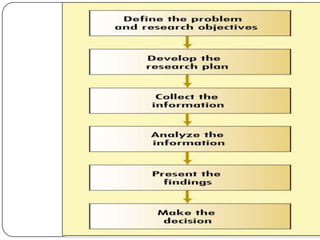
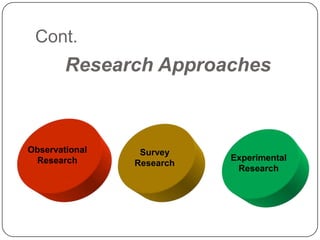
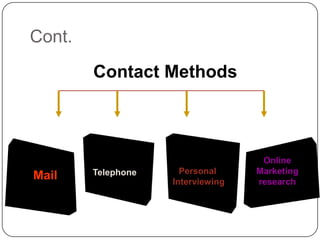
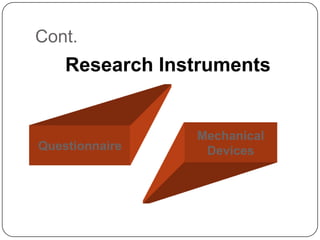
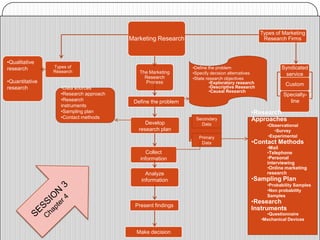
The document outlines key learning objectives for students regarding marketing research, including understanding good metrics and assessing returns on investment. It details the systematic process of marketing research, which involves defining the problem, developing a research plan, collecting and analyzing data, and presenting findings. Various types of research and methods for data collection are discussed, including qualitative and quantitative approaches.