Embed presentation
Download to read offline

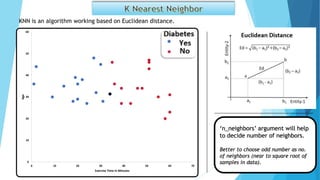
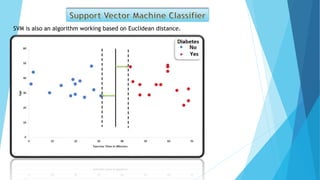
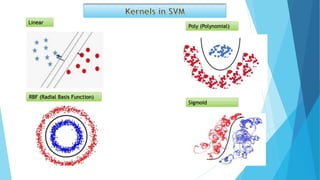

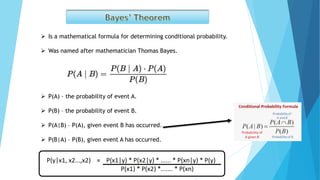

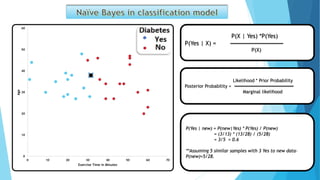

This document discusses several machine learning algorithms and concepts: KNN is a algorithm that uses Euclidean distance to determine the number of nearest neighbors based on the number of samples in the data. SVM and KNN both use Euclidean distance. Bayes' theorem is a formula for calculating conditional probability based on likelihood, prior probability, and posterior probability. An example shows how to apply Bayes' theorem to calculate the probability of a new data point being "Yes" given existing sample data.








