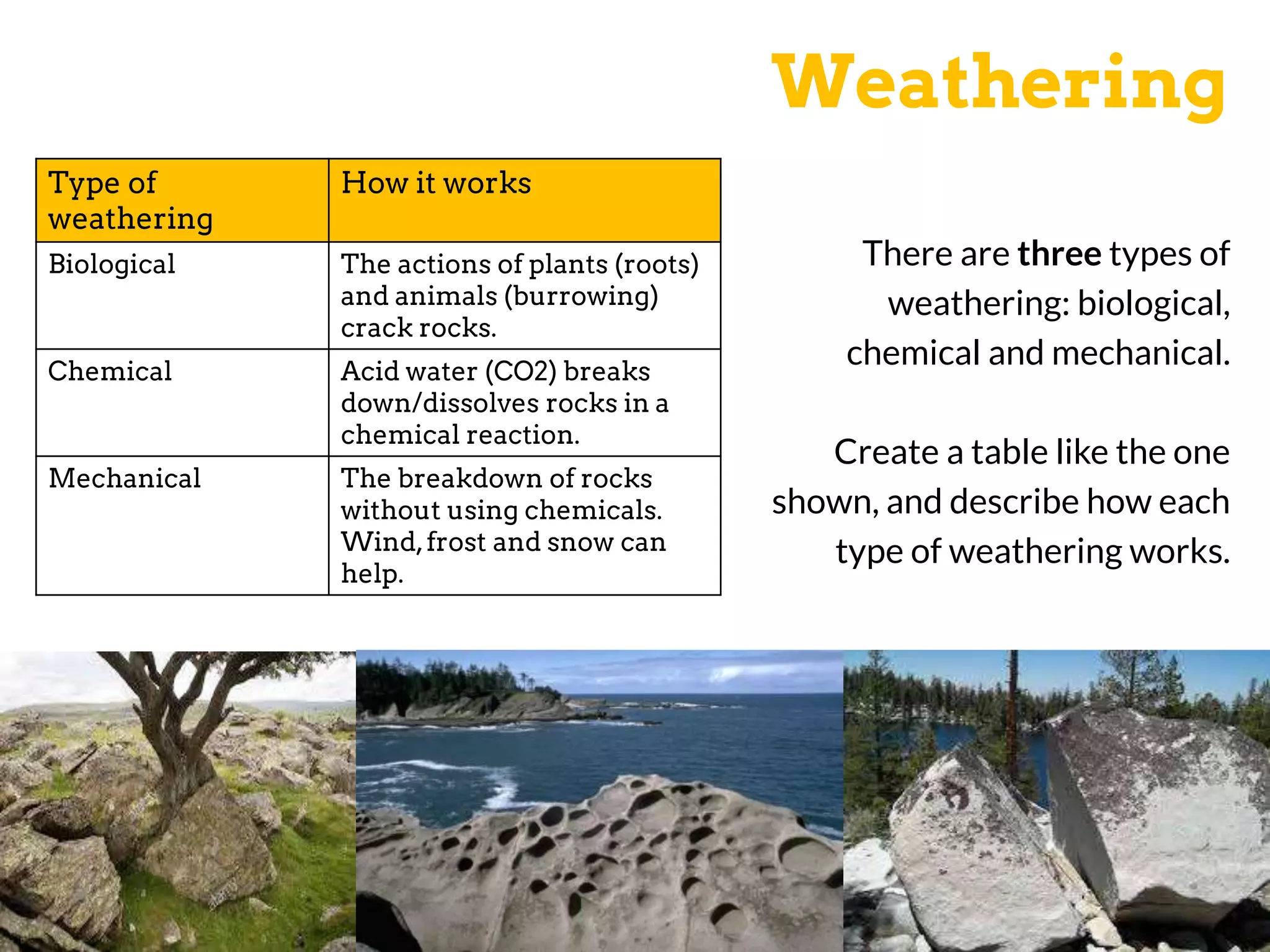
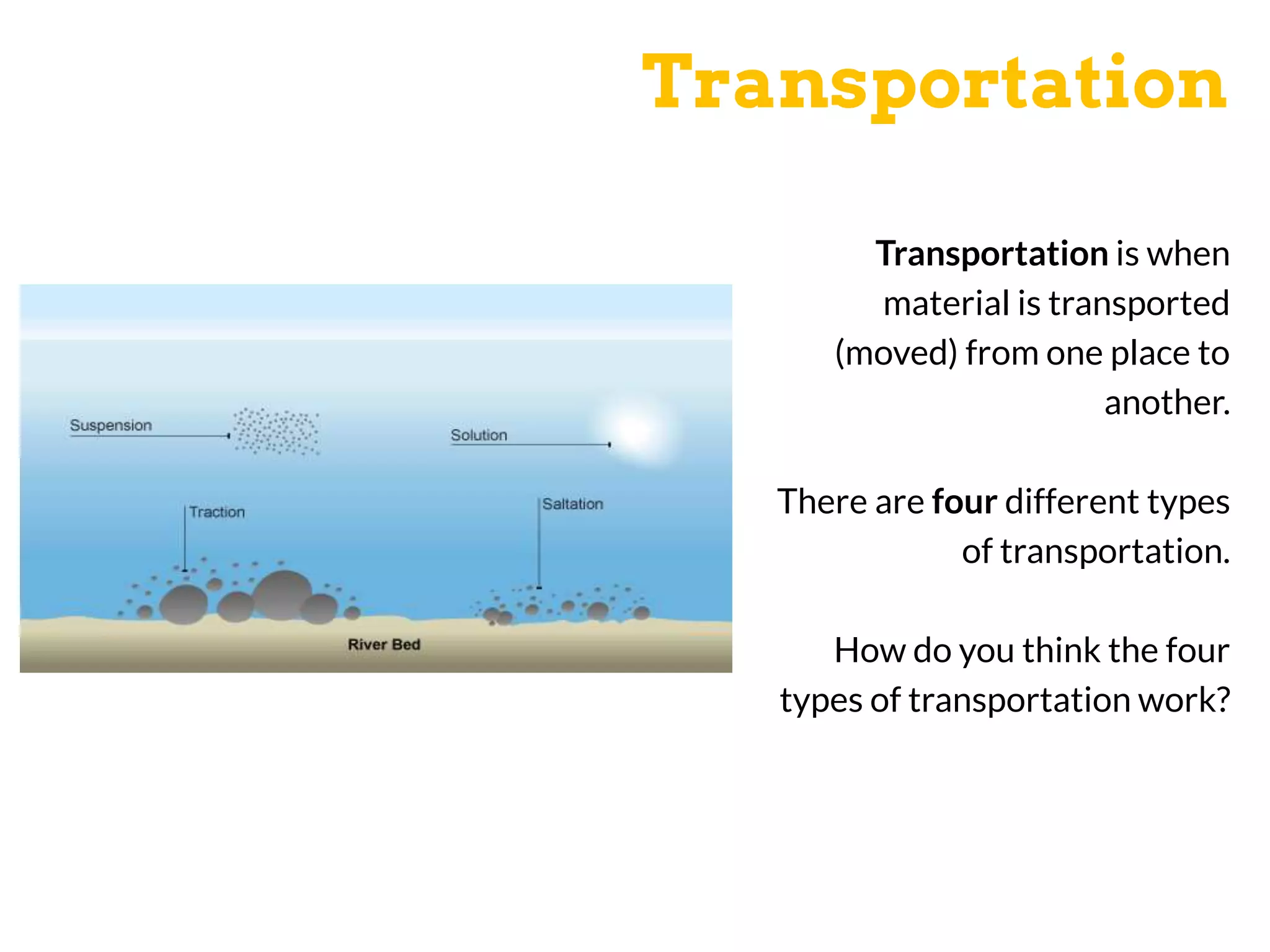
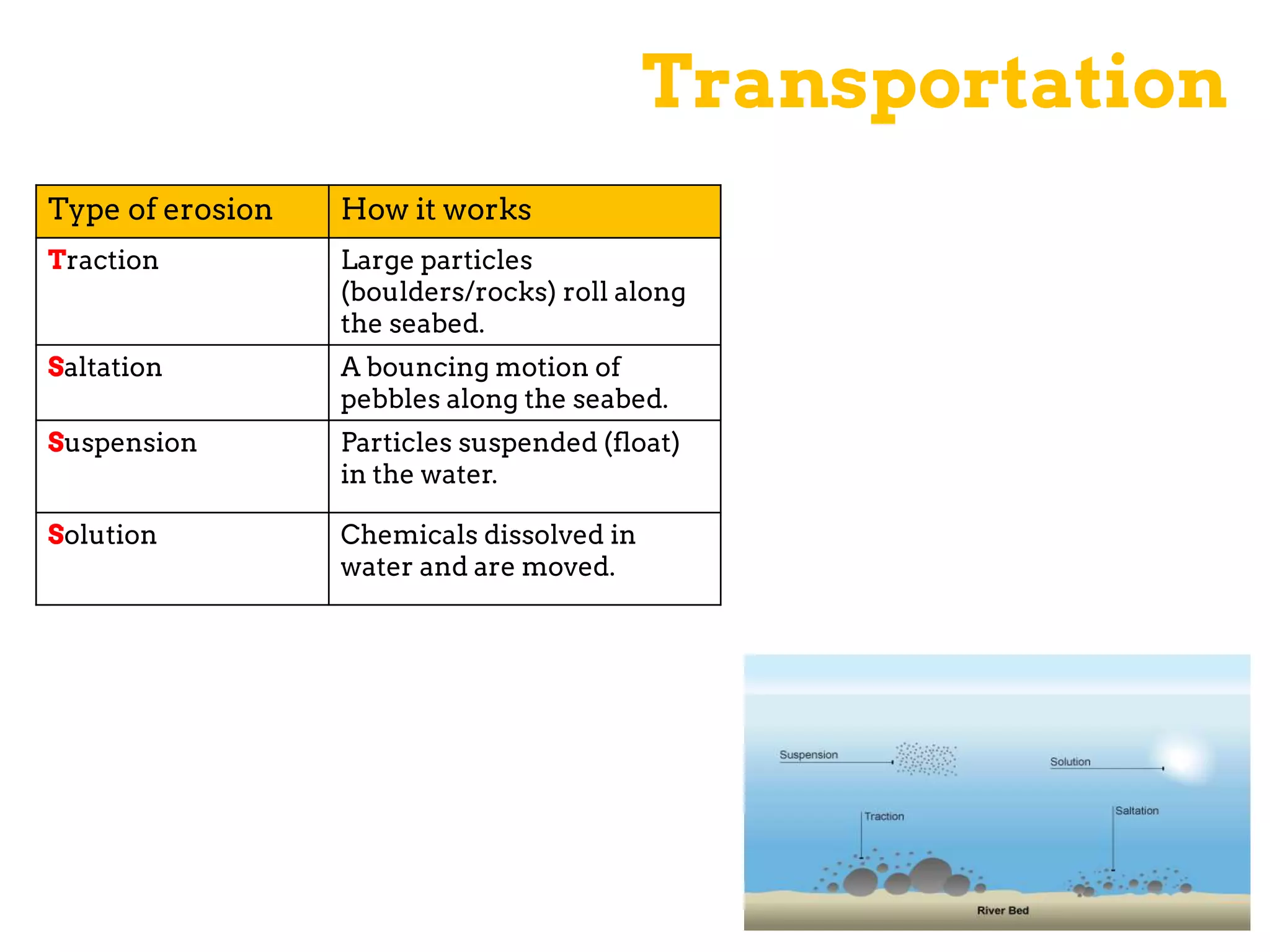
