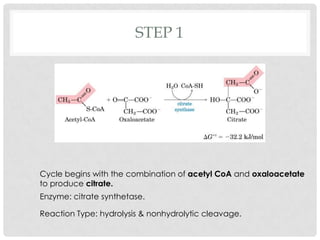
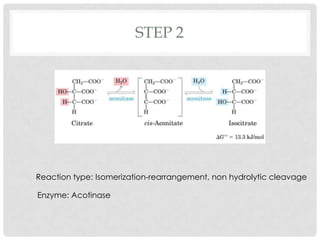
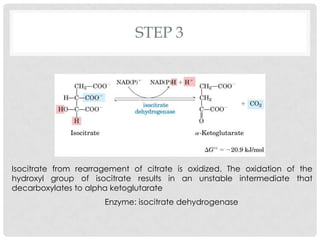
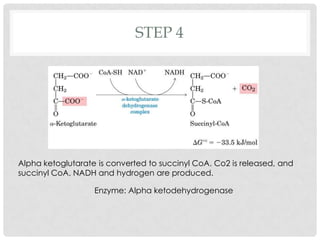
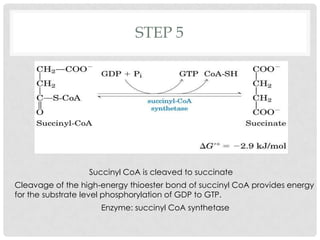
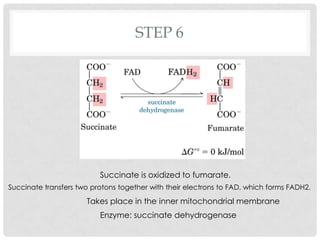
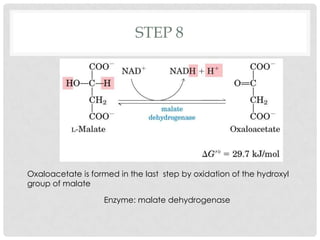
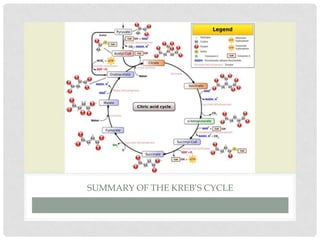
The Krebs cycle is a series of 8 reactions that occurs in the mitochondria of cells. It involves the oxidation of acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl CoA) along with the reduction of coenzymes. The cycle begins with the combination of acetyl CoA and oxaloacetate and results in the net production of carbon dioxide, NADH, FADH2, and ATP or GTP. Energy is generated as the NADH and FADH2 donate electrons to the electron transport chain, ultimately producing approximately 10 moles of ATP per cycle.