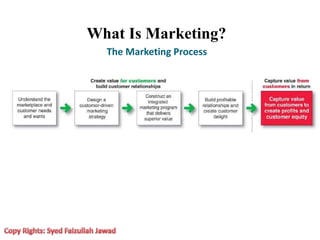
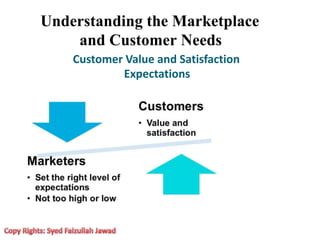
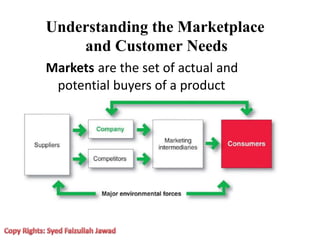
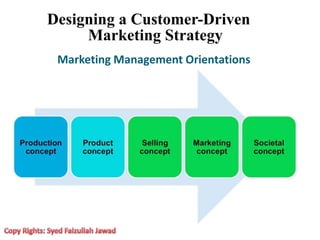
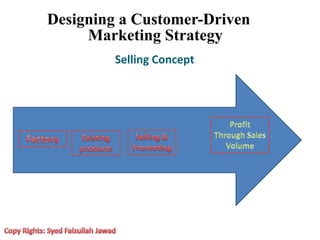
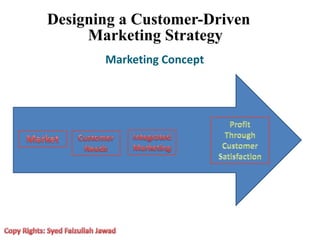
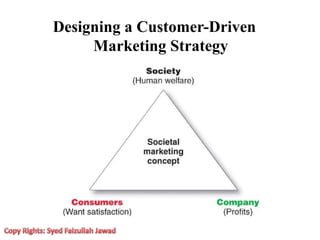
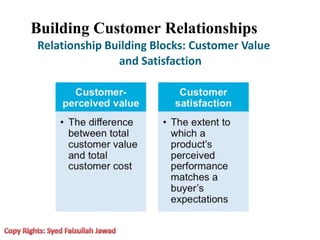
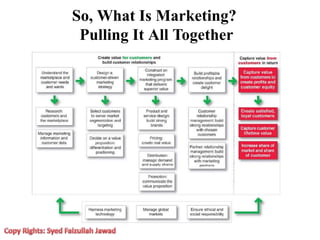
Marketing involves creating value for customers and building relationships to capture value in return. It is a process of understanding customer needs and offering products and services to satisfy those needs better than competitors. Marketers design strategies by selecting target customer segments and determining the best value proposition for those segments. They prepare integrated marketing programs using the marketing mix of product, price, promotion and place to implement strategies and build customer relationships that maximize customer lifetime value.