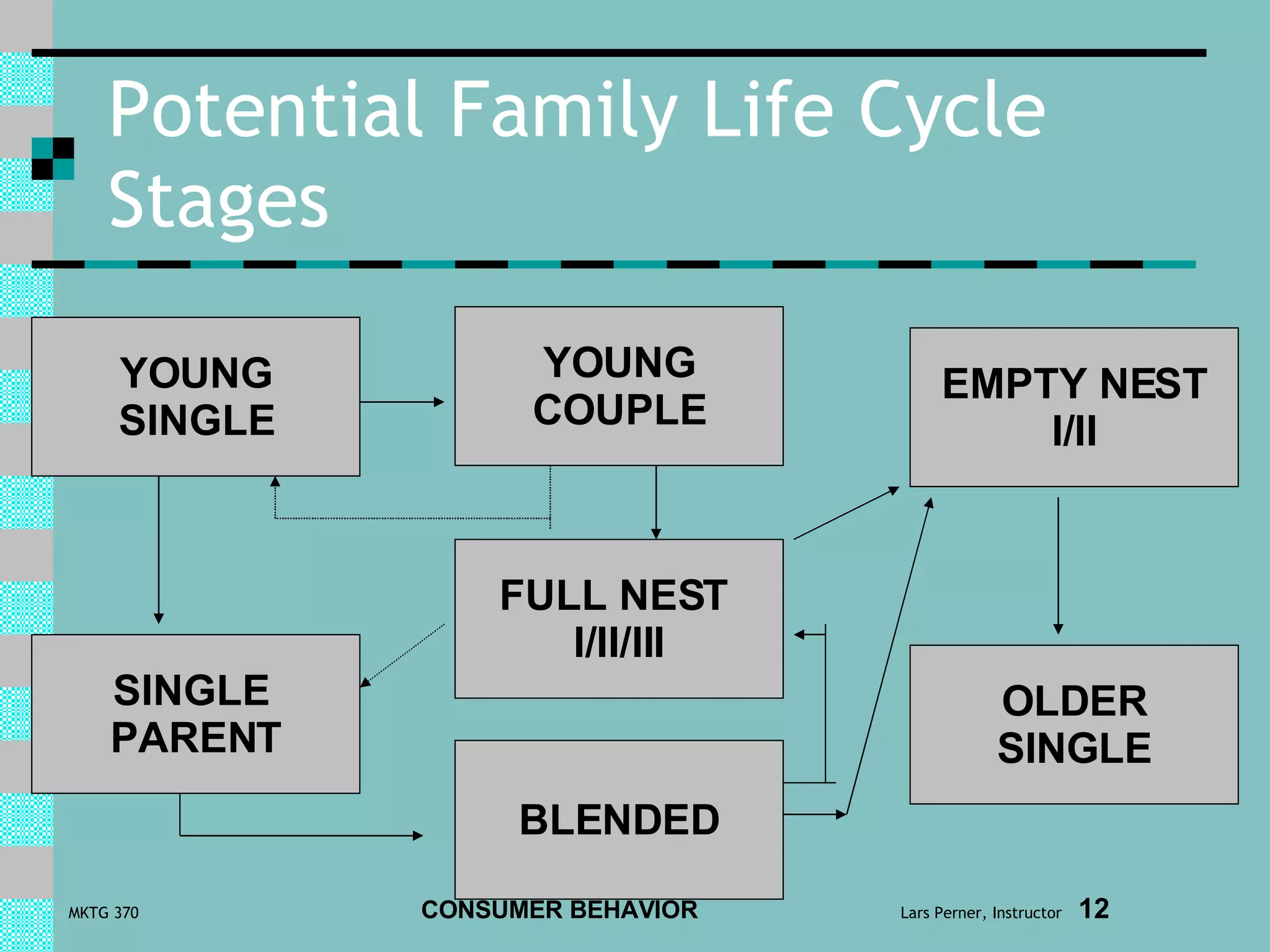
This document summarizes key concepts in consumer behavior, including psychological factors that influence decision making, sociocultural influences, and consumer decision processes. It discusses psychological concepts like attitudes, motivation, and learning; sociocultural factors like reference groups, culture, and the family life cycle; and consumer decision making processes from problem recognition to post-purchase evaluation. It also covers types of consumer decisions and influences on information search and decision strategies.