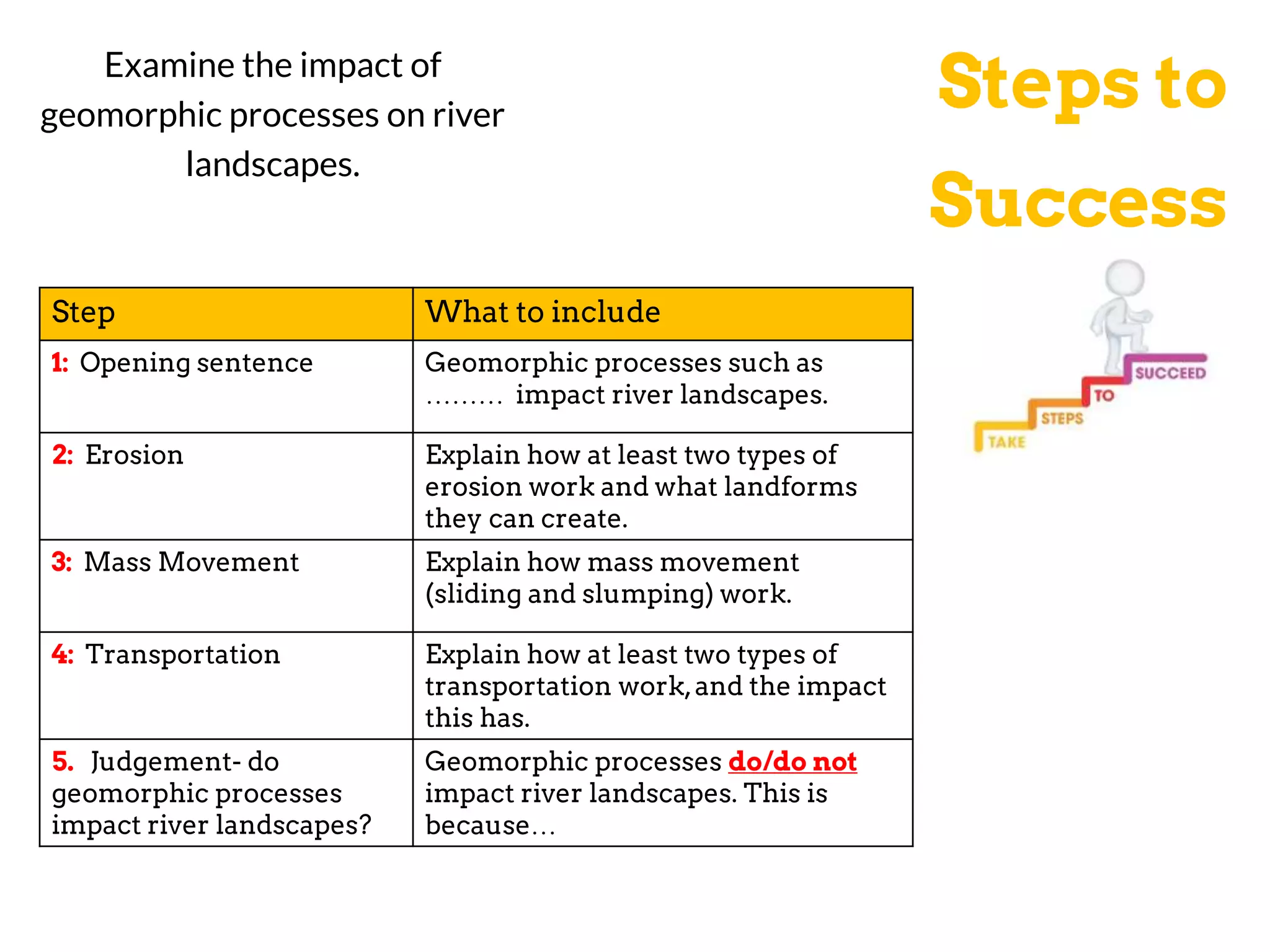
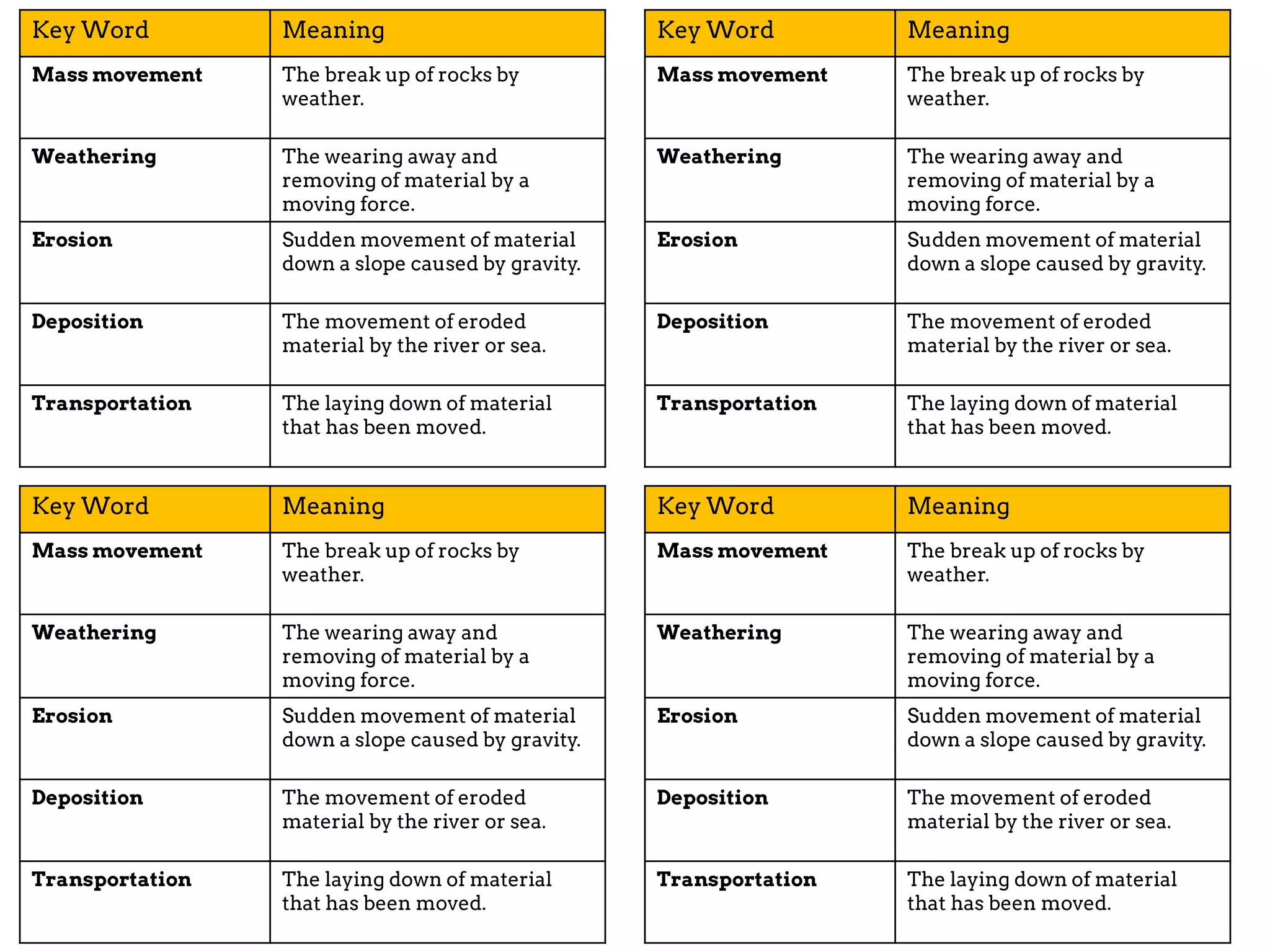
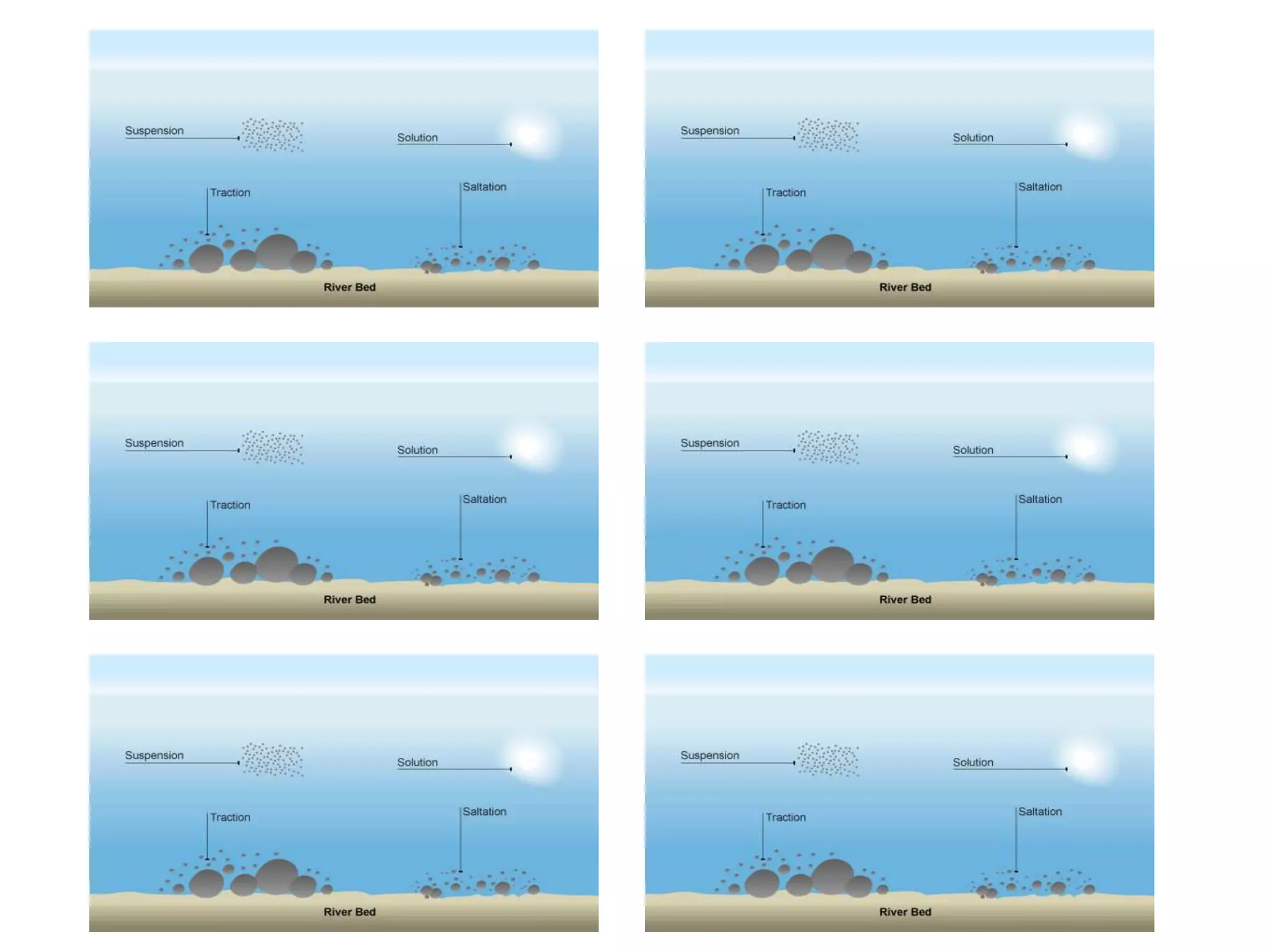
