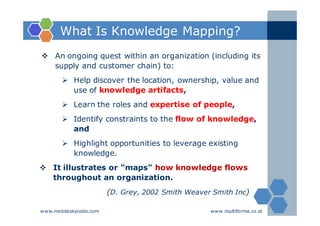
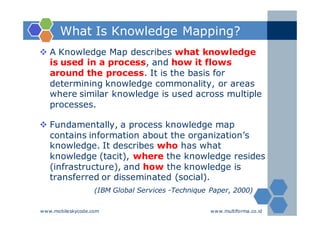
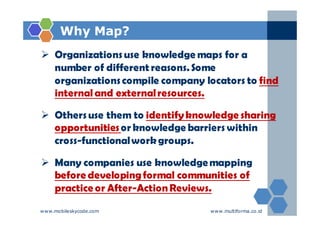
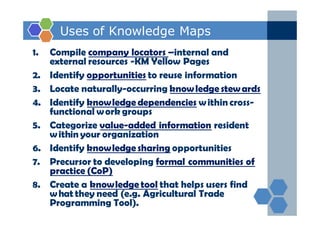
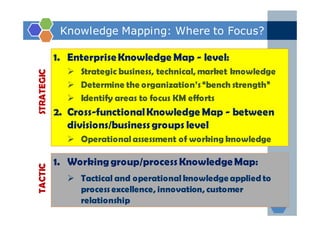
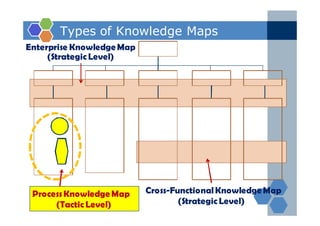
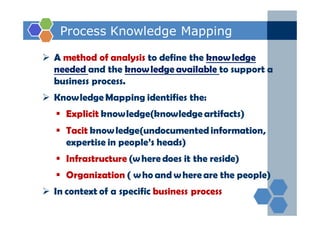
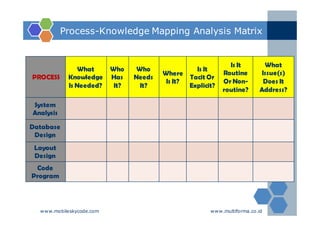
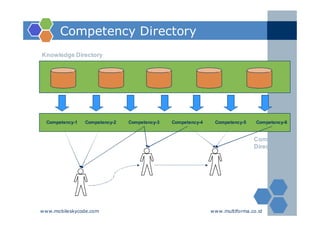
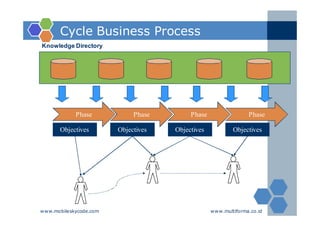
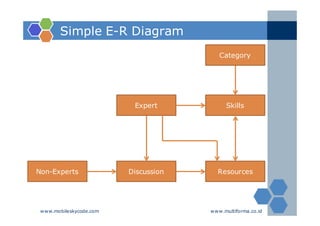
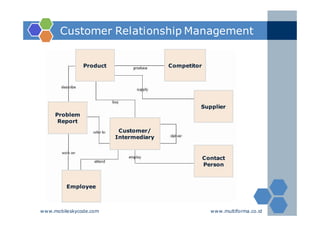
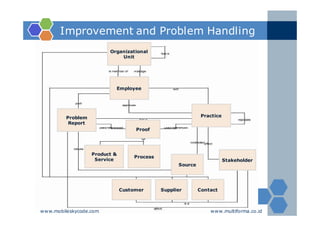
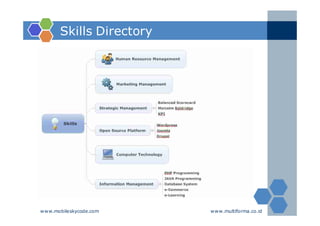
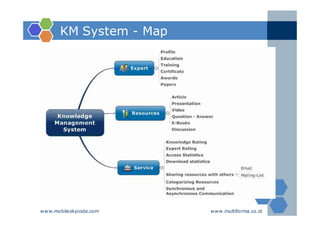
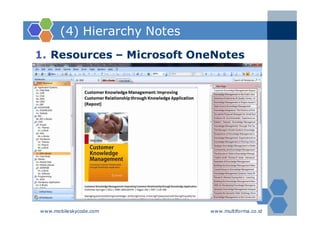
The document outlines an agenda for a two-day knowledge management strategy and program workshop covering topics such as knowledge management fundamentals, tools, mapping, and developing a KM strategy and roadmap. It also provides details on knowledge mapping, including definitions, why organizations map knowledge, and tools that can be used to develop knowledge maps such as flow diagrams, entity relationship diagrams, and mind mapping.