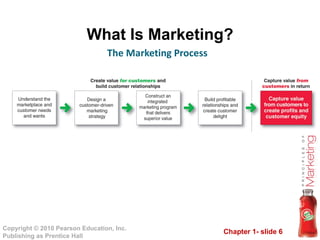
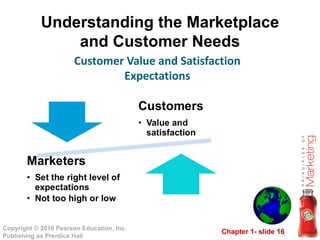
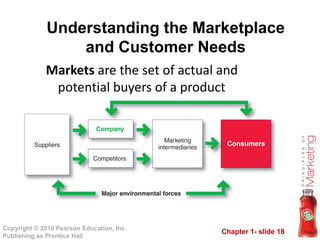
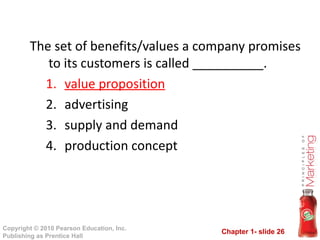
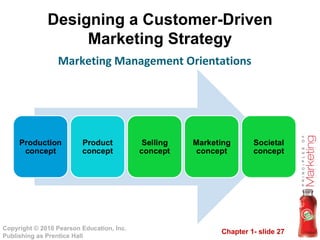
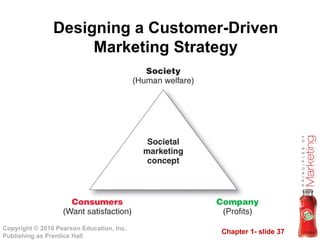
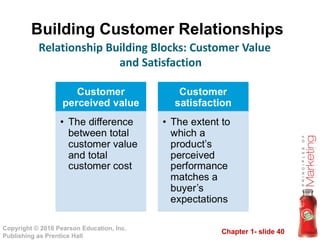
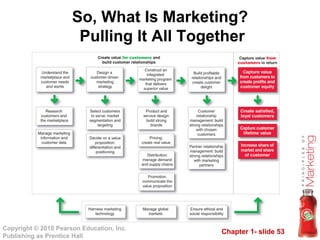
This document provides an overview of marketing concepts and processes. It defines marketing as satisfying customer needs and building customer relationships to capture value. It discusses understanding customer needs and the marketplace, designing a customer-driven marketing strategy through market segmentation and selecting target markets. It also covers preparing an integrated marketing plan using the marketing mix, building customer relationships through loyalty and retention, and capturing value from customers over their lifetime.