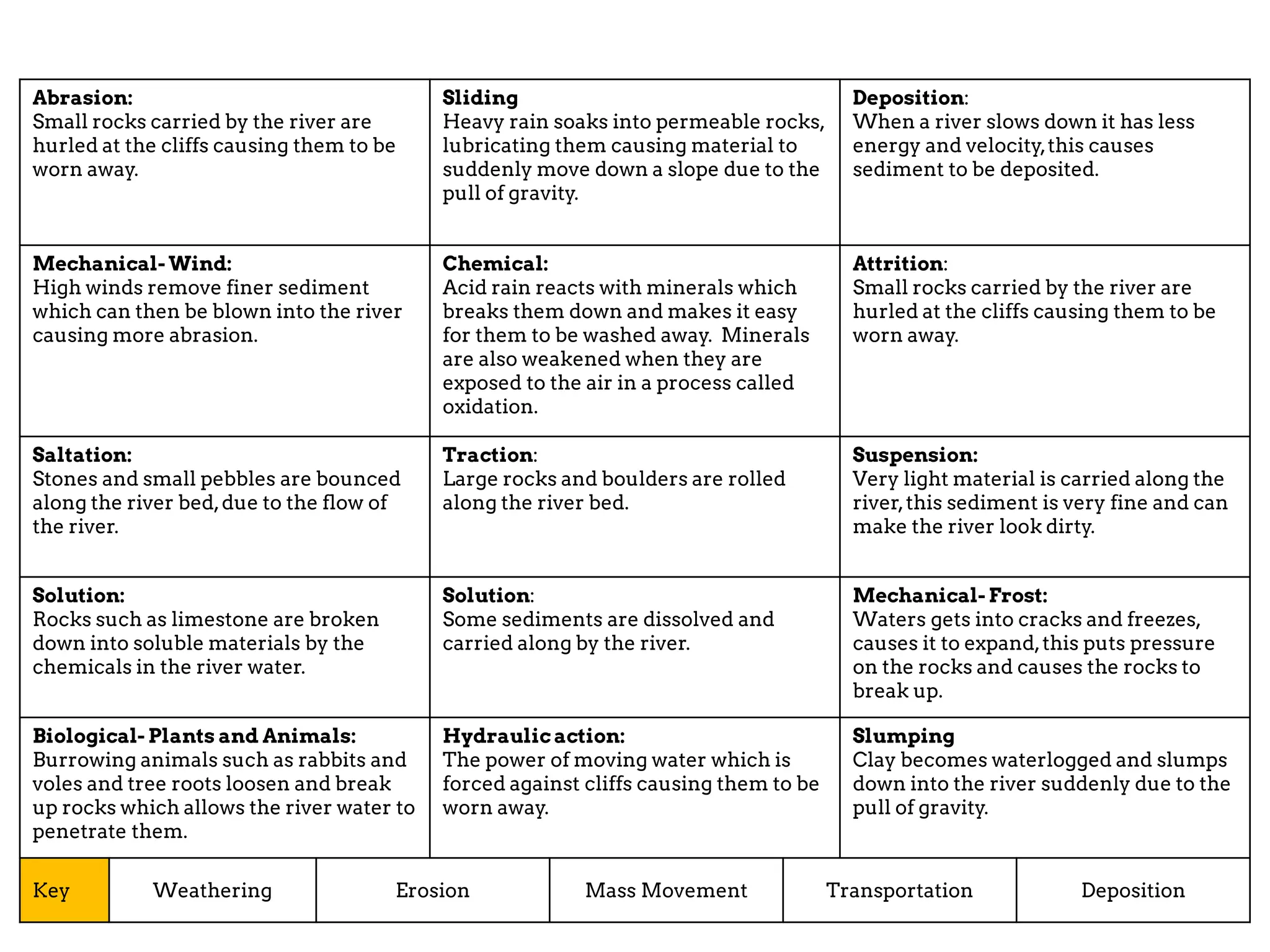
The document discusses various geomorphic processes that shape the land, including weathering, erosion, mass movement, deposition, and transportation. It provides examples of different types within each process, such as hydraulic action, abrasion, and attrition for erosion. Mass movement includes sliding and slumping. Transportation occurs through traction, saltation, suspension, and solution. Geomorphic processes impact river landscapes through erosion wearing away river banks and cliffs, mass movement carrying material downstream, and deposition forming landforms as the river's energy decreases.