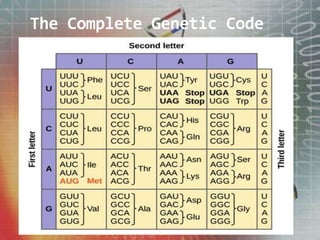
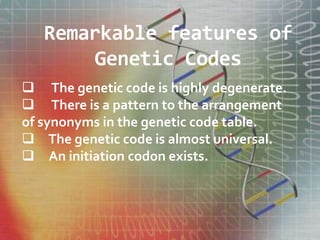
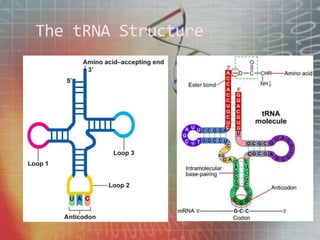
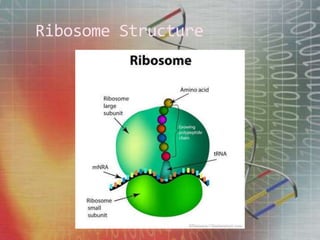
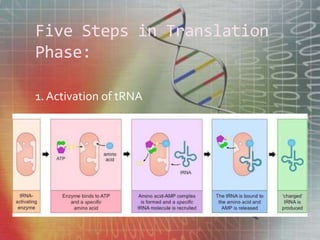
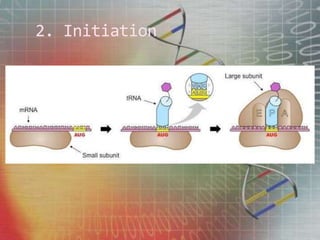
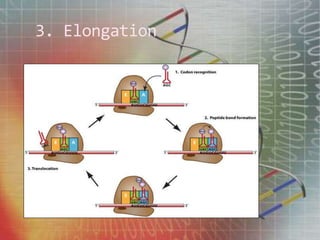
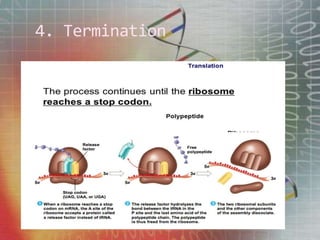
The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded in mRNA sequences is translated into proteins. It assigns each group of 3 nucleotides (codons) in mRNA to one of 20 possible amino acids used to build proteins or start/stop signals. Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules help translate codons to the correct amino acids. They have an anticodon loop that binds to mRNA codons and carry the corresponding amino acid. Ribosomes are complexes that facilitate protein synthesis. They bring together mRNA, tRNA, and amino acids to link amino acids in the correct order specified by the mRNA sequence.