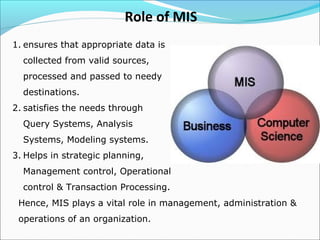
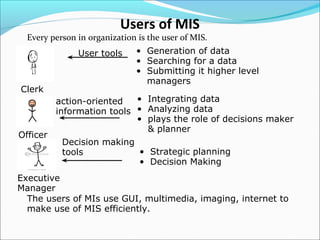
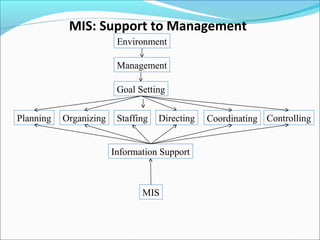
MIS uses computer technology to process and analyze large amounts of data, quickly search and retrieve information, and communicate information to users in a timely manner. It supports management functions like planning, organizing, staffing, directing, coordinating, and controlling. MIS helps ensure the appropriate data is collected, processed, and distributed to where it is needed. It provides information to support strategic planning, management control, operational control, and transaction processing.