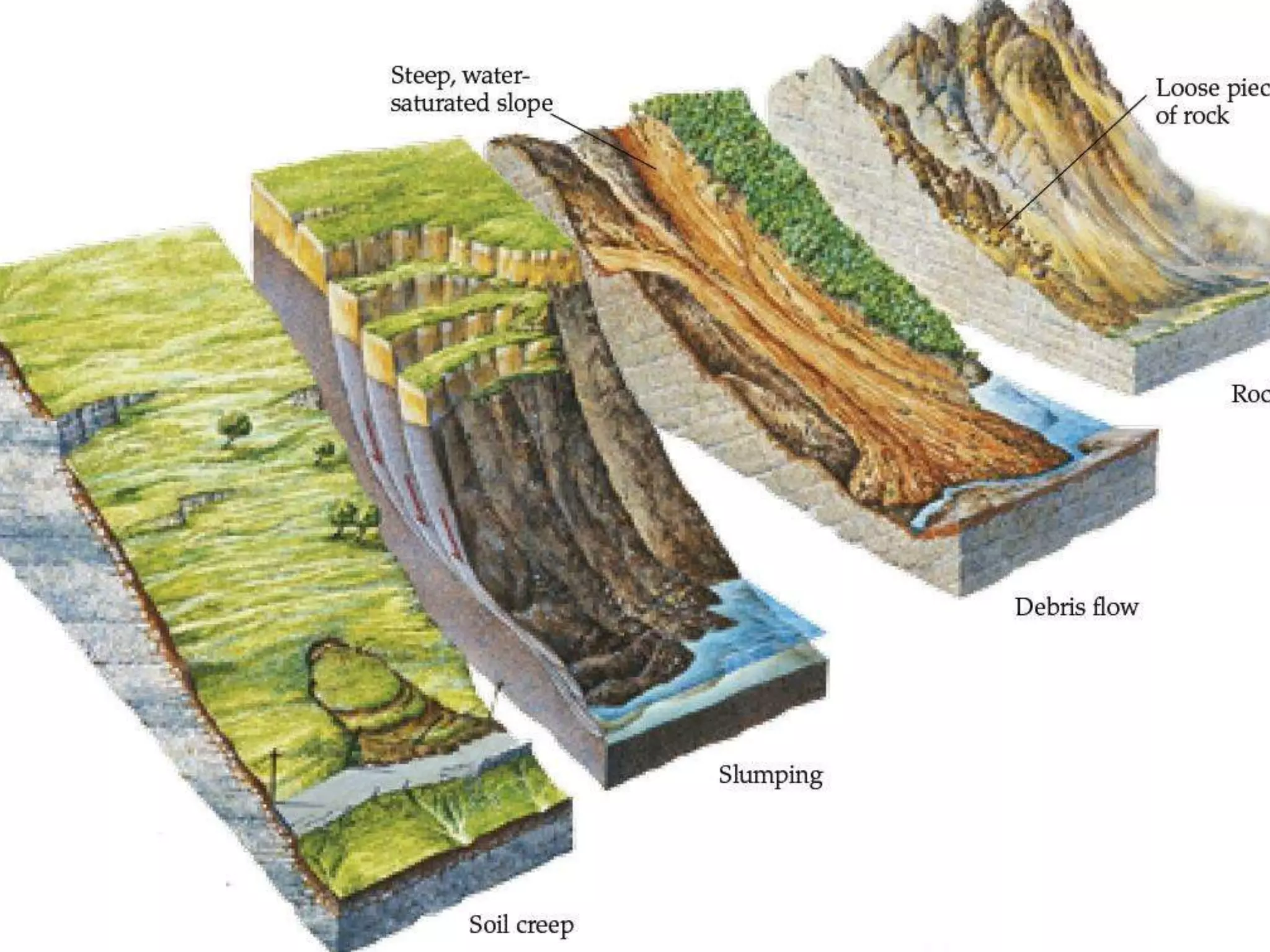
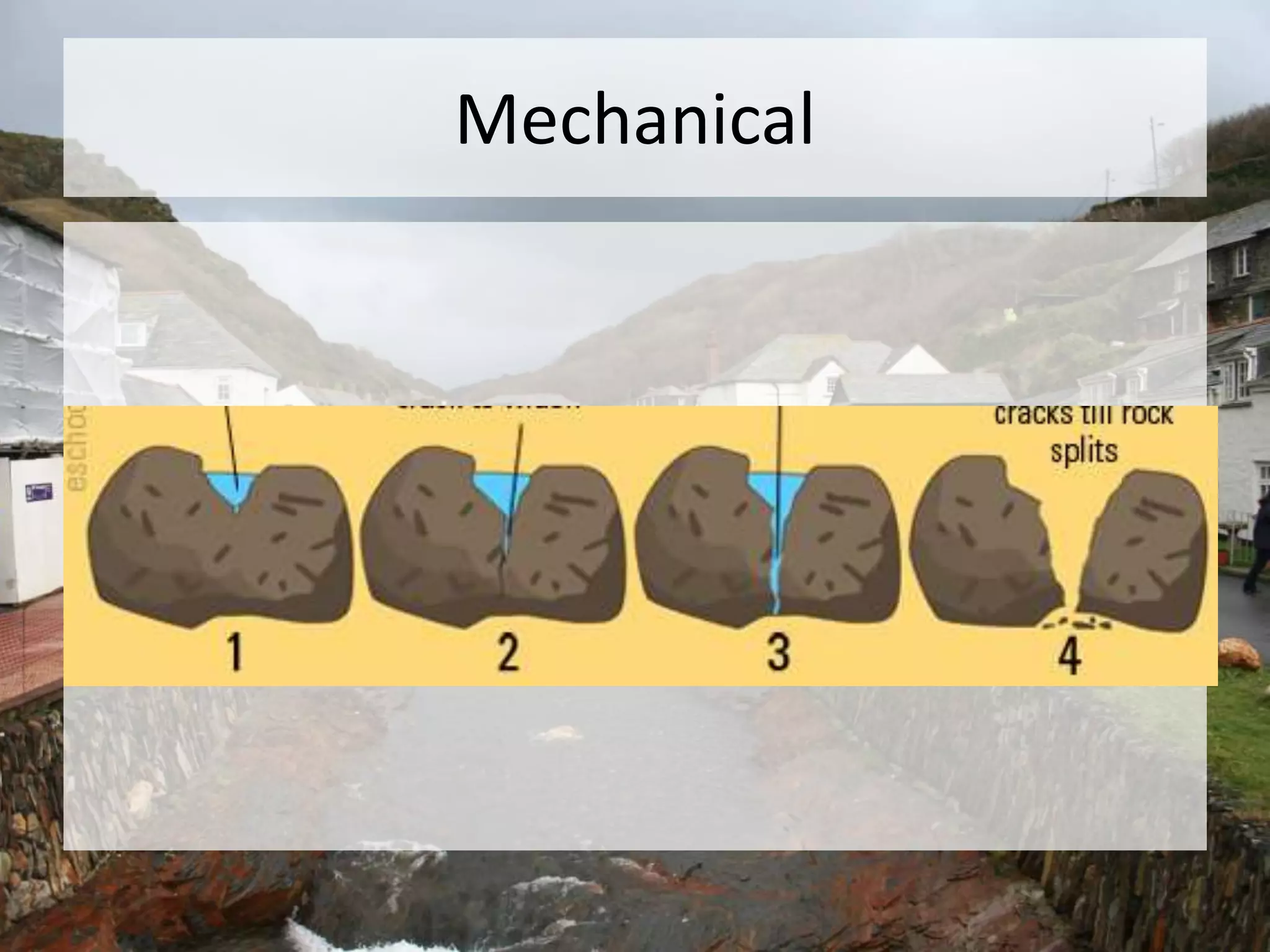
The five main river processes that shape the river landscape are erosion, transportation, deposition, mass movement, and weathering. Erosion processes include hydraulic action from water force, abrasion from rocks hitting the river bed, solution where rocks dissolve in water, and attrition where rocks wear down from bumping together. Transportation involves traction moving large rocks along the river bed, saltation bouncing small sediment particles, and suspension carrying very fine particles in the water. Deposition occurs when the river drops its sediment load due to decreasing velocity or volume. Mass movement comprises soil creep on slopes, landslides from undercutting, and debris flows like liquid down hills. Weathering includes mechanical, chemical, and biological processes breaking down rock and sediment.