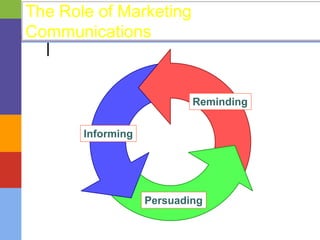
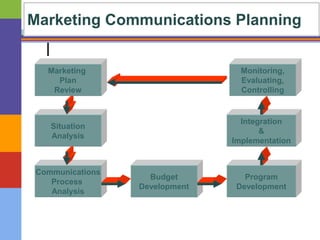
This document discusses integrated marketing communications (IMC), which is defined as strategically coordinating different communication channels to deliver a consistent message to target audiences. It outlines the marketing communications process, which involves situation analysis, setting objectives, budgeting, program development, integration and implementation, and monitoring and evaluation. It also discusses push, pull and combination strategies as well as legal and ethical considerations for different marketing communication elements like advertising, public relations, and direct marketing.