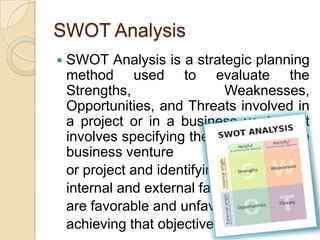
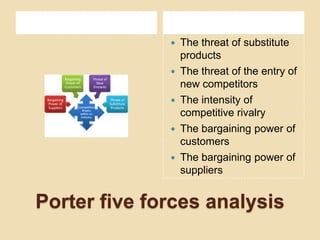
The document discusses various strategic analysis tools used to evaluate organizations and formulate business strategy, including PEST analysis, SWOT analysis, Porter's five forces model, value chain analysis, and scenario planning. It also covers the processes of strategic planning, formulation, implementation, and evaluation. These tools and processes are then applied in a case study analysis of the mobile network operator Ufone in Pakistan to assess its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats, and overall strategic position.